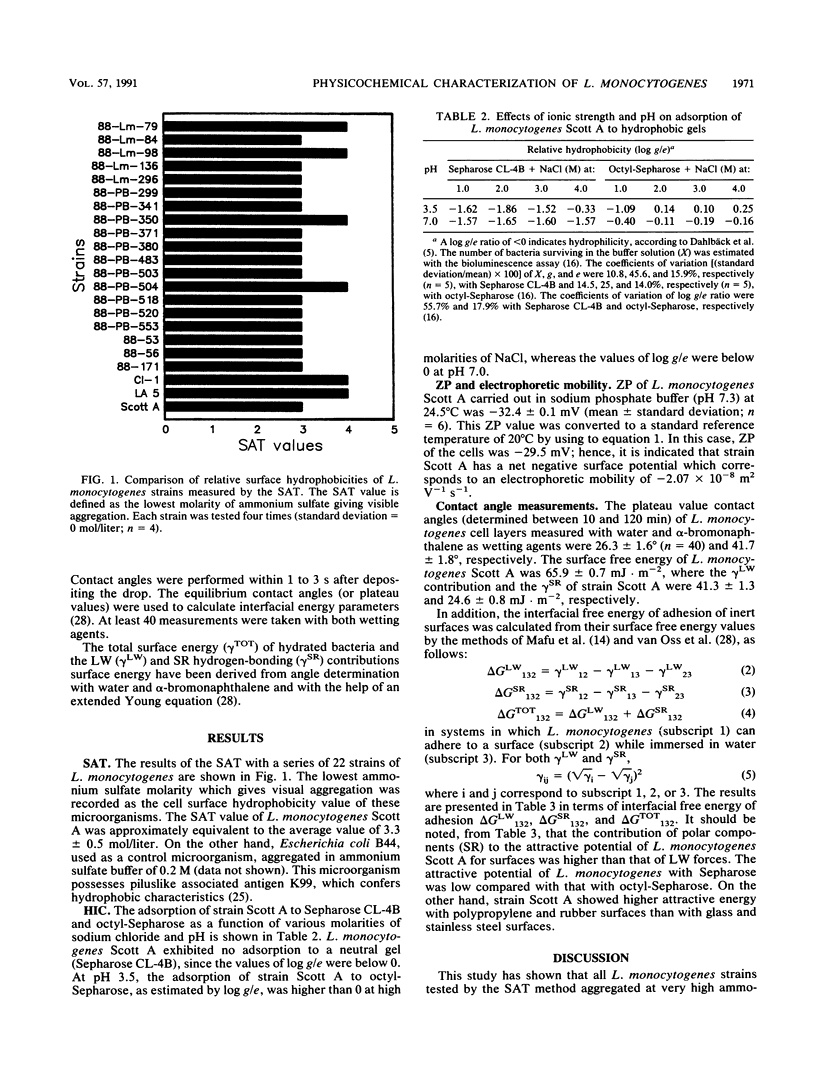
Abstract
This study investigated the physicochemical forces involving the adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to surfaces. A total of 22 strains of L. monocytogenes were compared for relative surface hydrophobicity with the salt aggregation test. Cell surface charges and hydrophobicity of L. monocytogenes Scott A were also determined by electrophoretic mobility, hydrophobic-interaction chromatography, and contact angle measurements. Electrokinetic measurements indicated that the strain Scott A has a negative electrophoretic mobility. Physicochemical characterization of L. monocytogenes by various methods indicates that this microorganism is hydrophilic. All L. monocytogenes strains tested with the salt aggregation test method aggregated a at very high ammonium sulfate molarities. The hydrophobicity-interaction chromatography results show that L. monocytogenes Scott A cells do not adhere to octyl-Sepharose unless the pH is low. Results from contact angle measurements showed that the surface free energy of strain Scott A was 65.9 mJ.m-2, classifying this microorganism as a hydrophilic bacterium. In addition, the interfacial free energy of adhesion of L. monocytogenes Scott A estimated for polypropylene and rubber was lower than that for glass and stainless steel. However, these theoretical implications could not be correlated with the attachment capabilities of L. monocytogenes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R., Lamberti F. V., Policova Z., Zingg W., van Oss C. J., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.90-97.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Sloyer J. L., Jr The electrophoretic mobility of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria: an electrokinetic analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):867–874. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hermansson M., Kjelleberg S., Norkrans B. The hydrophobicity of bacteria - an important factor in their initial adhesion at the air-water interface. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00422527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. S., Koohmaraie M. Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):832–836. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.832-836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hjertén S. A new test based on 'salting out' to measure relative surface hydrophobicity of bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Hjertén S., Wadström T. High surface hydrophobicity of autoaggregating Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from human infections studied with the salt aggregation test. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):522–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.522-526.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mafu A. A., Roy D., Goulet J., Savoie L., Roy R. Efficiency of sanitizing agents for destroying Listeria monocytogenes on contaminated surfaces. J Dairy Sci. 1990 Dec;73(12):3428–3432. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(90)79040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mafu A. A., Roy D., Savoie L., Goulet J. Bioluminescence assay for estimating the hydrophobic properties of bacteria as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1640–1643. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1640-1643.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E. Hydrophobic interaction--a mechanism of bacterial binding. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;33:32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo W., Rozgonyi F., Brown A., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Cell surface hydrophobicity and charge of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;62(3):241–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEldowney S., Fletcher M. Variability of the influence of physicochemical factors affecting bacterial adhesion to polystyrene substrata. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):460–465. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.460-465.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozgonyi F., Szitha K. R., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Standardization of salt aggregation test for reproducible determination of cell-surface hydrophobicity with special reference to Staphylococcus species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;59(5):451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb03345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1898–1901. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1898-1901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


