Abstract
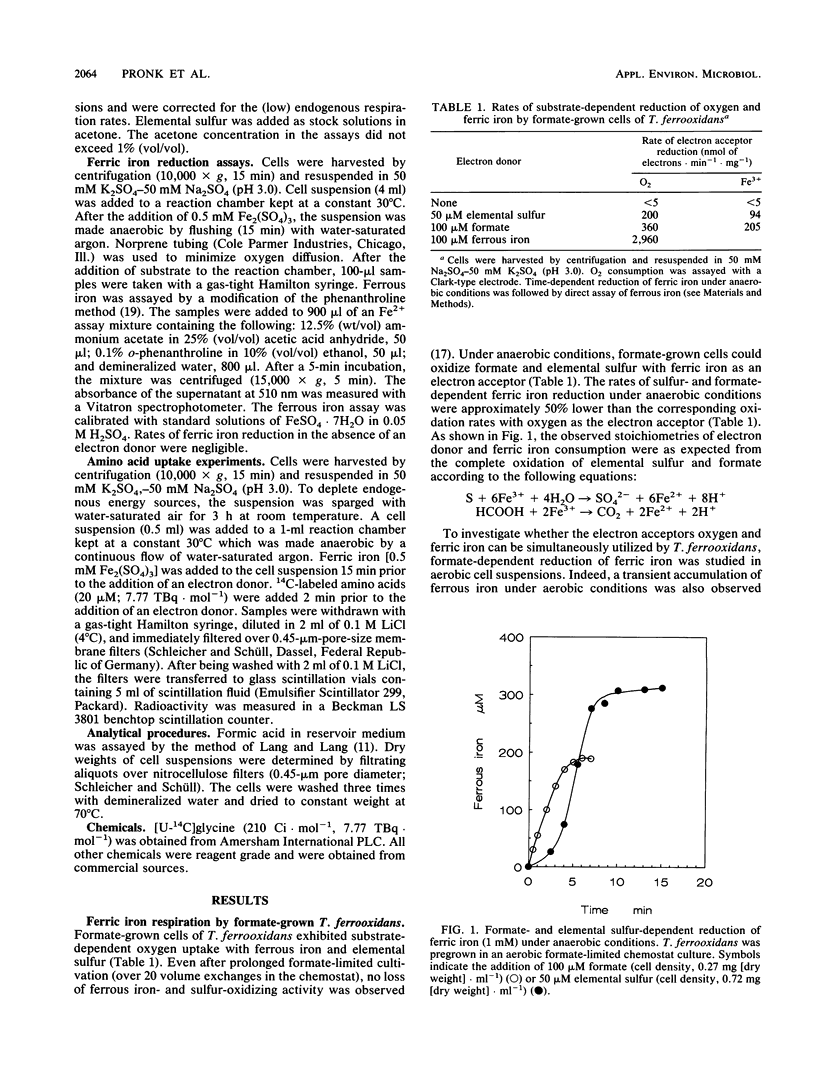
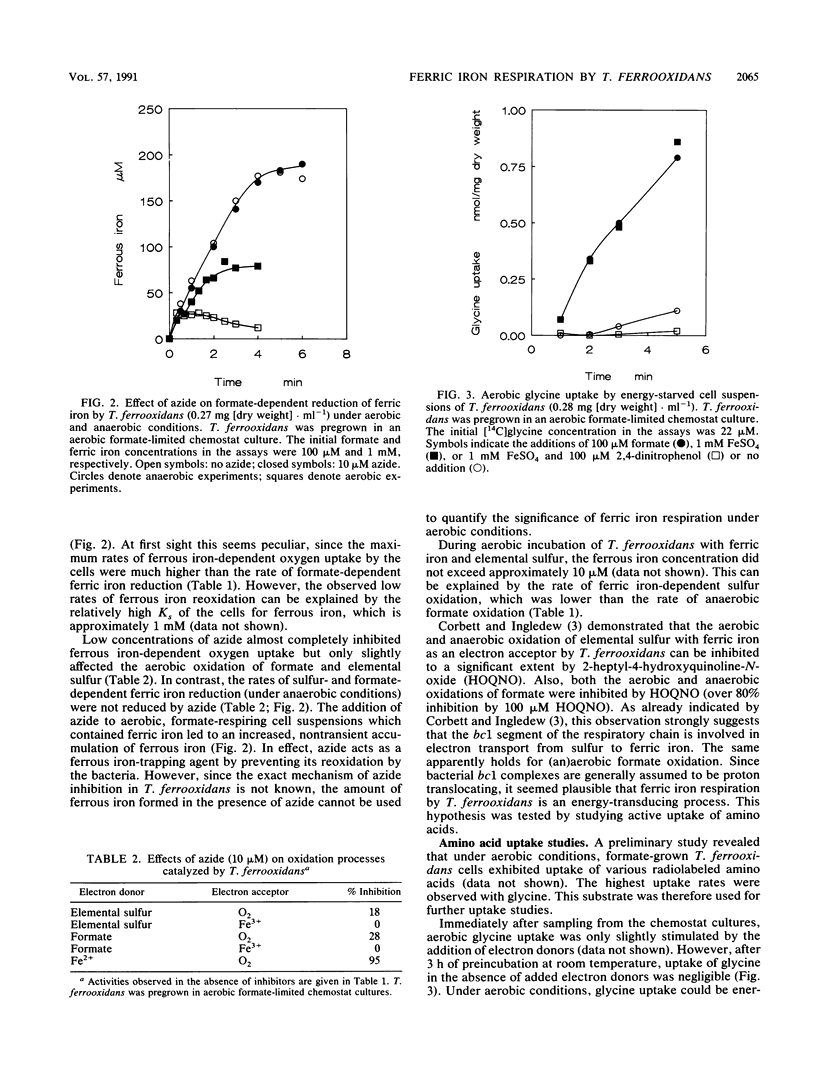
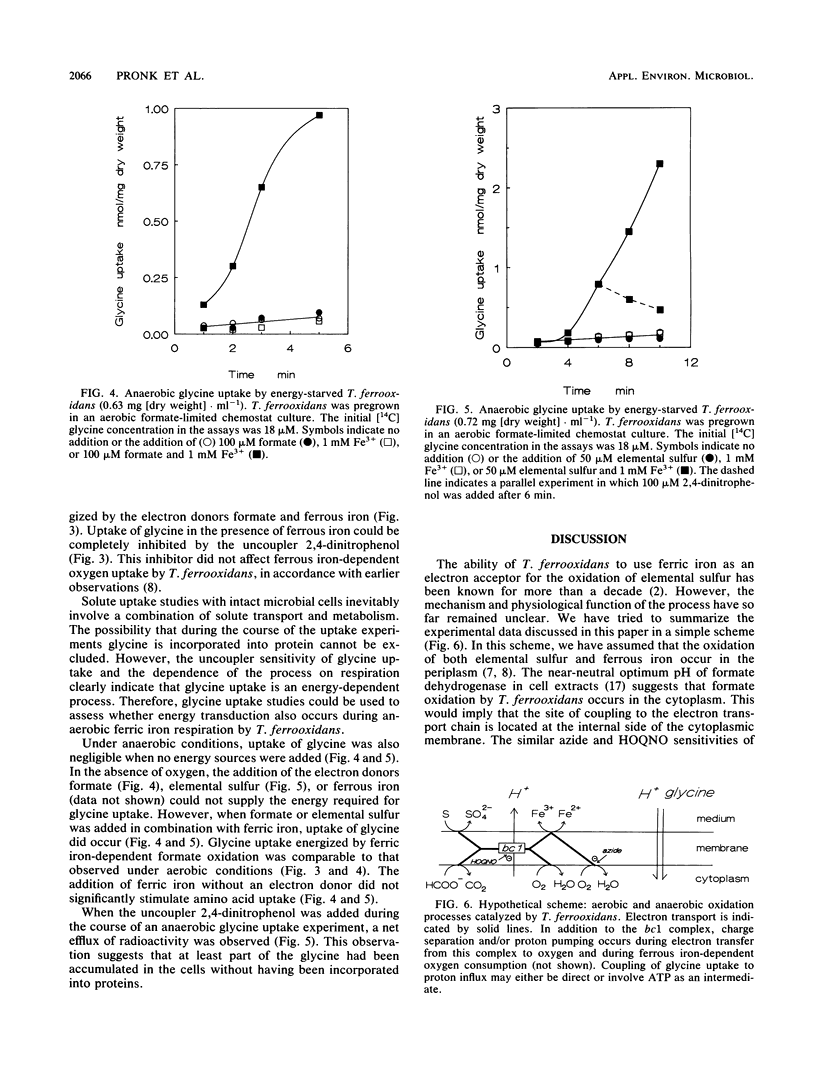
Formate-grown cells of the obligately chemolithoautotrophic acidophile Thiobacillus ferrooxidans were capable of formate- and elemental sulfur-dependent reduction of ferric iron under anaerobic conditions. Under aerobic conditions, both oxygen and ferric iron could be simultaneously used as electron acceptors. To investigate whether anaerobic ferric iron respiration by T. ferrooxidans is an energy-transducing process, uptake of amino acids was studied. Glycine uptake by starved cells did not occur in the absence of an electron donor, neither under aerobic conditions nor under anaerobic conditions. Uptake of glycine could be driven by formate- and ferrous iron-dependent oxygen uptake. Under anaerobic conditions, ferric iron respiration with the electron donors formate and elemental sulfur could energize glycine uptake. Glycine uptake was inhibited by the uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol. The results indicate that anaerobic ferric iron respiration can contribute to the energy budget of T. ferrooxidans.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkesteyn G. J. Pyrite oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans with special reference to the sulphur moiety of the mineral. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(3):423–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00443281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Gustafson J. Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):567–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.567-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobner E., Huber H., Stetter K. O. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, a facultative hydrogen oxidizer. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2922–2923. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2922-2923.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper A. B., DiSpirito A. A. In bacteria which grow on simple reductants, generation of a proton gradient involves extracytoplasmic oxidation of substrate. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):140–157. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.140-157.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The bioenergetics of an acidophilic chemolithotroph. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;683(2):89–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenen J. G., Veldkamp H. Effects of organic compounds on growth of chemostat cultures of Thiomicrospira pelophila, Thiobacillus thioparus and Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Dec 21;94(2):173–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00416691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Konings W. N., Kuenen J. G., Emmens M. Active transport of amino acids by membrane vesicles of Thiobacillus neapolitanus. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):311–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A. Organic nutrition of chemolithotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:433–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muyzer G., de Bruyn A. C., Schmedding D. J., Bos P., Westbroek P., Kuenen G. J. A Combined Immunofluorescence-DNA-Fluorescence Staining Technique for Enumeration of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in a Population of Acidophilic Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):660–664. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.660-664.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk J. T., Meijer W. M., Hazeu W., van Dijken J. P., Bos P., Kuenen J. G. Growth of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans on Formic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):2057–2062. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.2057-2062.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short K. A., Blakemore R. P. Iron respiration-driven proton translocation in aerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.729-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Domatsu C., Munakata O., Tano T., Imai K. Role of a Ferric Ion-Reducing System in Sulfur Oxidation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1401–1406. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1401-1406.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Mizunashi W., Inagaki K., Tano T. Purification and some properties of sulfur:ferric ion oxidoreductase from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4916–4922. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4916-4922.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



