Abstract
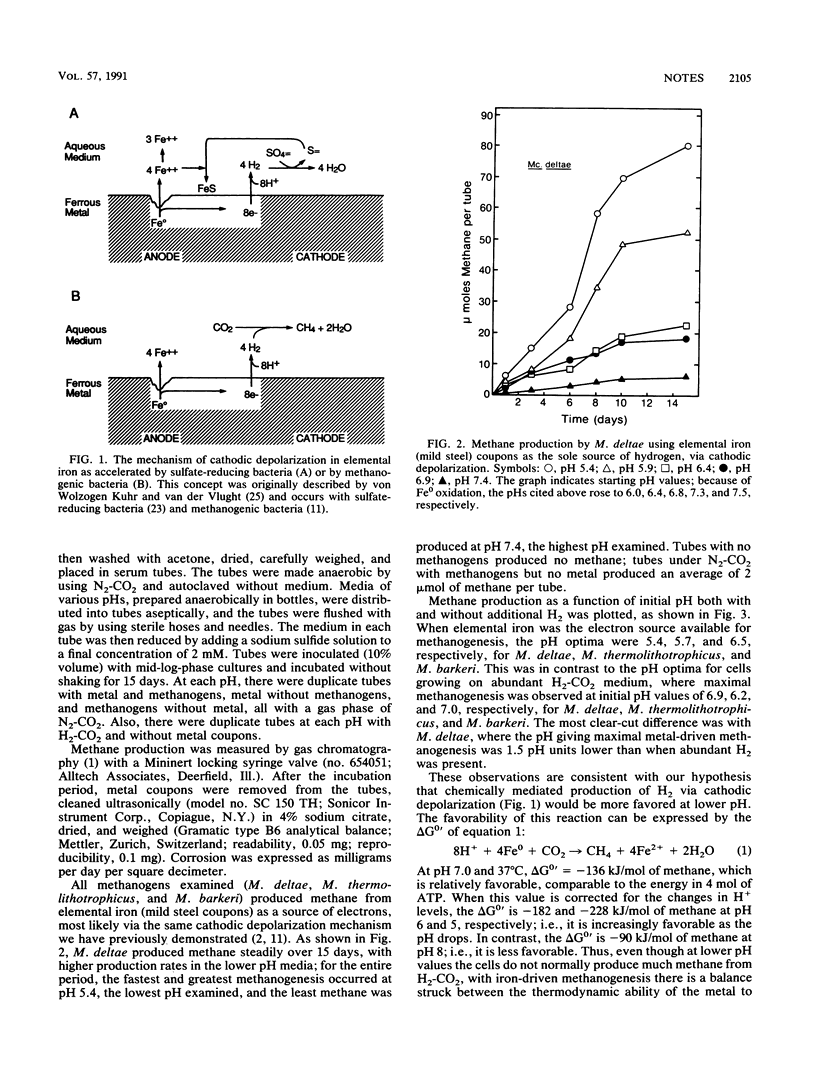
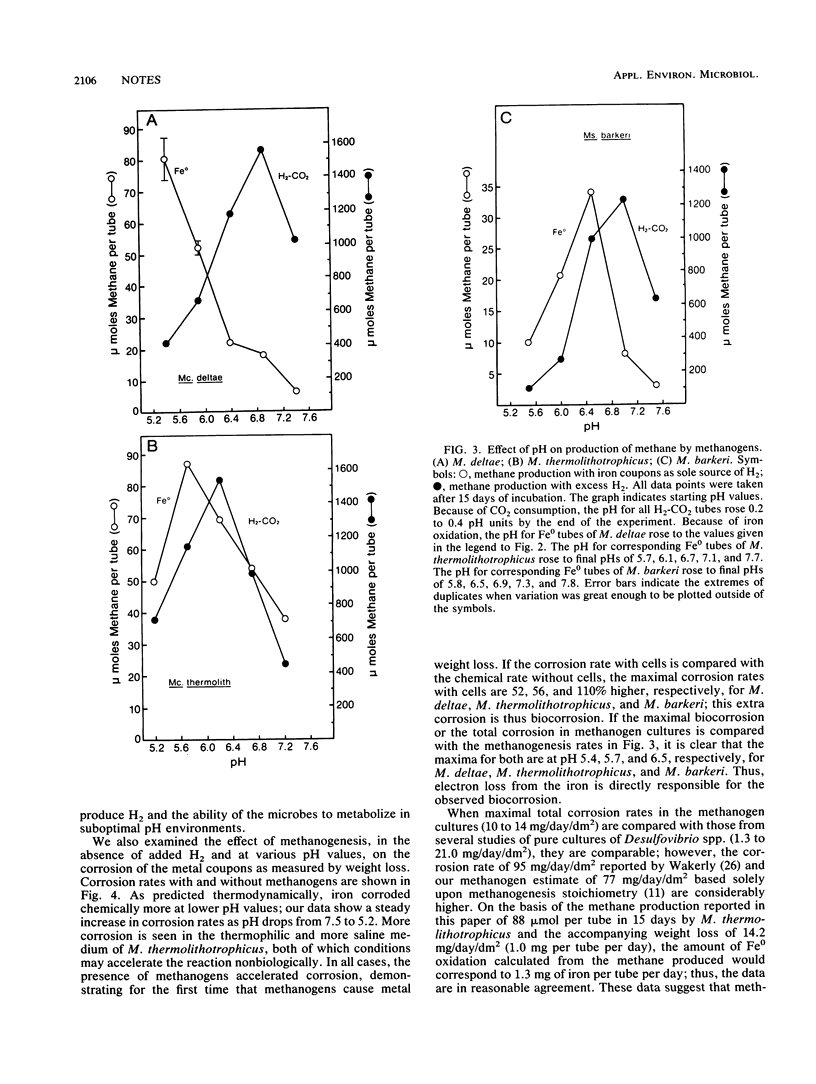
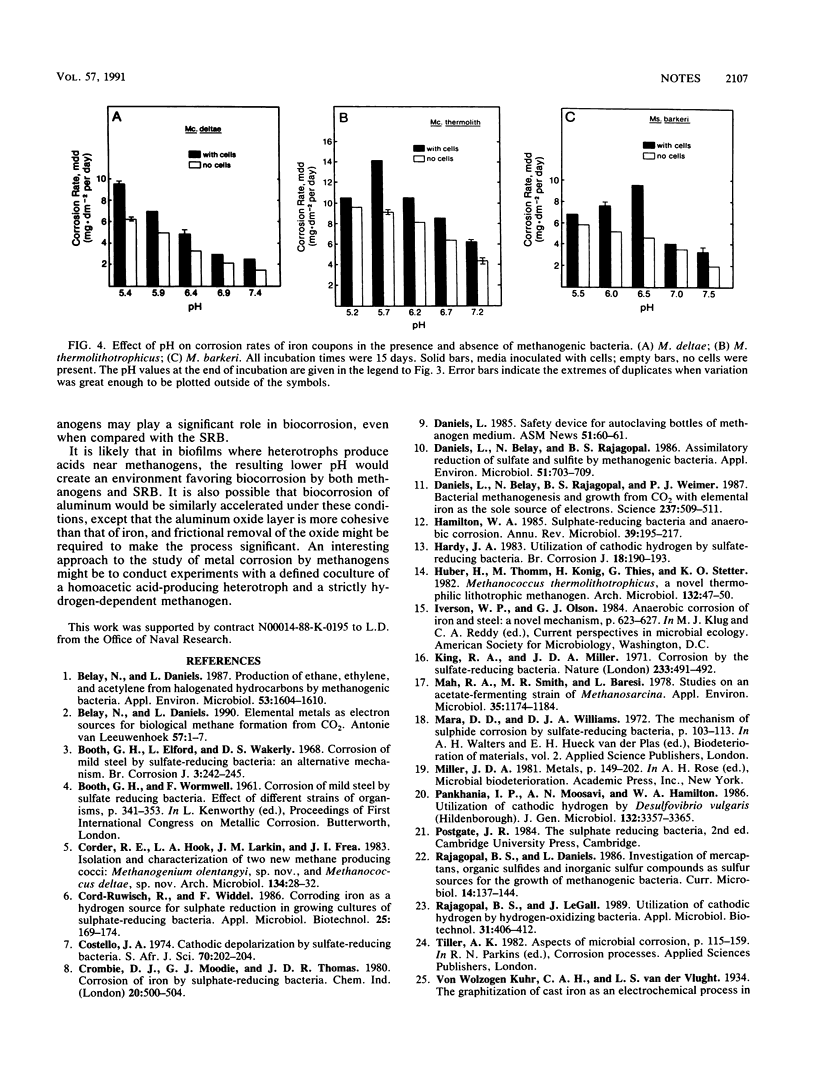
Methanogens can use H2 produced by cathodic depolarization-mediated oxidation of elemental iron to produce methane. Thermodynamic consideration of the cathodic depolarization mechanism predicts more oxidation of Fe0 at lower pH. Methanogenic responses to pH by Methanococcus deltae, Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus, and Methanosarcina barkeri were examined. When grown on H2-CO2, these bacteria had pH optima from 6.2 to 7.0, but when all H2 was supplied from Fe0, methanogenic pH optima were lower, 5.4 to 6.5. Corrosion was monitored with and without cultures and at various pHs; more corrosion occurred when cultures were present, biologically induced corrosion was greatest at the pH optima for methanogenesis from Fe0, and corrosion without cultures increased with a drop in pH.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belay N., Daniels L. Elemental metals as electron sources for biological methane formation from CO2. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990 Jan;57(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00400329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belay N., Daniels L. Production of ethane, ethylene, and acetylene from halogenated hydrocarbons by methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1604–1610. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1604-1610.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Belay N., Rajagopal B. S. Assimilatory reduction of sulfate and sulfite by methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):703–709. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.703-709.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Belay N., Rajagopal B. S., Weimer P. J. Bacterial Methanogenesis and Growth from CO2 with Elemental Iron as the Sole Source of Electrons. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):509–511. doi: 10.1126/science.237.4814.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. A. Sulphate-reducing bacteria and anaerobic corrosion. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:195–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. A., Miller J. D. Corrosion by the sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature. 1971 Oct 15;233(5320):491–492. doi: 10.1038/233491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Smith M. R., Baresi L. Studies on an acetate-fermenting strain of Methanosarcina. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1174–1184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1174-1184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Van Kavelaar M. J., Michel C. B., Ng T. K. Effect of Phosphate on the Corrosion of Carbon Steel and on the Composition of Corrosion Products in Two-Stage Continuous Cultures of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):386–396. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.386-396.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



