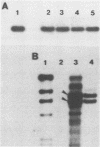
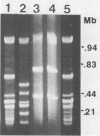
Abstract
Prevotella ruminicola (formerly Bacteroides ruminicola) is an anaerobic, gram-negative, polysaccharide-degrading bacterium which is found in the rumina of cattle. Since P. ruminicola is thought to make an important contribution to digestion of plant material in rumina, the ability to alter this strain genetically might help improve the efficiency of rumen fermentation. However, previously there has been no way to introduce foreign DNA into P. ruminicola strains. In this study we transferred a shuttle vector, pRDB5, from the colonic species Bacteroides uniformis to P. ruminicola B(1)4. The transfer frequency was 10(-6) to 10(-7) per recipient. pRDB5 contains sequences from pBR328, a cryptic colonic Bacteroides plasmid pB8-51, and a colonic Bacteroides tetracycline resistance (Tcr) gene. pRDB5 was mobilized out of B. uniformis by a self-transmissible Bacteroides chromosomal element designated Tcr Emr 12256. pRDB5 replicated in Escherichia coli as well as in Bacteroides spp. and was also mobilized from E. coli to B. uniformis by using IncP plasmid R751. However, direct transfer from E. coli to P. ruminicola B(1)4 was not detected. Thus, to introduce cloned DNA into P. ruminicola B(1)4, it was necessary first to mobilize the plasmid from E. coli to B. uniformis and then to mobilize the plasmid from B. uniformis to P. ruminicola B(1)4.
Full text
PDF
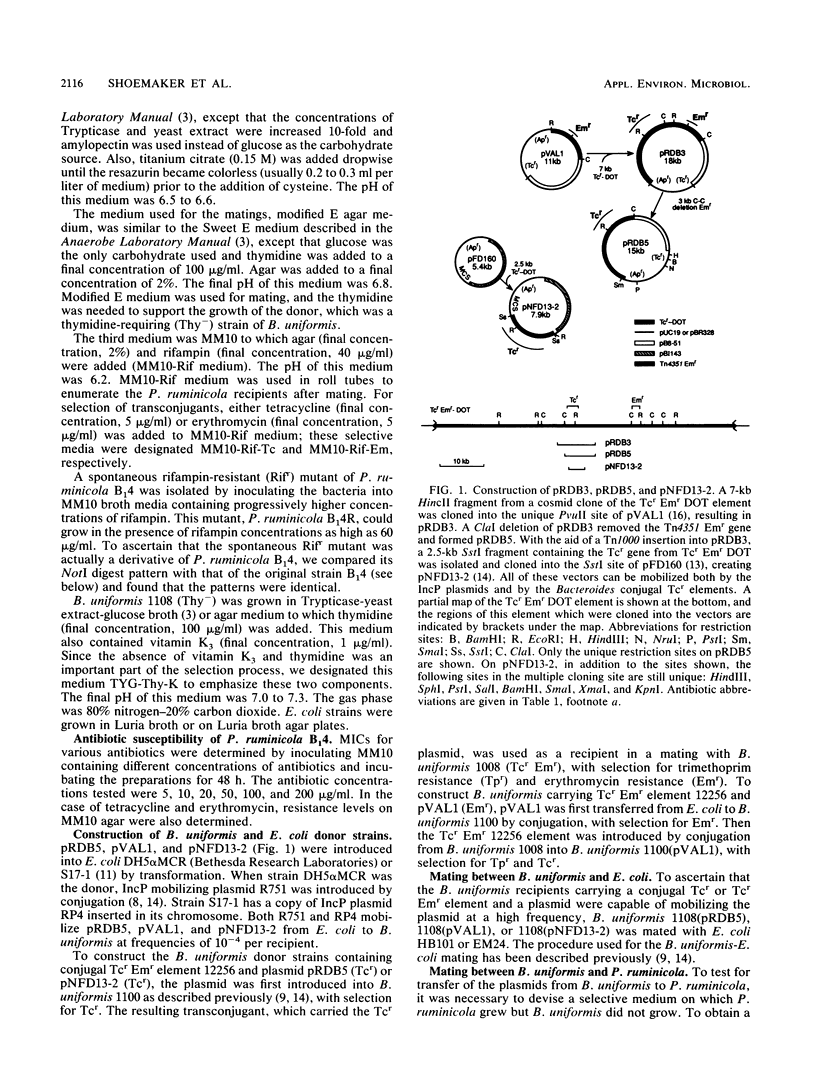



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint H. J., Thomson A. M., Bisset J. Plasmid-associated transfer of tetracycline resistance in Bacteroides ruminicola. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):855–860. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.855-860.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelson D. A., Rasmussen J. L., Smith C. J., Macrina F. L. Extrachromosomal systems and gene transmission in anaerobic bacteria. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):87–109. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Shoemaker N. B., Guthrie E. P. Recent advances in Bacteroides genetics. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(1):49–71. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Collins D. M. Prevotella, a new genus to include Bacteroides melaninogenicus and related species formerly classified in the genus Bacteroides. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;40(2):205–208. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Barber R. D., Salyers A. A. Cloning and characterization of a Bacteroides conjugal tetracycline-erythromycin resistance element by using a shuttle cosmid vector. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1294–1302. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1294-1302.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Getty C., Guthrie E. P., Salyers A. A. Regions in Bacteroides plasmids pBFTM10 and pB8-51 that allow Escherichia coli-Bacteroides shuttle vectors to be mobilized by IncP plasmids and by a conjugative Bacteroides tetracycline resistance element. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):959–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.959-965.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. A cryptic 65-kilobase-pair transposonlike element isolated from Bacteroides uniformis has homology with Bacteroides conjugal tetracycline resistance elements. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1694–1702. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1694-1702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J. Development and use of cloning systems for Bacteroides fragilis: cloning of a plasmid-encoded clindamycin resistance determinant. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.294-301.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. M., Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. The region of a Bacteroides conjugal chromosomal tetracycline resistance element which is responsible for production of plasmidlike forms from unlinked chromosomal DNA might also be involved in transfer of the element. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4271–4279. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4271-4279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Flint H. J. Electroporation induced transformation of Bacteroides ruminicola and Bacteroides uniformis by plasmid DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Oct 1;52(1-2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine P. J., Shoemaker N. B., Salyers A. A. Mobilization of Bacteroides plasmids by Bacteroides conjugal elements. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1319-1324.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. R., Hespell R. B. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a xylanase gene from Bacteroides ruminicola 23. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):893–896. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.893-896.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]