Abstract
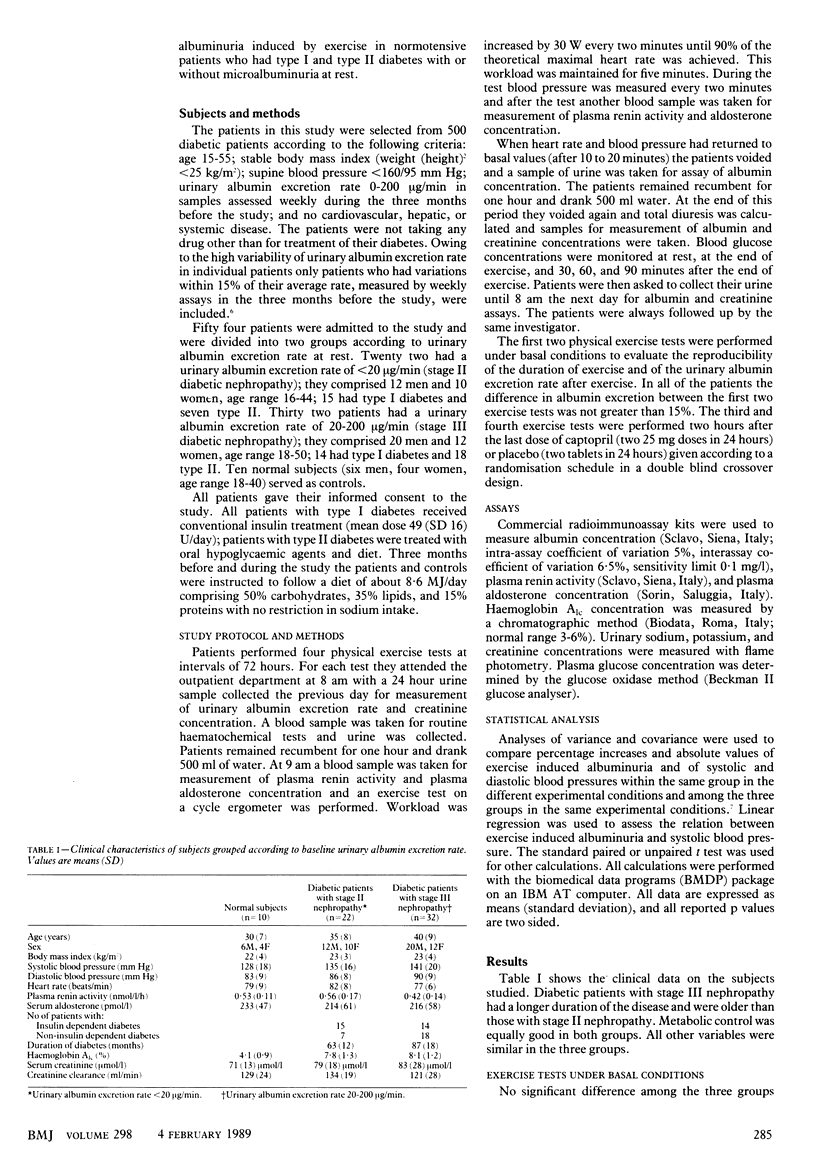
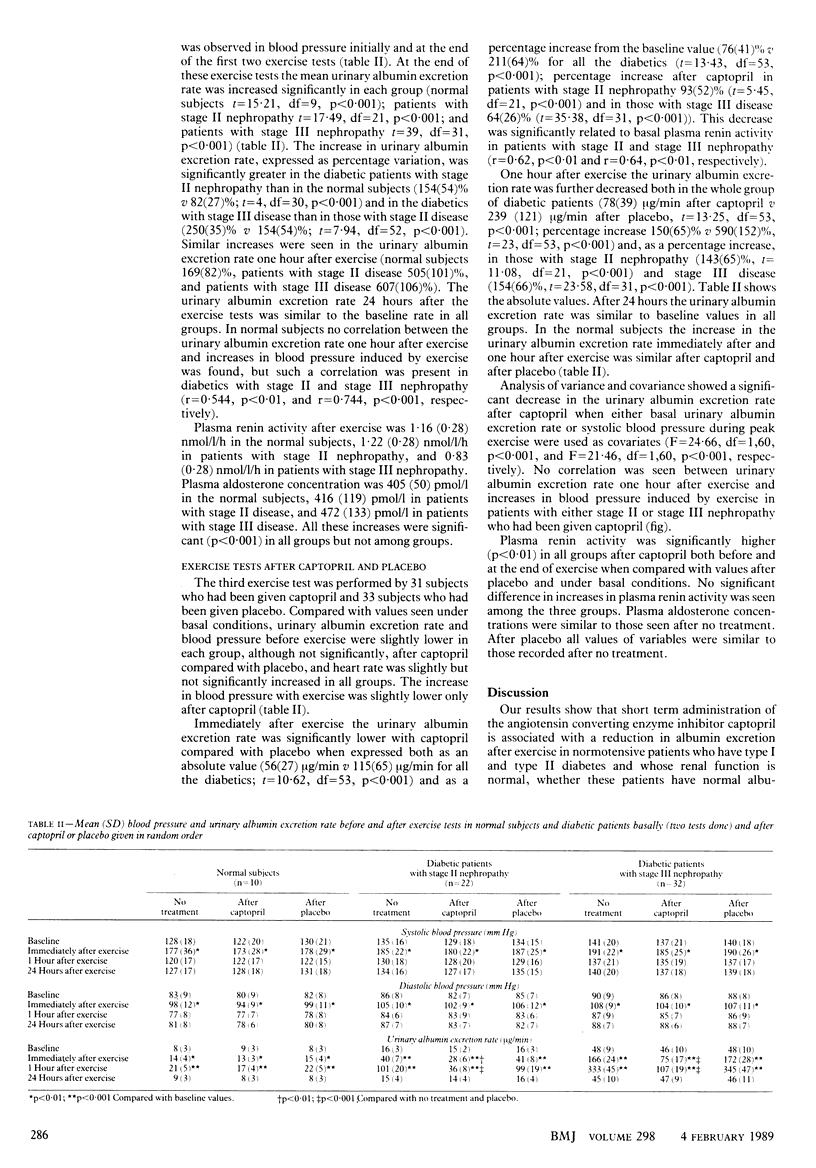
OBJECTIVE--To investigate whether captopril has any effect on microalbuminuria induced by exercise in normotensive diabetic patients with early stage nephropathy. DESIGN--Randomised, double blind, crossover trial. SETTING--Outpatient department. PATIENTS--22 diabetics with stage II nephropathy (urinary albumin excretion rate less than 20 micrograms/min; 15 with type I diabetes and seven with type II), 32 patients with stage III nephropathy (urinary albumin excretion rate 20-200 micrograms/min; 14 with type I diabetes and 18 with type II), and 10 normal subjects. INTERVENTIONS--Four exercise tests on a cycle ergometer: the first two under basal conditions and the third and fourth after subjects had received captopril (two 25 mg doses in 24 hours) or placebo (two tablets in 24 hours). END POINT--Exercised until 90% of maximum heart rate achieved. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS--Mean urinary excretion one hour after the first two exercise tests was 21 micrograms/min in normal subjects, 101 micrograms/min in diabetic patients with stage II nephropathy, and 333 micrograms/min in those with stage III nephropathy. Similar results were obtained after placebo. After captopril the urinary excretion rate one hour after exercise was significantly decreased in diabetics with stage II (36 micrograms/min) and stage III (107 micrograms/min) disease compared with placebo but not in normal subjects. Systolic and diastolic pressures were similar in the three groups after placebo and captopril had been given. CONCLUSIONS--Captopril significantly reduces microalbuminuria induced by exercise in normotensive diabetics without affecting systemic blood pressure. Captopril may reduce renal intracapillary pressure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen A. R., Christiansen J. S., Andersen J. K., Kreiner S., Deckert T. Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia. 1983 Dec;25(6):496–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00284458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blood pressure and salt supplies in West Africa. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel E., Mathiesen E., Edsberg B., Bahnsen M., Parving H. H. Acute reduction of arterial blood pressure reduces urinary albumin excretion in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. Diabetologia. 1986 Apr;29(4):211–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00454877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson I. G., Greene S. A., Smith M. A., Smith R. F., Griffin N. K., Baum J. D. Urine albumin to creatinine ratio-response to exercise in diabetes. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Apr;60(4):305–310. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.4.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto V. A., Huttunen N. P., Vierikko P. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion corrects exercise-induced albuminuria in juvenile diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 7;282(6266):778–779. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6266.778-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre M., Leblanc H., Suarez L., Guyenne T. T., Ménard J., Passa P. Converting enzyme inhibition and kidney function in normotensive diabetic patients with persistent microalbuminuria. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jun 6;294(6585):1448–1452. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6585.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrary R. F., Pitts T. O., Puschett J. B. Diabetic nephropathy: natural course, survivorship and therapy. Am J Nephrol. 1981;1(3-4):206–218. doi: 10.1159/000166541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen C. K., Vittinghus E. The stages in diabetic renal disease. With emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):64–78. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Long-term antihypertensive treatment inhibiting progression of diabetic nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Sep 11;285(6343):685–688. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6343.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R., Gundersen H. J., Hørlyck A., Kroustrup J. P., Nyberg G., Westberg G. Diabetic glomerulopathy. Structural characteristics of the early and advanced stages. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):79–82. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguma Y., Kitamoto Y., Futaki G., Ueda H., Monma H., Ishizaki M., Takahashi H., Sekino H., Sasaki Y. Effect of captopril on heavy proteinuria in azotemic diabetics. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 26;313(26):1617–1620. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512263132601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Pickup J. C., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Effect of control of blood glucose on urinary excretion of albumin and beta2 microglobulin in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 22;300(12):638–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903223001202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G., Pickup J. C., Bilous R. W., Keen H., Mackintosh D. Correction of exercise-induced microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetics after 3 weeks of subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):818–823. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vittinghus E., Mogensen C. E. Graded exercise and protein excretion in diabetic man and the effect of insulin treatment. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):725–729. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., Dunn B. R., Meyer T. W., Anderson S., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Prevention of diabetic glomerulopathy by pharmacological amelioration of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1925–1930. doi: 10.1172/JCI112521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


