Abstract
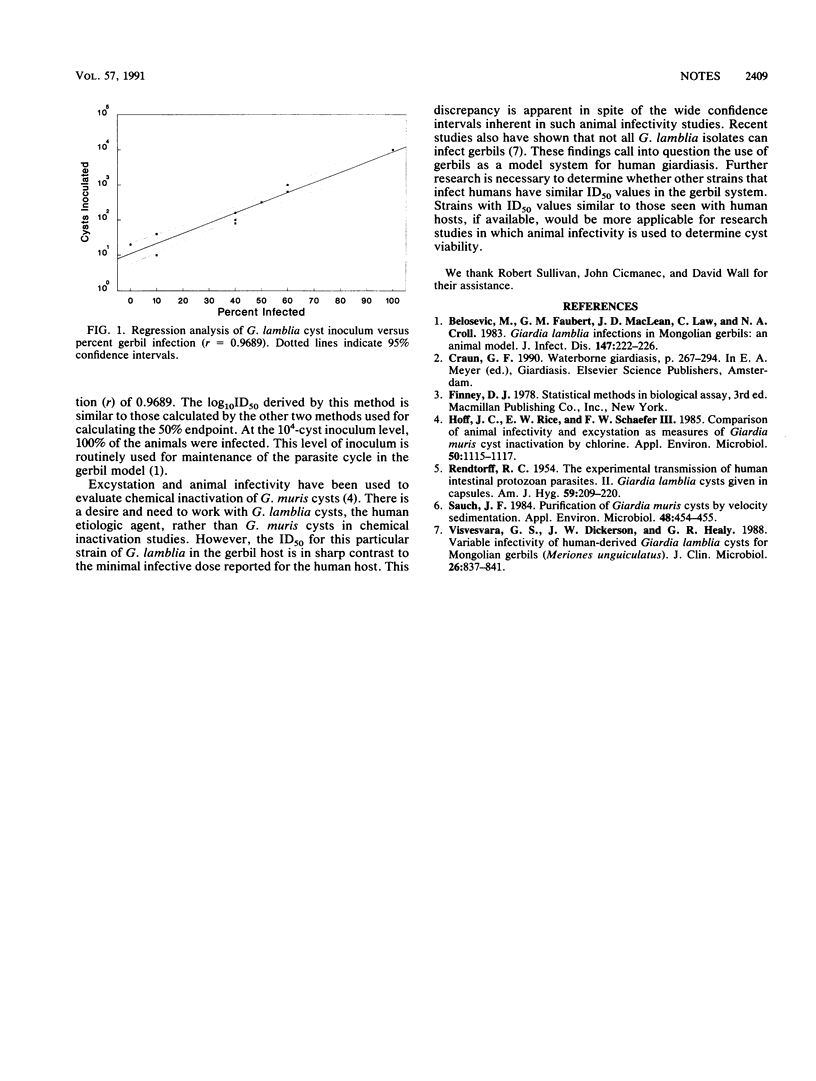
The purpose of this study was to determine the 50% infective dose for Giardia lamblia (CDC:0284:1) cysts in Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). The log10 50% infective dose results calculated by probit analysis and the Spearman-Karber method were 2.45 and 2.50, respectively.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belosevic M., Faubert G. M., MacLean J. D., Law C., Croll N. A. Giardia lamblia infections in Mongolian gerbils: an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff J. C., Rice E. W., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Comparison of animal infectivity and excystation as measures of Giardia muris cyst inactivation by chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1115–1117. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1115-1117.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENDTORFF R. C. The experimental transmission of human intestinal protozoan parasites. II. Giardia lamblia cysts given in capsules. Am J Hyg. 1954 Mar;59(2):209–220. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauch J. F. Purification of Giardia muris cysts by velocity sedimentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):454–455. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.454-455.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Dickerson J. W., Healy G. R. Variable infectivity of human-derived Giardia lamblia cysts for Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.837-841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



