Abstract
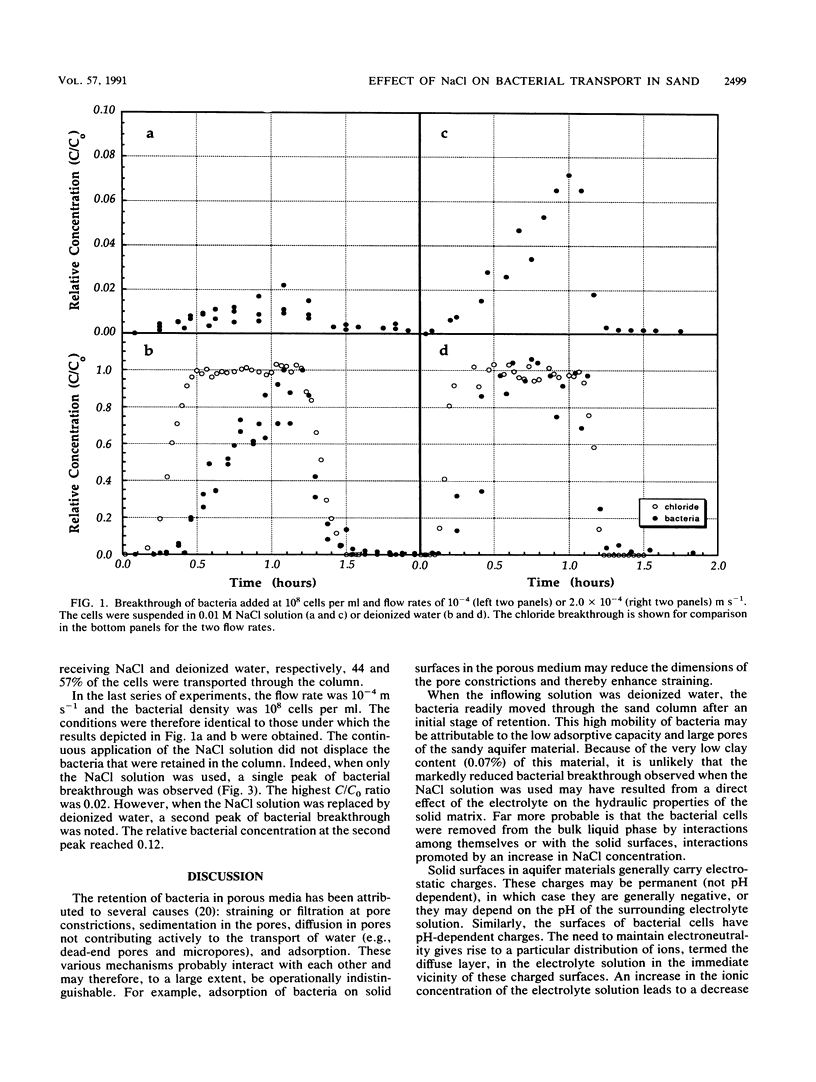
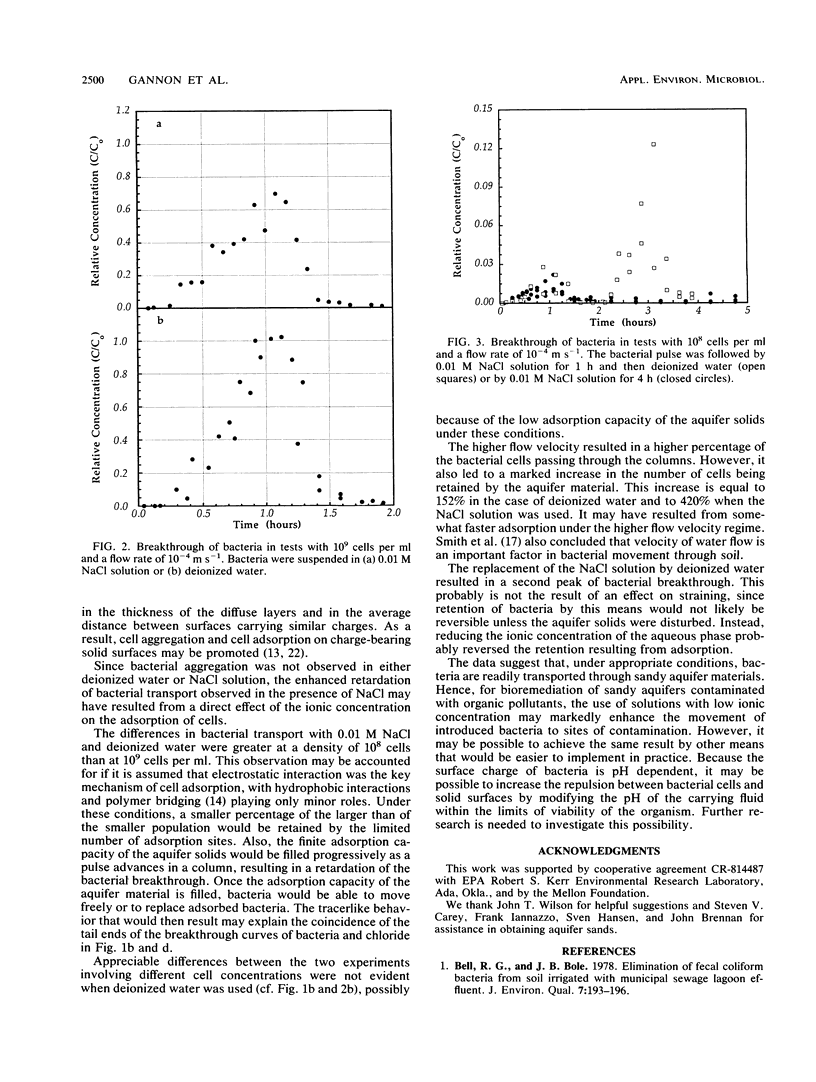
Determinations were made of the influence of NaCl concentration, cell density, and flow velocity on the transport of Pseudomonas sp. strain KL2 through columns of aquifer sand under saturated conditions. A pulse-type boundary condition was used. The experiments were conducted by using 0.3-m-long Plexiglas columns with an internal diameter of 0.05 m. When a 1-h pulse of a 0.01 M NaCl solution containing 10(8) cells per ml was added at a flow rate of 10(-4) m s-1, the bacterial density in the effluent never exceeded 2.2% of the density of cells added, and only 1.5% of the bacteria passed through the aquifer material. In contrast, when the bacteria were applied in distilled water, the relative cell density in the effluent approached 100%, and 60% of the bacteria were transported through the aquifer solids. Under these conditions, the breakthrough of Pseudomonas sp. strain KL2 was slower than chloride. When the flow rate was 2.0 x 10(-4) m s-1, the cell density in the effluent reached 7.3% of that added in 0.01 M NaCl solution, but only 3.9% of the bacteria were transported through the aquifer particles. On the other hand, the density in the effluent approached 100% of that added in deionized water, and 77% of the added bacteria were recovered. When the density of added cells was 10(9) cells per ml at a flow rate of 10(-4) m s-1, the densities in the effluent reached 70 and 100% of those added in salt solution and deionized water, respectively, and 44 and 57% of the bacteria were transported through the aquifer solids.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gannon J. T., Manilal V. B., Alexander M. Relationship between Cell Surface Properties and Transport of Bacteria through Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):190–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.190-193.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Lance J. C. Poliovirus removal from primary and secondary sewage effluent by soil filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):247–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.247-251.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Dean C. H., Knuckles M. E., Wagner R. A. Interactions and survival of enteric viruses in soil materials. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):92–101. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.92-101.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


