Abstract
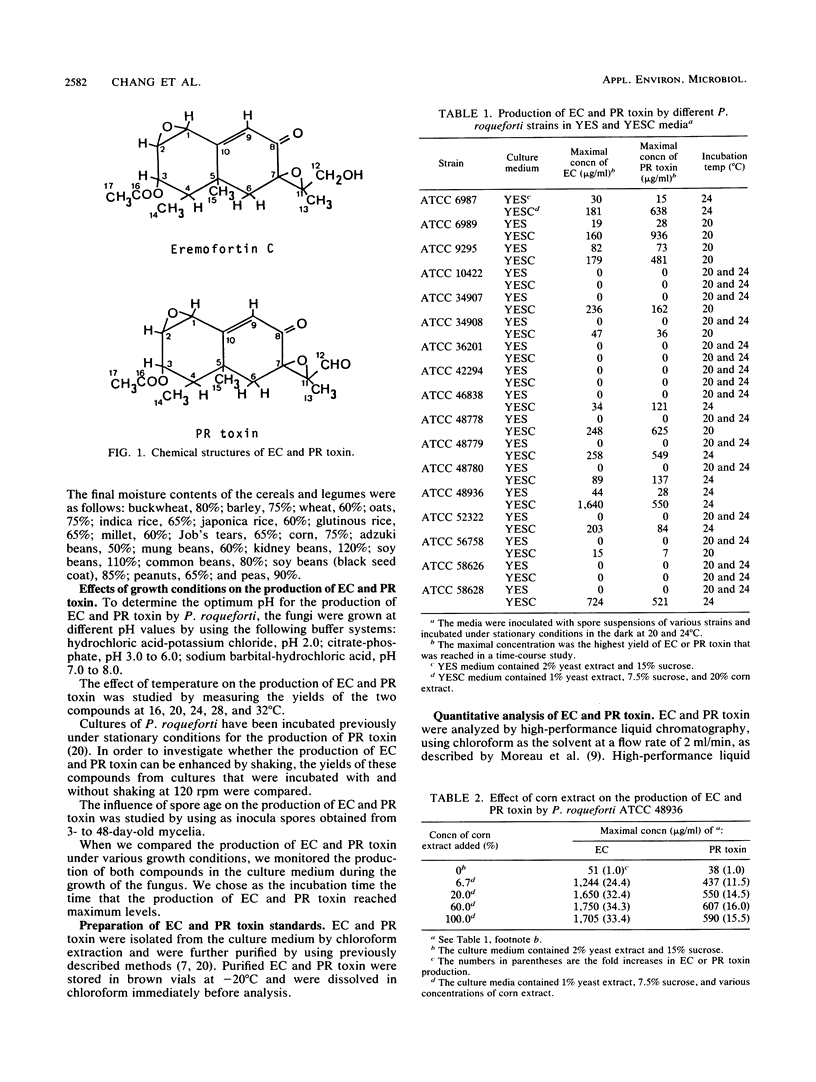
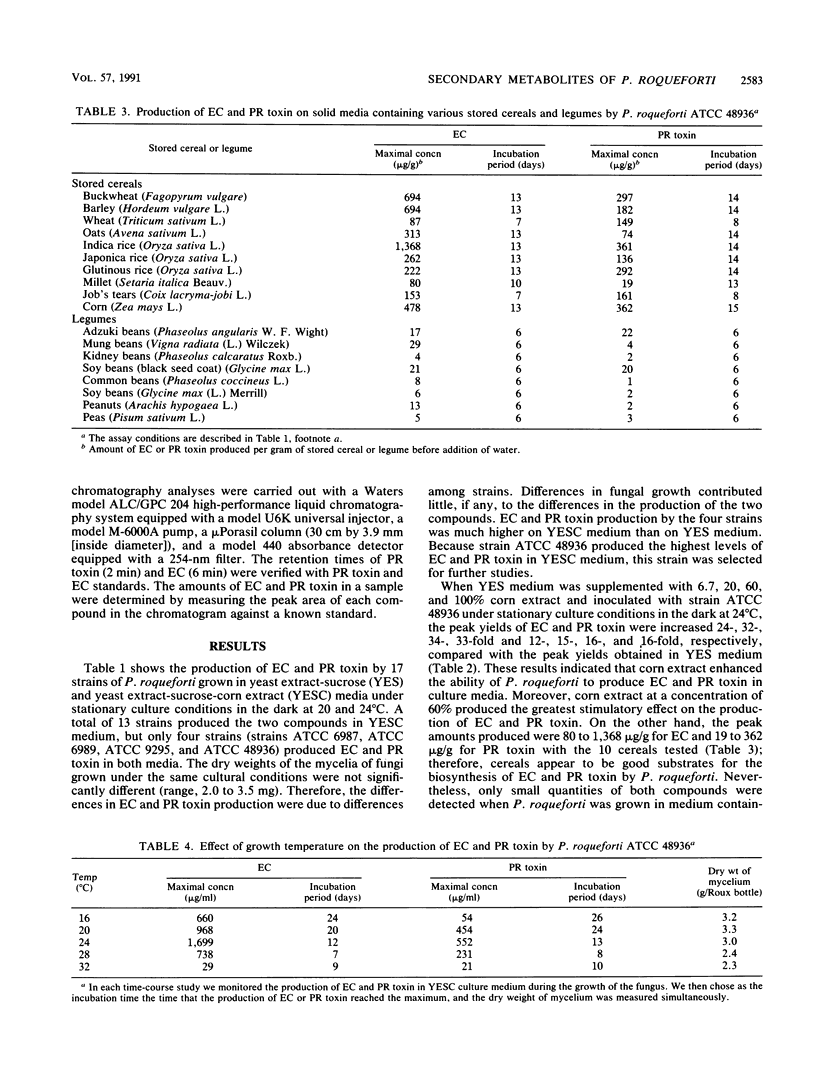
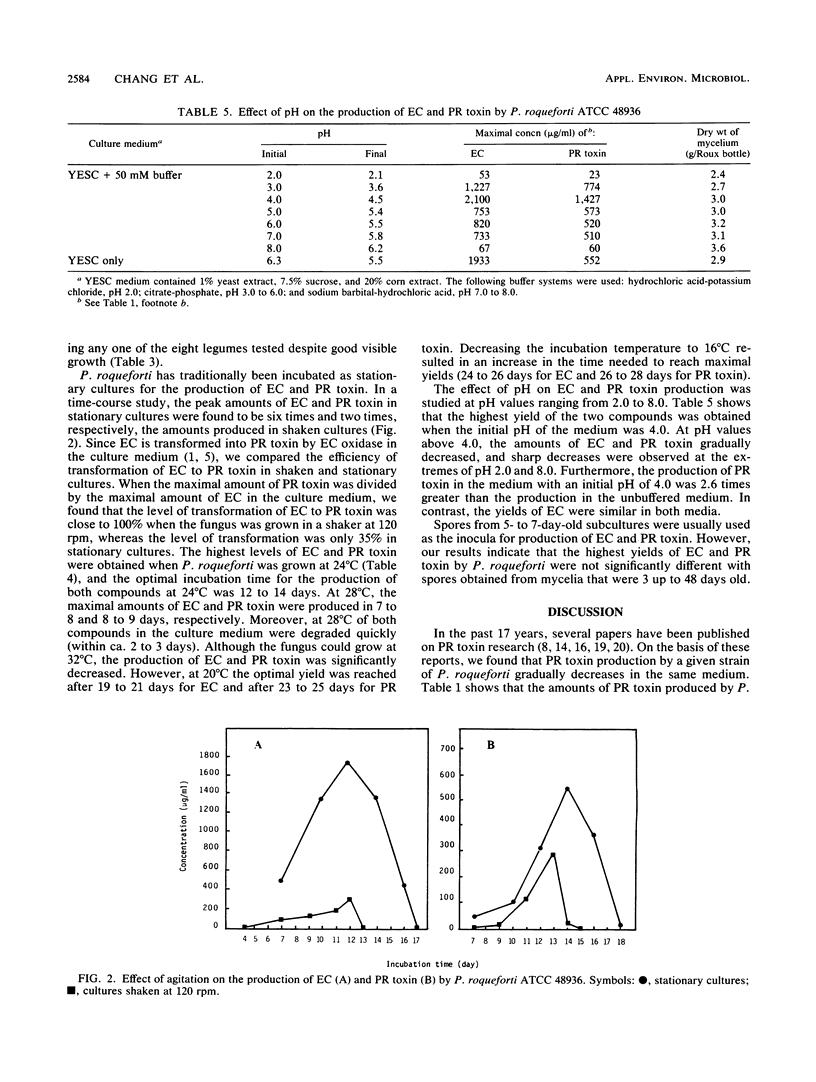
Eremofortin C (EC) and PR toxin are secondary metabolites of Penicillium roqueforti. Of 17 strains from the American Type Culture Collection that were studied for their ability to produce EC and PR toxin, 13 produced these metabolites. Toxin production by strains grown in solid media (10 cereals and 8 other agricultural products) was also investigated. Production of EC and PR toxin by fungi grown on cereals was greater than production of EC and PR toxin by fungi grown on legumes; fungi grown on corn produced the greatest amount of PR toxin. Addition of corn extracts to the culture medium greatly increased the production of EC and PR toxin in a coordinated manner, with no significant change in mycelial dry weight. The fungi produced the highest levels of EC and PR toxin at 20 to 24 degrees C depending on the strain. Toxin production was higher in stationary cultures than in cultures that were gently shaken at 120 rpm. The optimum pH for production of both EC and PR toxin was around pH 4.0. With regard to spore age, toxin levels did not change significantly when we used spores obtained from fungi that were grown at 24 degrees C for 3 up to 48 days.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang S. C., Wei Y. H., Liu M. L., Wei R. D. Isolation and Some Properties of the Enzyme That Transforms Eremofortin C to PR Toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1455–1460. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1455-1460.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. C., Chen C. F., Wei R. D. Acute toxicity of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. Toxicon. 1982;20(2):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh K. P., Yu S., Wei Y. H., Chen C. F., Wei R. D. Inhibitory effect in vitro of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti, on the mitochondrial HCO-3-ATPase of the rat brain, heart and kidney. Toxicon. 1986;24(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. H., Fang S. C., Wei R. D. The effects of Penicillium roqueforti toxin on the activity of rat hepatic DNA polymerases. Toxicology. 1984 Oct;33(1):43–57. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(84)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau S., Cacan M. Eremofortin C.A new metabolite obtained from penicillium roqueforti cultures and from biotransformation of PR toxin. J Org Chem. 1977 Jul 22;42(15):2632–2634. doi: 10.1021/jo00435a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau S., Lablache-Combier A., Biguet J. Production of Eremofortins A, B, and C Relative to Formation of PR Toxin by Penicillium roqueforti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):770–776. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.770-776.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau S., Masset A., Biguet J. Resolution of Penicillium roqueforti toxin and eremofortins A, B, and C by high-performance liquid chromatography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1059–1062. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1059-1062.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulé Y., Jammali M., Darracq N. Inhibition of protein synthesis by PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulé Y., Jemmali M., Rousseau N. Mechanism of the inhibition of transcription by PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. Chem Biol Interact. 1976 Aug;14(3-4):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(76)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulé Y., Moreau S., Bousquet J. F. Relationships between the chemical structure and the biological properties of some eremophilane compounds related to PR toxin. Chem Biol Interact. 1977 May;17(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(77)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Morace G., delle Monache F., Samson R. A. Studies on the PR toxin of Penicillium roqueforti. Mycopathologia. 1978 Dec 29;66(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00429600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. M., Kennedy B. P., Harwig J., Blanchfield B. J. Study of conditions of production of roquefortine and other metabolites of Penicillin roqueforti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):249–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.249-253.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R. D., Liu G. X. PR toxin production in different Penicillium roqueforti strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):797–799. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.797-799.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R. D., Still P. E., Smalley E. B., Schnoes H. K., Strong F. M. Isolation and partial characterization of a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):111–114. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.111-114.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R., Ong T., Whong W., Frezza D., Bronzetti G., Zeiger E. Genetic effects of PR toxin in eukaryotic microorganisms. Environ Mutagen. 1979;1(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/em.2860010111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y. H., Ding W. H., Wei R. D. Biochemical effects of PR toxin on rat liver mitochondrial respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):400–411. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


