Abstract
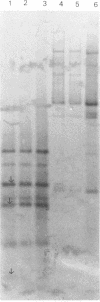
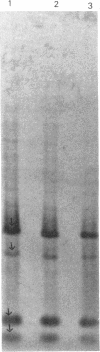
Three strains of Xenorhabdus nematophilus (A24, F1, NC116) and strain Dan of Xenorhabdus bovienii were tested to evaluate whether the phase variation observed in these bacteria was in any way connected with plasmids. The plasmid patterns of both phases of A24 and F1 strains were the same, whereas the two NC116 phases had only one band each. No difference was observed between the undigested or digested plasmid patterns of the two phases from the three strains. No plasmid was detected in either phase of strain Dan. The plasmid probes were prepared from the six bands of A24 phase 1. By hybridization studies, three plasmids in two forms (open circular and supercoiled) were detected in the strain A24. Two were estimated at 12 kb, and the smallest was about 4 kb. Attempts to hybridize plasmid probes with either undigested or digested chromosomal DNA of the two phases of strain A24 were unsuccessful. The results suggest that neither a difference in plasmid content nor a plasmid recombination with the chromosome is involved in phase variation. The hybridizations revealed homologous DNA sequences among the three plasmids of strain A24 and among the plasmids of strains such as A24 and NC116, which were isolated from geographically distant countries, suggesting that plasmids may encode similar proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J., Boemare N. E. A numerical taxonomic study of the genus Xenorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae) and proposed elevation of the subspecies of X. nematophilus to species. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1835–1845. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baya A. M., Brayton P. R., Brown V. L., Grimes D. J., Russek-Cohen E., Colwell R. R. Coincident plasmids and antimicrobial resistance in marine bacteria isolated from polluted and unpolluted Atlantic Ocean samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1285–1292. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1285-1292.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Simon M. I. Phase variation and the Hin protein: in vivo activity measurements, protein overproduction, and purification. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.71-79.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson P., Schrempf H. Genetic instability and DNA amplification in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4796–4803. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4796-4803.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Pardo M. A., Leija A., Martínez E., Romero D., Piñero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Genomic instability in Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1191-1196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada H. S., Sizemore R. K. Incidence of Plasmids in Marine Vibrio spp. Isolated from an Oil Field in the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.199-202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson M., Jones G. W., Kjelleberg S. Frequency of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance, pigmentation, and plasmids in bacteria of the marine air-water interface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2338–2342. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2338-2342.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Demuyter P., Moutier L., Laakel M., Decaris B., Simonet J. M. Hypervariability, a new phenomenon of genetic instability, related to DNA amplification in Streptomyces ambofaciens. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):419–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.419-423.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lereclus D., Lecadet M. M., Ribier J., Dedonder R. Molecular relationships among plasmids of Bacillus thuringiensis: conserved sequences through 11 crystalliferous strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):391–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00729459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Betlach M. Genome organization in Halobacterium halobium: a 70 kb island of more (AT) rich DNA in the chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00332938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poinar G. O., Jr, Hess R. T., Lanier W., Kinney S., White J. H. Preliminary observations of a bacteriophage infecting Xenorhabdus luminescens (Enterobacteriaceae). Experientia. 1989 Feb 15;45(2):191–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01954872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poinar G. O., Jr, Thomas G. M. Significance of Achromobacter nematophilus Poinar and Thomas (Achromobacteraceae: Eubacteriales) in the development of the nematode, DD-136 (Neoaplectana sp. Steinernematidae). Parasitology. 1966 May;56(2):385–390. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000070980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. S., Boyle J. A. Plasmid homologies in Edwardsiella ictaluri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3253–3255. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3253-3255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]