Abstract
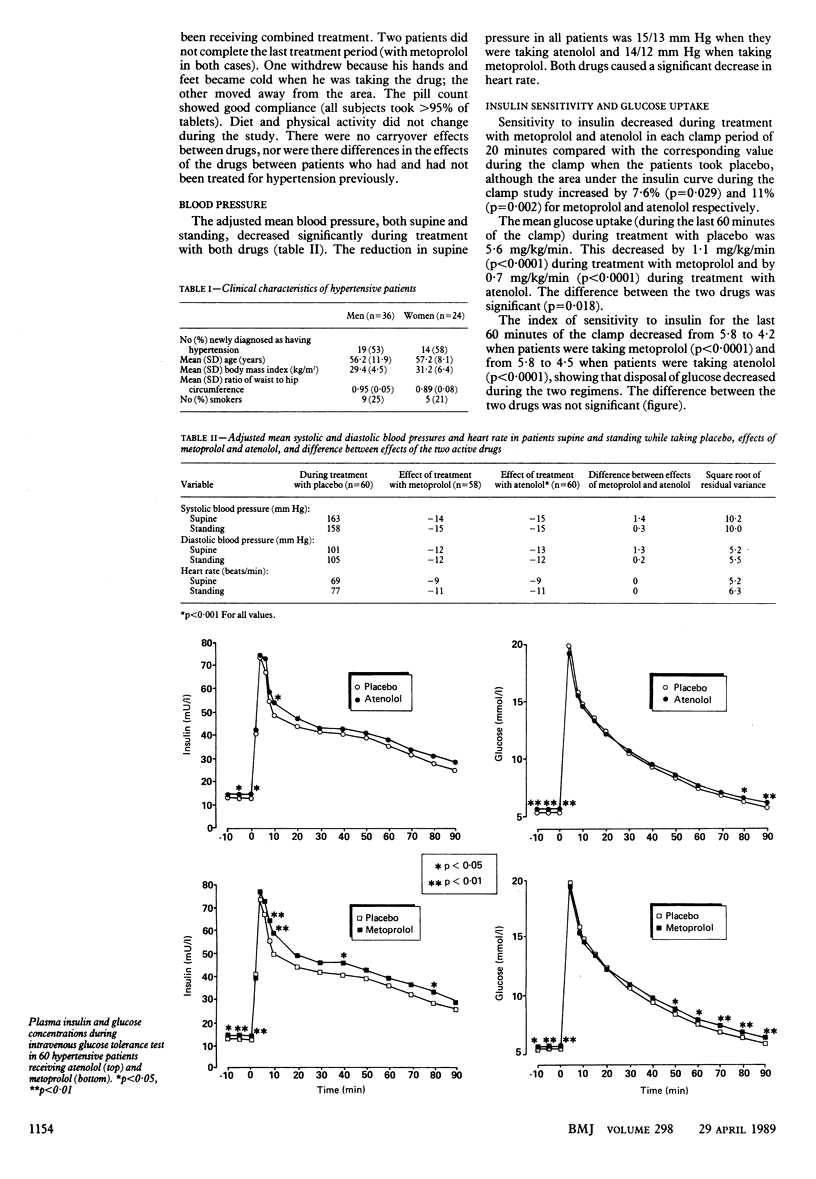
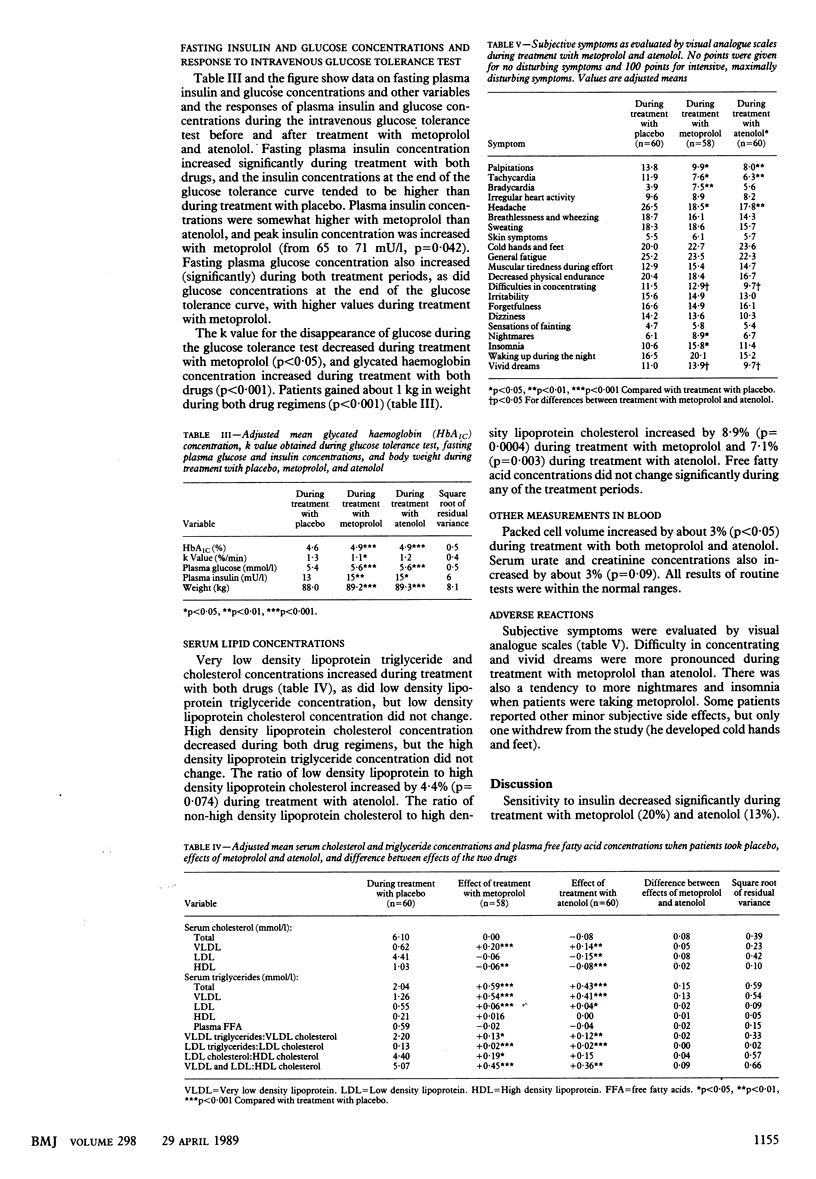
OBJECTIVE--To compare the effects of metoprolol and atenolol on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and on insulin response to an intravenous glucose load. DESIGN--Randomised, double blind, double dummy, controlled crossover trial. SETTING--University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden. PATIENTS--60 Patients with primary hypertension (diastolic blood pressure when resting supine 95-119 mm Hg on at least two occasions during four to six weeks of treatment with placebo) randomised to receive either metoprolol (n = 30) or atenolol (n = 30) during the first treatment period. INTERVENTIONS--Placebo was given for a run in period of four to six weeks. Metoprolol 100 mg twice daily or atenolol 25 mg twice daily was then given for 16 weeks. The two drugs were then exchanged and treatment continued for a further 16 weeks. END POINT--Evaluation of effects of treatment with metoprolol and atenolol on glucose, insulin, and lipid metabolism and glucose disposal mediated by insulin. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS--Reduction of blood pressure was similar and satisfactory during treatment with both drugs. Glucose uptake mediated by insulin was measured during a euglycaemic hyperinsulinaemic clamp to evaluate patients' sensitivity to insulin. Glucose uptake decreased from 5.6 to 4.5 mg/kg/min when patients were taking metoprolol and from 5.6 to 4.9 mg/kg/min when they were taking atenolol. Both drugs caused a small increase in fasting plasma insulin and blood glucose concentrations and glycated haemoglobin concentration. Despite decreased sensitivity to insulin the increase in insulin concentration in response to an intravenous glucose tolerance test was small, suggesting inhibition of release of insulin. Very low density lipoprotein and low density lipoprotein triglyceride concentrations were increased with both drugs and high density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration was decreased. Low density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration was not affected. CONCLUSIONS--Long term use of metoprolol and atenolol causes metabolic abnormalities that may be related to the increased incidence of diabetes in patients with hypertension who are treated pharmacologically. These results may help to explain why the two drugs have failed consistently to reduce the incidence of coronary heart disease in several large scale studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson C., Blohmé C., Lapidus L., Lundgren H. Diabetes in hypertensive women: an effect of antihypertensive drugs or the hypertensive state per se? Diabet Med. 1988 Apr;5(3):261–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1988.tb00981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson C., Blohmé G., Lapidus L., Lindquist O., Lundgren H., Nyström E., Petersen K., Sigurdsson J. A. Do antihypertensive drugs precipitate diabetes? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 1;289(6457):1495–1497. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6457.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Finegood D. T., Ader M. Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo. Endocr Rev. 1985 Winter;6(1):45–86. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum J., DiBianco R., Becker K. L., Muesing R., Costello R. B., Singh S. N., Gottdiener J. S., Fletcher R. D. Glucose and lipid metabolism during acebutolol and propranolol therapy of angina in nondiabetic patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Mar;33(3):294–300. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratusch-Marrain P. R., Smith D., DeFronzo R. A. The effect of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):973–982. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen-Sjöbom N., Lins P. E., Adamson U., Curstedt T., Hamberger B. Effects of metoprolol on the counter-regulation and recognition of prolonged hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1987;222(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Harris M. D., Rosenberg C. S. Inverse relationship of metabolic clearance rate of insulin to body mass index. Metabolism. 1987 Mar;36(3):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. L., Simpson N., Metcalfe J., Page R. L. Metabolic consequences of atenolol and propranolol in treatment of essential hypertension. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 13;1(6156):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6156.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Felig P., Wahren J. Regulation of splanchnic and peripheral glucose uptake by insulin and hyperglycemia in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Thorin D., Felber J. P., Simonson D. C., Thiebaud D., Jequier E., Golay A. Effect of beta and alpha adrenergic blockade on glucose-induced thermogenesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):633–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI111253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg G., Hansson B. G. Glucose tolerance and insulin release in hypertensive patients treated with the cardioselective beta-receptor blocking agent metoprolol. Acta Med Scand. 1977;202(5):393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb16850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagher B., Liedholm H., Monti M., Moritz U. Thermogenesis in human skeletal muscle as measured by direct microcalorimetry and muscle contractile performance during beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 May;70(5):435–441. doi: 10.1042/cs0700435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Giorico M. A., Oleggini M., Graziadei L., Pedrinelli R., Brandi L., Bevilacqua S. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 6;317(6):350–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708063170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrand H., Aberg H. Insulin response to intravenous glucose during long-term treatment with propranolol. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Jul-Aug;196(1-2):39–40. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helderman J. H., Elahi D., Andersen D. K., Raizes G. S., Tobin J. D., Shocken D., Andres R. Prevention of the glucose intolerance of thiazide diuretics by maintenance of body potassium. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):106–111. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland A., Hjermann I., Leren P., Holme I. Possible metabolic side effects of beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 1;1(6116):828–828. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6116.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland A., Strømmen R., Hagelund C. H., Tretli S. Enalapril, atenolol, and hydrochlorothiazide in mild to moderate hypertension. A comparative multicentre study in general practice in Norway. Lancet. 1986 Apr 19;1(8486):872–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90985-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Johansson S., Vedin A., Wilhelmsson C., Smith U. The effect of beta-blockade on glucose tolerance and insulin release in adult diabetes. Acta Med Scand. 1980;208(3):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb01175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKKOS D., LUFT R. On the intravenous glucose tolerance test. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1957 Jul;25(3):312–334. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0250312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauch K. W., Hartl W., Guenther B., Wicklmayr M., Rett K., Dietze G. Captopril enhances insulin responsiveness of forearm muscle tissue in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;17(5):448–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1987.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson J. O., Jerntorp P., Sundkvist G., Englund H., Nylund V. Measurement of hemoglobin A1c by a new liquid-chromatographic assay: methodology, clinical utility, and relation to glucose tolerance evaluated. Clin Chem. 1986 Oct;32(10):1867–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser P. Physical performance and muscle metabolism during beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1984;536:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen A. The effect of acebutolol on plasma lipids, blood glucose and serum insulin levels. Acta Med Scand. 1984;216(1):57–60. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1984.tb03771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithell H., Lindgärde F., Hellsing K., Lundqvist G., Nygaard E., Vessby B., Saltin B. Body weight, skeletal muscle morphology, and enzyme activities in relation to fasting serum insulin concentration and glucose tolerance in 48-year-old men. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):19–25. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Sorel G., Savi L. The action of beta-adrenergic blocking and stimulating agents on insulin secretion. Characterization of the type of beta receptor. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01212541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicardi V., Camellini L., Bellodi G., Coscelli C., Ferrannini E. Evidence for an association of high blood pressure and hyperinsulinemia in obese man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jun;62(6):1302–1304. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-6-1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauras N., Blizzard R. M., Thorner M. O., Rogol A. D. Selective beta 1-adrenergic receptor-blockade with atenolol enhances growth hormone releasing hormone and mediated growth hormone release in man. Metabolism. 1987 Apr;36(4):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micossi P., Pollavini G., Raggi U., Librenti M. C., Garimberti B., Beggi P. Effects of metoprolol and propranolol on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 1984 Feb;16(2):59–63. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky S., Pattavina C. G. Hyperosmolar nonketotic diabetic coma: a complication of propranolol therapy. Metabolism. 1973 May;22(5):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollare T., Lithell H., Selinus I., Berne C. Application of prazosin is associated with an increase of insulin sensitivity in obese patients with hypertension. Diabetologia. 1988 Jul;31(7):415–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00271585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Mechanism and significance of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):990–995. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter K. J., Kerp L. Beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents induce different counter-regulatory responses to insulin. J Pharmacol. 1983;14 (Suppl 2):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P., Gödicke W., Voigt S., Hajdu I., Weiss M. Postprandial hyperinsulinemia in patients with mild essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):182–186. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Warren D. J. Effect of acute oral beta adrenergic blockade on muscle blood flow in man. Cardiovasc Res. 1982 Apr;16(4):205–208. doi: 10.1093/cvr/16.4.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman K., Groop L., Groop P. H., Kala R., Tolppanen E. M., Fyhrquist F. Effect of beta-blocking drugs on beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in hypertensive non-diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00546701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Untreated mild hypertension. A report by the Management Committee of the Australian Therapeutic Trial in Mild Hypertension. Lancet. 1982 Jan 23;1(8265):185–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedin A., Wilhelmsson C., Björntorp P. Induction of diabetes and oral glucose tolerance tests during and after chronic beta-blockade. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1975;575:37–40. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1975.tb06484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Metabolic effects of beta-adrenoreceptor blockers. Drugs. 1976;11(Suppl 1):121–126. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197600111-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen L., Berglund G., Elmfeldt D., Fitzsimons T., Holzgreve H., Hosie J., Hörnkvist P. E., Pennert K., Tuomilehto J., Wedel H. Beta-blockers versus diuretics in hypertensive men: main results from the HAPPHY trial. J Hypertens. 1987 Oct;5(5):561–572. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198710000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- William-Olsson T., Fellenius E., Björntorp P., Smith U. Differences in metabolic responses to beta-adrenergic stimulation after propranolol or metoprolol administration. Acta Med Scand. 1979;205(3):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb06031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. D., Barber S. G., Kendall M. J., Poole P. H. Beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs and blood sugar control in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 20;1(6157):159–161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6157.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


