Abstract
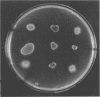
In this study, 468 Listeria strains were checked for the presence of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) activity by using a simple assay that consisted of overlaying colonies formed on agar plates with L-alpha-phosphatidylinositol as substrate. In this assay, PI-PLC-active colonies show turbid halos around the colonies as a result of the release of insoluble diacylglycerol from the substrate. This activity was detected only in the pathogenic species Listeria monocytogenes and was not present in any of the 167 strains of Listeria seeligeri, Listeria welshimeri, Listeria innocua, Listeria murrayi, and Listeria grayi tested. Hence, screening for PI-PLC activity permits discrimination between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Listeria species. In particular, the hemolytic but nonpathogenic species L. seeligeri can now be separated from the hemolytic and pathogenic species L. monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. The use of this assay will improve the specific detection and/or isolation of pathogenic Listeria species from clinical samples or food enrichment cultures.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibb W. F., Gellin B. G., Weaver R., Schwartz B., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M. W., Pinner R. W., Broome C. V. Analysis of clinical and food-borne isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in the United States by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2133-2141.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butman B. T., Plank M. C., Durham R. J., Mattingly J. A. Monoclonal antibodies which identify a genus-specific Listeria antigen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1564–1569. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1564-1569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassiday P. K., Graves L. M., Swaminathan B. Replica plating of colonies from Listeria-selective agars to blood agar to improve the isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2274–2275. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2274-2275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Listeriosis. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1313–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. Foodborne listeriosis. Lancet. 1990 Nov 10;336(8724):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92778-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Acquired resistance to facultative intracellular bacteria: relationship between persistence, cross-reactivity at the T-cell level, and capacity to stimulate cellular immunity of different Listeria strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):234–241. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.234-241.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Johnson A., Croan D., Flynn P., Whippie K., Kimball M., Lawrie J., Curiale M. Comparative studies of nucleic acid hybridization assay for Listeria in foods. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):669–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Kathariou S., Goebel W. Hemolysin supports survival but not entry of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):79–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.79-82.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T. Detection of listeriolysin, the thiol-dependent hemolysin in Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria ivanovii, and Listeria seeligeri. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2350–2357. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2350-2357.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Chakraborty T. Detection of a gene encoding a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C that is co-ordinately expressed with listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimeister-Wächter M., Haffner C., Domann E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Identification of a gene that positively regulates expression of listeriolysin, the major virulence factor of listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8336–8340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Chakraborty T., Leimeister-Wächter M., Dufrenne J., Heuvelman K. J., Maas H., Jansen W., Wernars K., Guinee P. Specific gene probe for detection of biotyped and serotyped Listeria strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):902–906. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.902-906.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Schrettenbrunner A., Seeliger H. P. Différenciation biochimique des groupes génomiques de Listeria monocytogenes (sensu lato). Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jan-Feb;134A(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siragusa G. R., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria innocua, and Listeria welshimeri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1897–1904. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1897-1904.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernars K., Heuvelman C. J., Chakraborty T., Notermans S. H. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for direct detection of Listeria monocytogenes in soft cheese. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;70(2):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Netten P., Perales I., van de Moosdijk A., Curtis G. D., Mossel D. A. Liquid and solid selective differential media for the detection and enumeration of L. monocytogenes and other Listeria spp. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jul;8(4):299–316. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]