Abstract
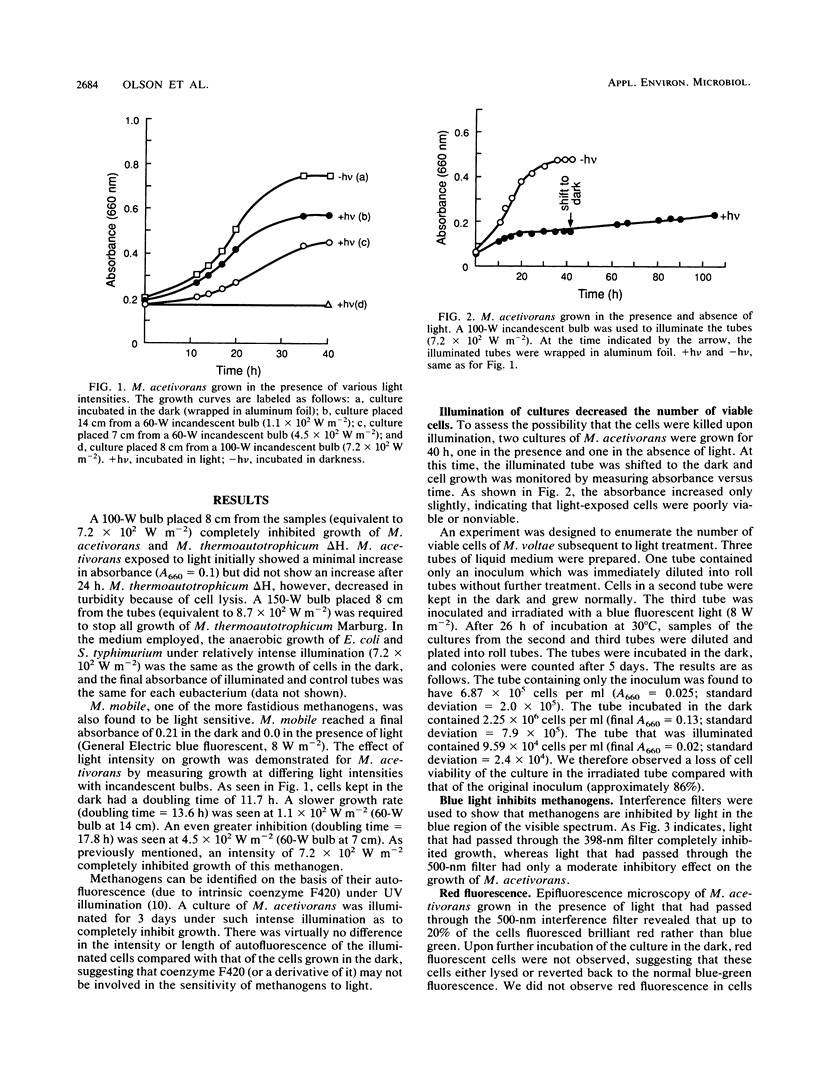
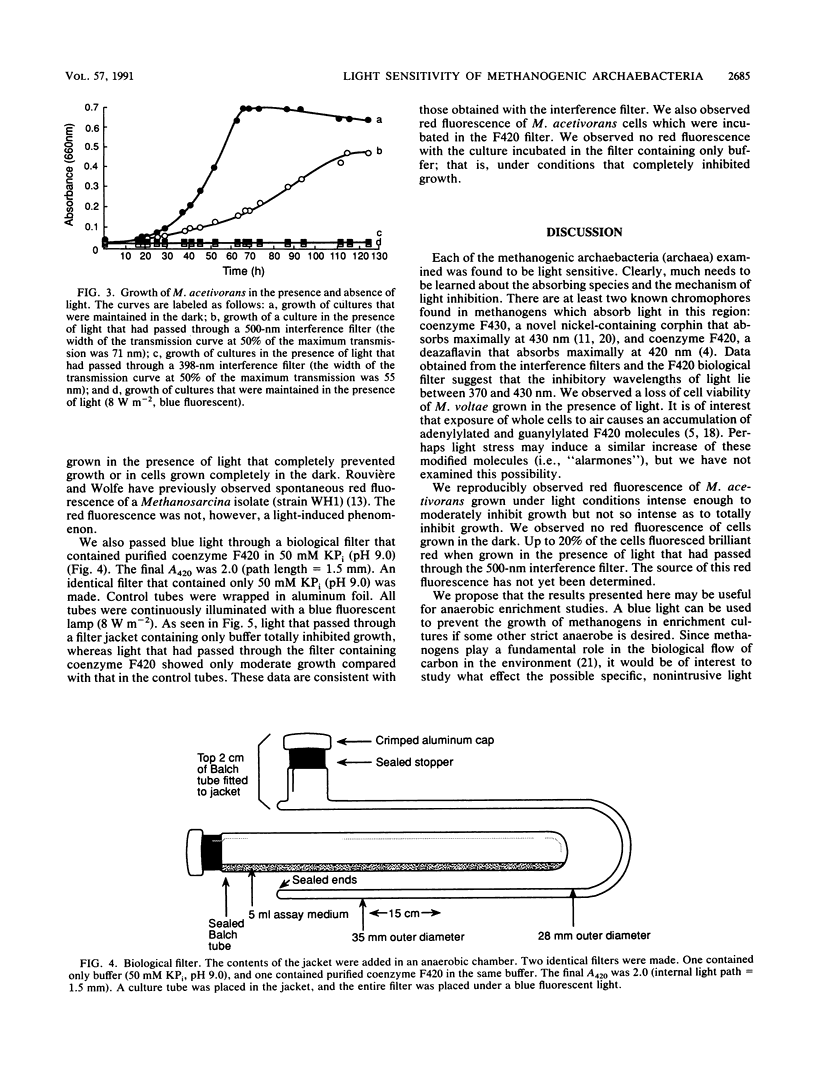
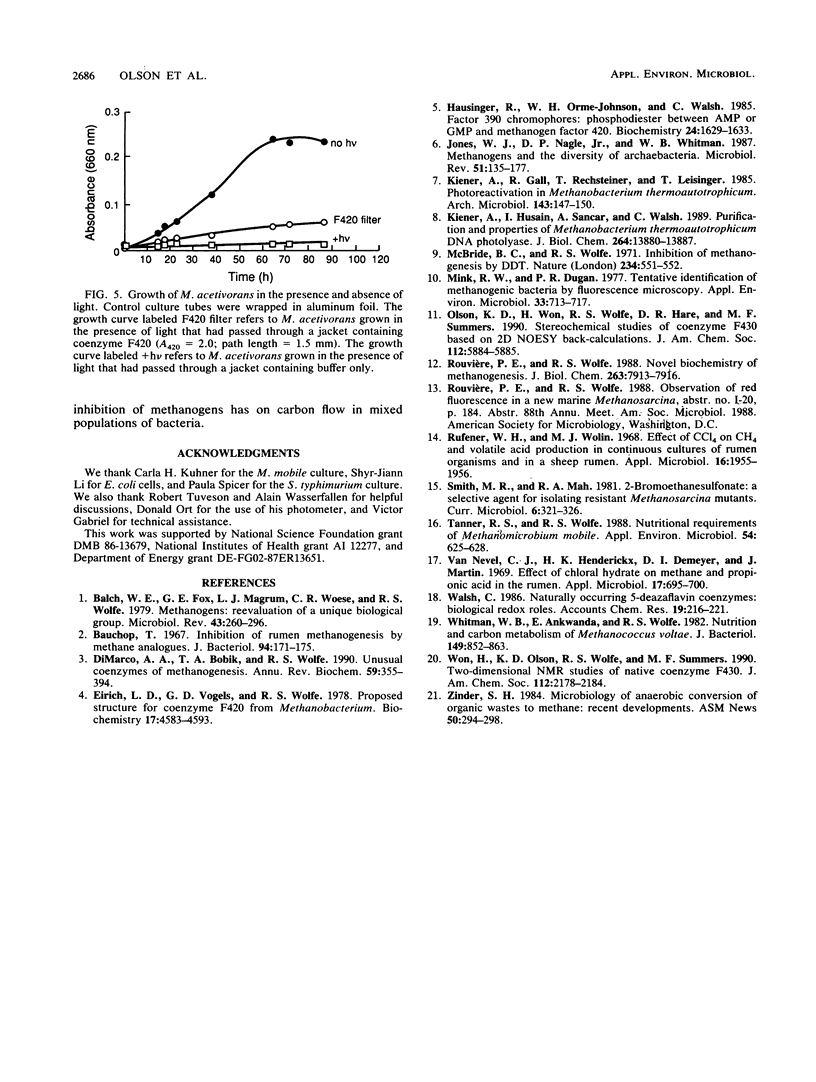
Representatives of four families of methanogenic archaebacteria (archaea), Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum delta H, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg, Methanosarcina acetivorans, Methanococcus voltae, and Methanomicrobium mobile, were found to be light sensitive. The facultative anaerobic eubacteria Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, however, were tolerant of light when grown anaerobically under identical light conditions. Interference filters were used to show that growth of the methanogens is inhibited by light in the blue end of the visible spectrum (370 to 430 nm).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauchop T. Inhibition of rumen methanogenesis by methane analogues. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):171–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.171-175.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarco A. A., Bobik T. A., Wolfe R. S. Unusual coenzymes of methanogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:355–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirich L. D., Vogels G. D., Wolfe R. S. Proposed structure for coenzyme F420 from Methanobacterium. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4583–4593. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P., Orme-Johnson W. H., Walsh C. Factor 390 chromophores: phosphodiester between AMP or GMP and methanogen factor 420. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 26;24(7):1629–1633. doi: 10.1021/bi00328a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener A., Husain I., Sancar A., Walsh C. Purification and properties of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13880–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S. Inhibition of methanogenesis by DDT. Nature. 1971 Dec 31;234(5331):551–552. doi: 10.1038/234551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mink R. W., Dugan P. R. Tentative identification of methanogenic bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):713–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.713-717.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière P. E., Wolfe R. S. Novel biochemistry of methanogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7913–7916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufener W. H., Jr, Wolin M. J. Effect of CCl4 on CH4 and volatile acid production in continuous cultures of rumen organisms and in a sheep rumen. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1955–1956. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1955-1956.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner R. S., Wolfe R. S. Nutritional requirements of Methanomicrobium mobile. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):625–628. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.625-628.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nevel C. J., Henderickx H. K., Demeyer D. I., Martin J. Effect of chloral hydrate on methane and propionic acid in the rumen. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):695–700. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.695-700.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Ankwanda E., Wolfe R. S. Nutrition and carbon metabolism of Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):852–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.852-863.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



