Abstract
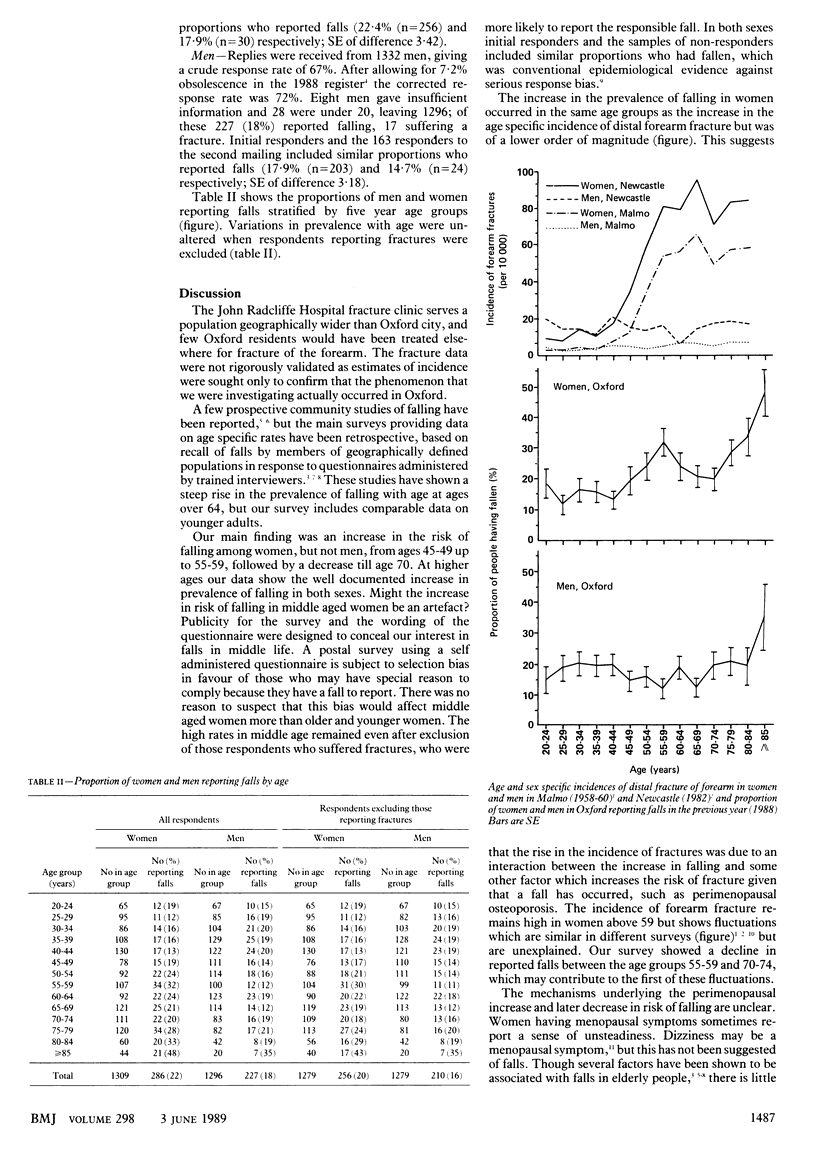
A postal survey of 2000 women and 2000 men sampled from the electoral roll in Oxford was undertaken to ascertain whether changes with age in the risk of falling might explain the stepwise increases in age specific incidence rates of distal forearm fracture which occur in women at around the age of 50. Corrected response rates were 83% for women and 72% for men. In women, but not in men, there was a rise in the risk of falling from 45 years, peaking in the 55-59 year age group, and sinking to a nadir at ages 70-74. In both sexes rates rose in extreme old age. These variations were not attributable to preferential response from people who had suffered a fracture. It is concluded that changes in the risk of falling interact with osteoporosis to produce a perimenopausal rise in the incidence of forearm fractures and contribute to the fluctuations in incidence of these fractures in old age.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALFFRAM P. A., BAUER G. C. Epidemiology of fractures of the forearm. A biomechanical investigation of bone strength. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962 Jan;44-A:105–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. J., Spears G. F., Borrie M. J., Fitzgerald J. L. Falls, elderly women and the cold. Gerontology. 1988;34(4):205–208. doi: 10.1159/000212954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton L. J., 3rd, Riggs B. L. Risk factors for injury after a fall. Clin Geriatr Med. 1985 Aug;1(3):525–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. W., Evans J. G. Fractures of the distal forearm in Newcastle: an epidemiological survey. Age Ageing. 1985 May;14(3):155–158. doi: 10.1093/ageing/14.3.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudham D., Evans J. G. Factors associated with falls in the elderly: a community study. Age Ageing. 1981 Aug;10(3):141–146. doi: 10.1093/ageing/10.3.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinetti M. E., Speechley M., Ginter S. F. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 29;319(26):1701–1707. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812293192604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



