Abstract
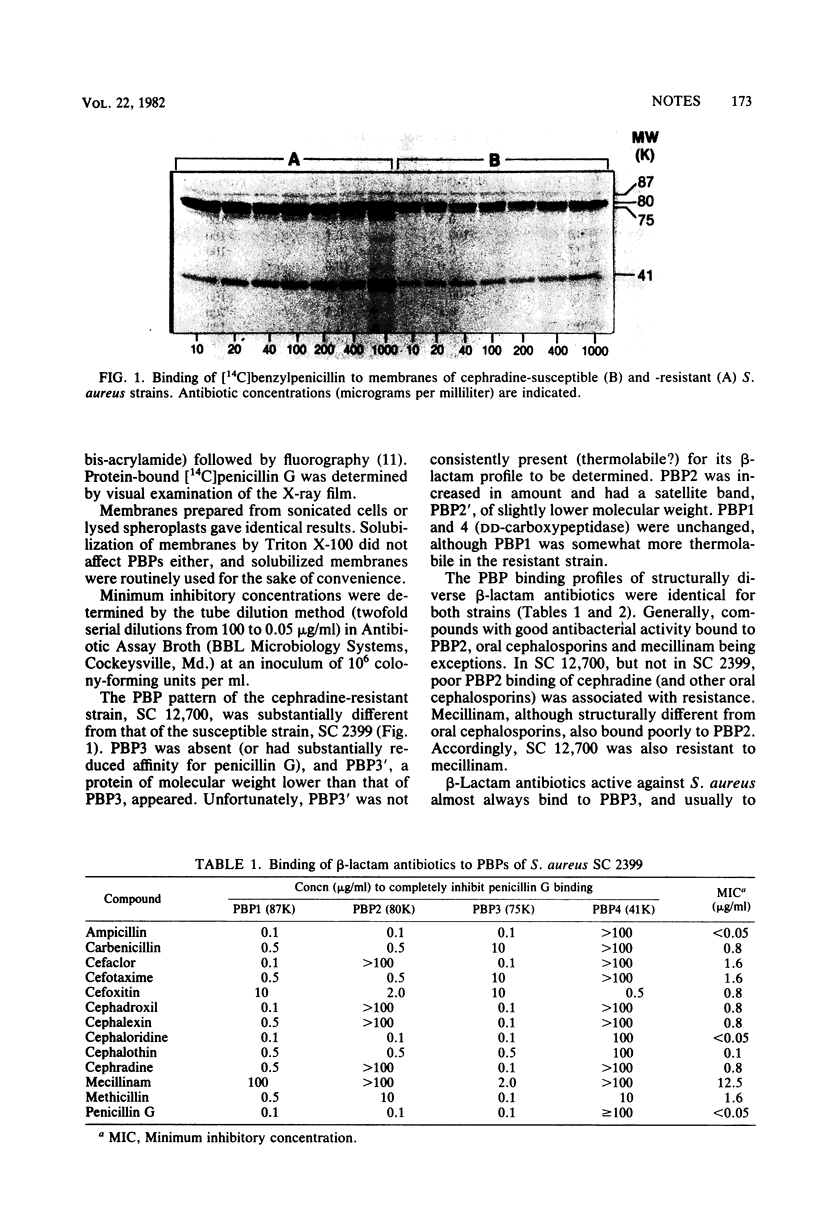
The penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) of a clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus specifically resistant to oral cephalosporins were compared with those of a susceptible strain. In the resistant strain, PBP3 (75,000 molecular weight) was missing or had substantially (greater than 100-fold) reduced affinity for penicillin; PBP2 (80,000 molecular weight) was increased in amount and contained a satellite band, PBP2'; PBPs 1 and 4 were unchanged. Oral cephalosporins bound poorly to PBP2 in both susceptible and resistant strains, but only in the latter did binding correlate with antibiotic activity. The results are consistent with the suggestion that PBP2 is essential in S. aureus. PBP2 might in addition compensate for PBP3 when the latter is missing. In the susceptible strain the lack of correlation between binding to PBP2 and beta-lactam antibiotic activity is due to the very high affinity of the also essential PBP3 for beta-lactam antibiotics.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. F., Reynolds P. E. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. F., Reynolds R. E. Bacillus megaterium resistance to cloxacillin accompanied by a compensatory change in penicillin binding proteins. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):167–168. doi: 10.1038/280167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Tarpay M., Tomasz A. Multiple changes of penicillin-binding proteins in penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):364–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarich J. W., Strominger J. L. A membrane enzyme from Staphylococcus aureus which catalyzes transpeptidase, carboxypeptidase, and penicillinase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Lord V. L. New type of beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1049–1050. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J. Heme-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:172–178. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawara H., Horikawa S. Penicillin-binding proteins of Streptomyces cacaoi, Streptomyces olivaceus, and Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Shepherd S. T., Chase H. A. Identification of the binding protein which may be the target of penicillin action in Bacillus megaterium. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):568–570. doi: 10.1038/271568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Escherichia coli resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics through a decrease in the affinity of a target for lethality. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):713–715. doi: 10.1038/274713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Cimarusti C. M., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Floyd D. M., Georgopapadakou N. H., Koster W. M., Liu W. C., Parker W. L., Principe P. A. Monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):489–491. doi: 10.1038/291489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




