Abstract
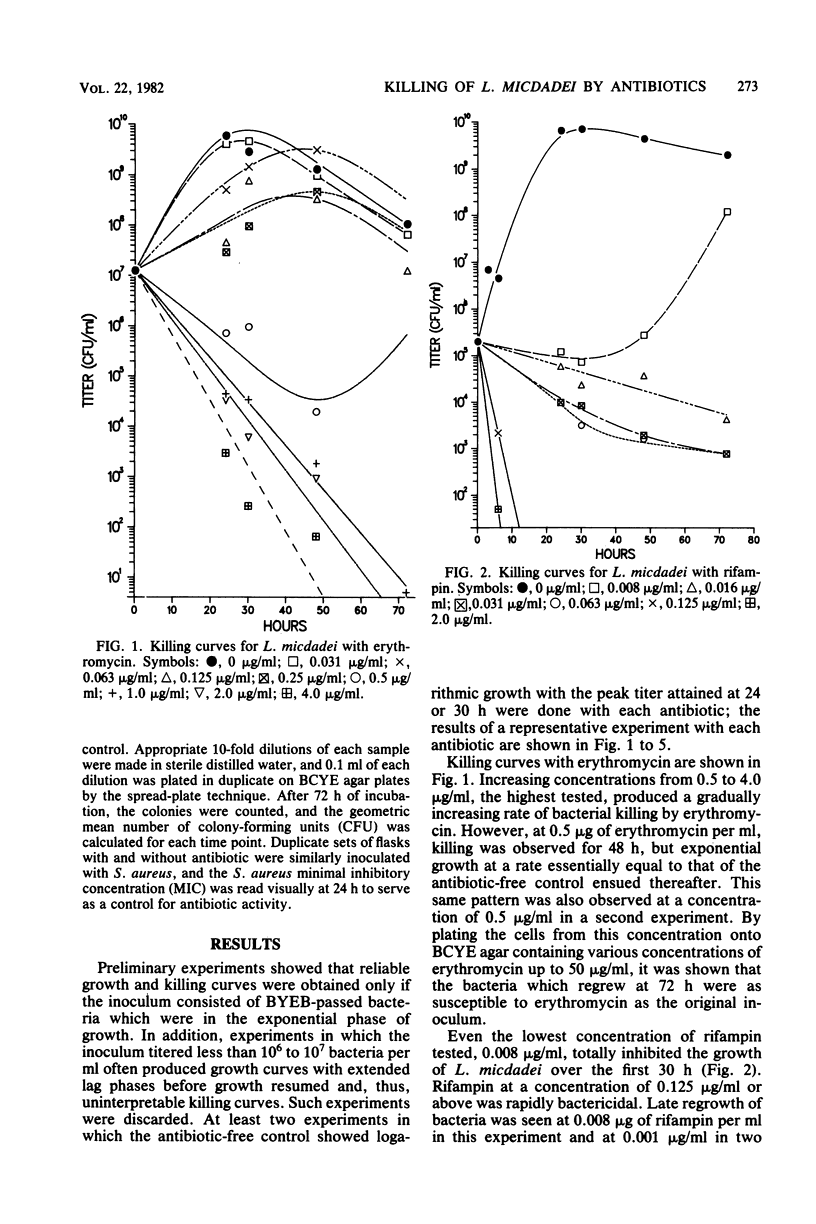
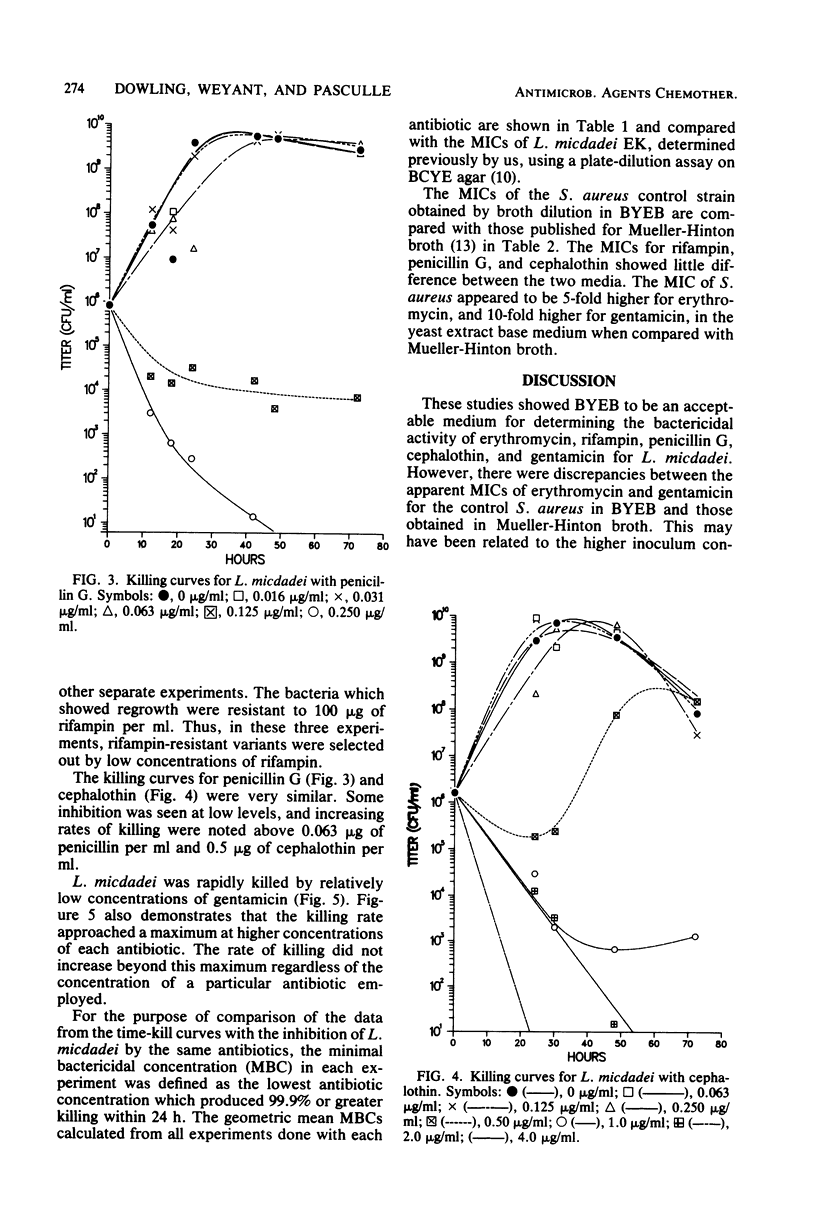
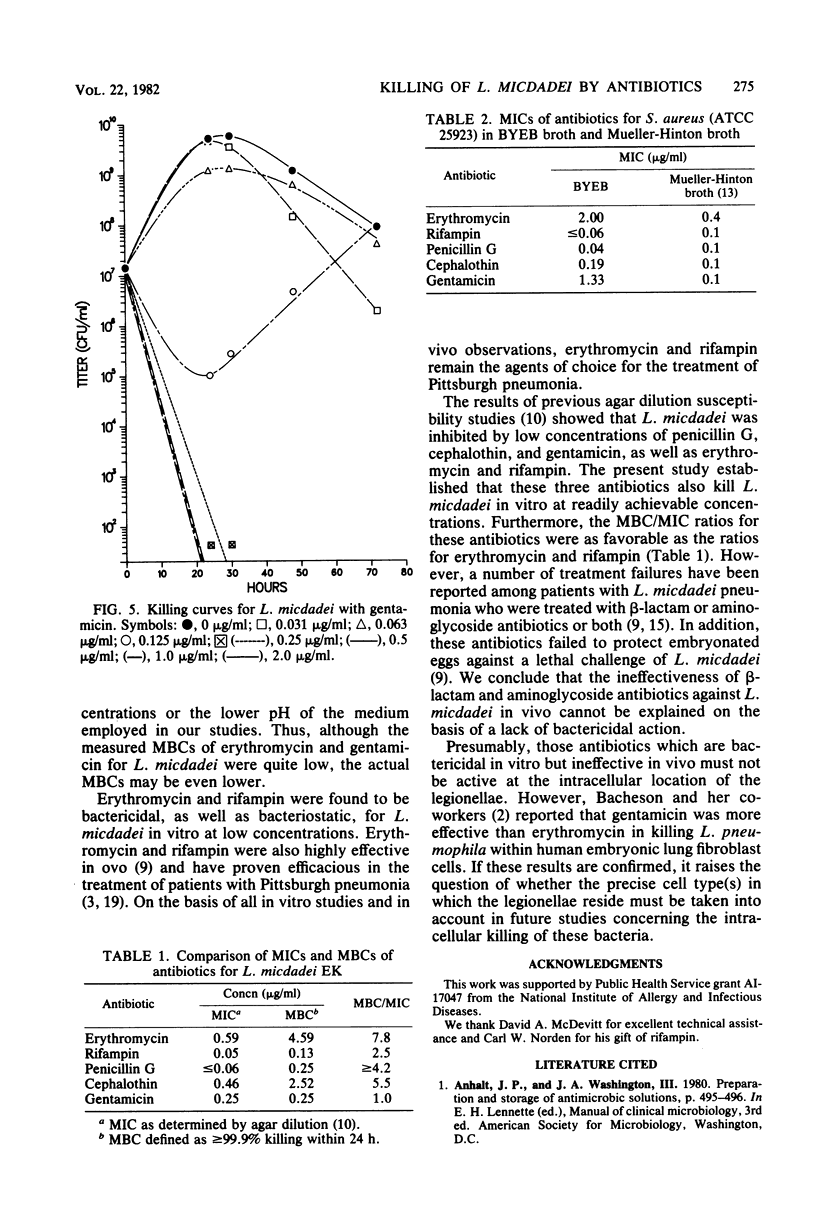
The bactericidal activity of five antibiotics for Legionella micdadei was determined by the construction of time-kill curves. Erythromycin, rifampin, penicillin G, cephalothin, and gentamicin were bactericidal for L. micdadei at readily achievable concentrations. The minimal bactericidal concentrations, defined as those producing 99.9% killing within 24 h, were: erythromycin, 4.6; rifampin, 0.13; penicillin G, 0.25; cephalothin, 2.5; and gentamicin, 0.25 micrograms/ml. The ratios of the minimal bactericidal to minimal inhibitory concentrations for these antibiotics ranged from 1 to 8. Thus, the poor in vivo activity of beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics against L. micdadei cannot be ascribed to a lack of killing by these agents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacheson M. A., Friedman H. M., Benson C. E. Antimicrobial susceptibility of intracellular Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):691–692. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to twenty antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Wachsmuth I., Bopp C., Feeley J. C., Tsai T. F. Antibiotic treatment of guinea-pigs infected with agent of Legionnaires' disease. Lancet. 1978 Jan 28;1(8057):175–178. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90611-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Moss C. W., McDougal L. K., Bozeman F. M., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. The rickettsia-like organisms TATLOCK (1943) and HEBA (1959): bacteria phenotypically similar to but genetically distinct from Legionella pneumophila and the WIGA bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. J., Thacker W. L., Shepard C. C., McDade J. E. In vivo susceptibility of the Legionnaires disease bacterium to ten antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):419–422. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Pazin G. J., Sr, Puerzer M., Yee R. B., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Hakala T. R. Opportunistic lung infection due to "Pittsburgh Pneumonia Agent". N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):953–958. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Dowling J. N., Weyant R. S., Sniffen J. M., Cordes L. G., Gorman G. M., Feeley J. C. Susceptibility of Pittsburgh pneumonia agent (Legionella micdadei) and other newly recognized members of the genus Legionella to nineteen antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):793–799. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Myerowitz R. L., Rinaldo C. R., Jr New bacterial agent of pneumonia isolated from renal-transplant recipients. Lancet. 1979 Jul 14;2(8133):58–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Stratton C. W., Reller L. B. Minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of 44 antimicrobial agents against three standard control strains in broth with and without human serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1050–1055. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Allen R. G. Liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.19-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. H., Donowitz G. R., Walker G. K., Harding S. A., Sande M. A. Opportunistic pneumonia: a clinicopathological study of five cases caused by an unidentified acid-fast bacterium. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):959–961. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravolatz L. D., Pohlod D. J., Quinn E. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila Serogroups I--IV. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(3):215–219. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-3.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Kirven L. A. In vitro activity of antimicrobial agents on Legionnaires disease bacterium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):78–80. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Schafer F. J., Pasculle A. W. Successful treatment of Legionella micdadei (Pittsburgh pneumonia agent) pneumonia with erythromycin. Am J Med. 1981 Nov;71(5):836–840. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


