Abstract
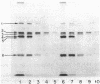
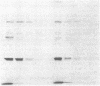
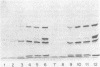
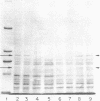
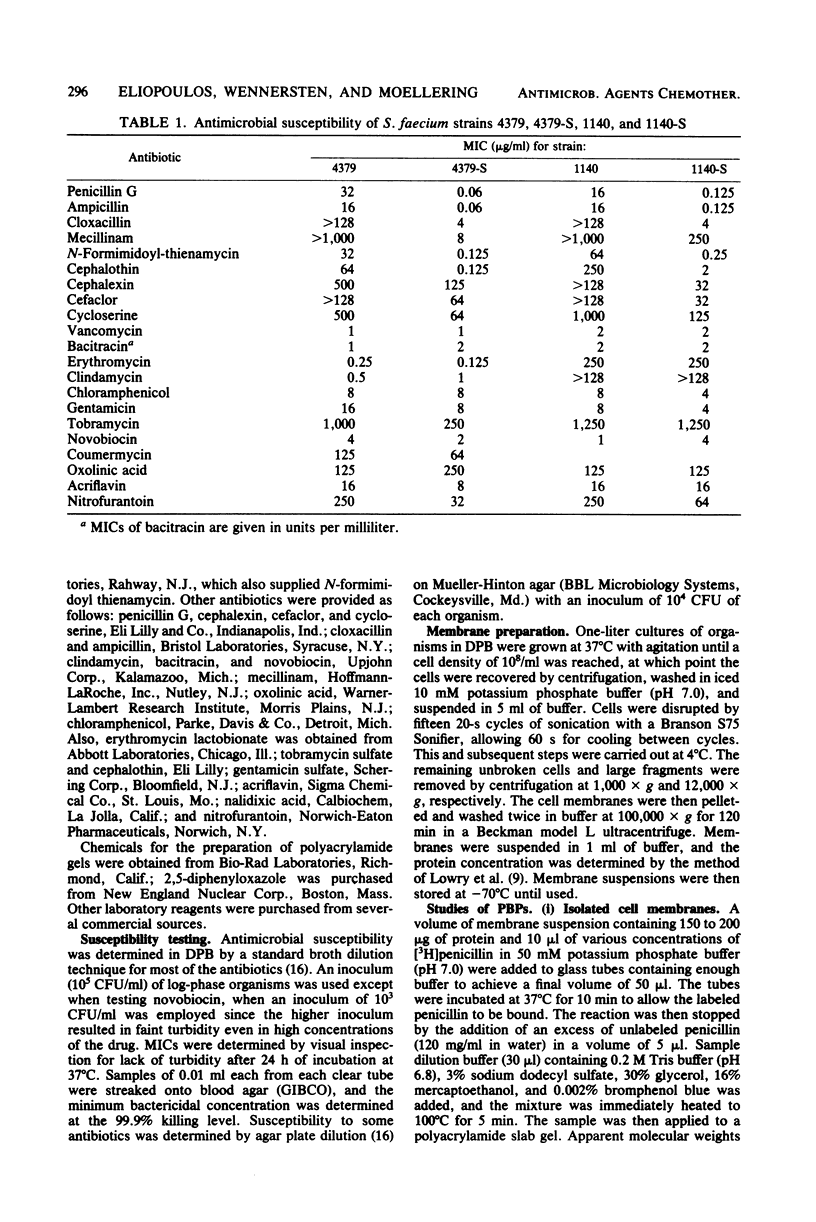
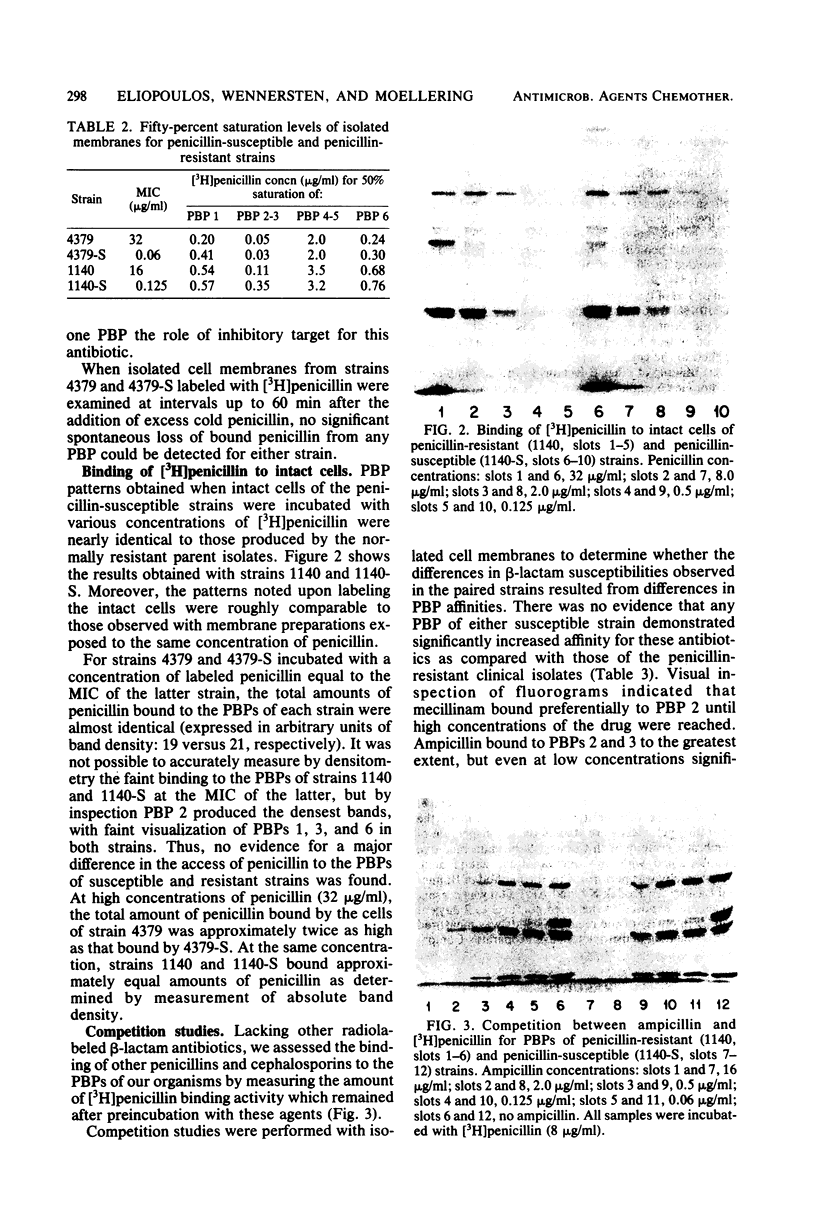
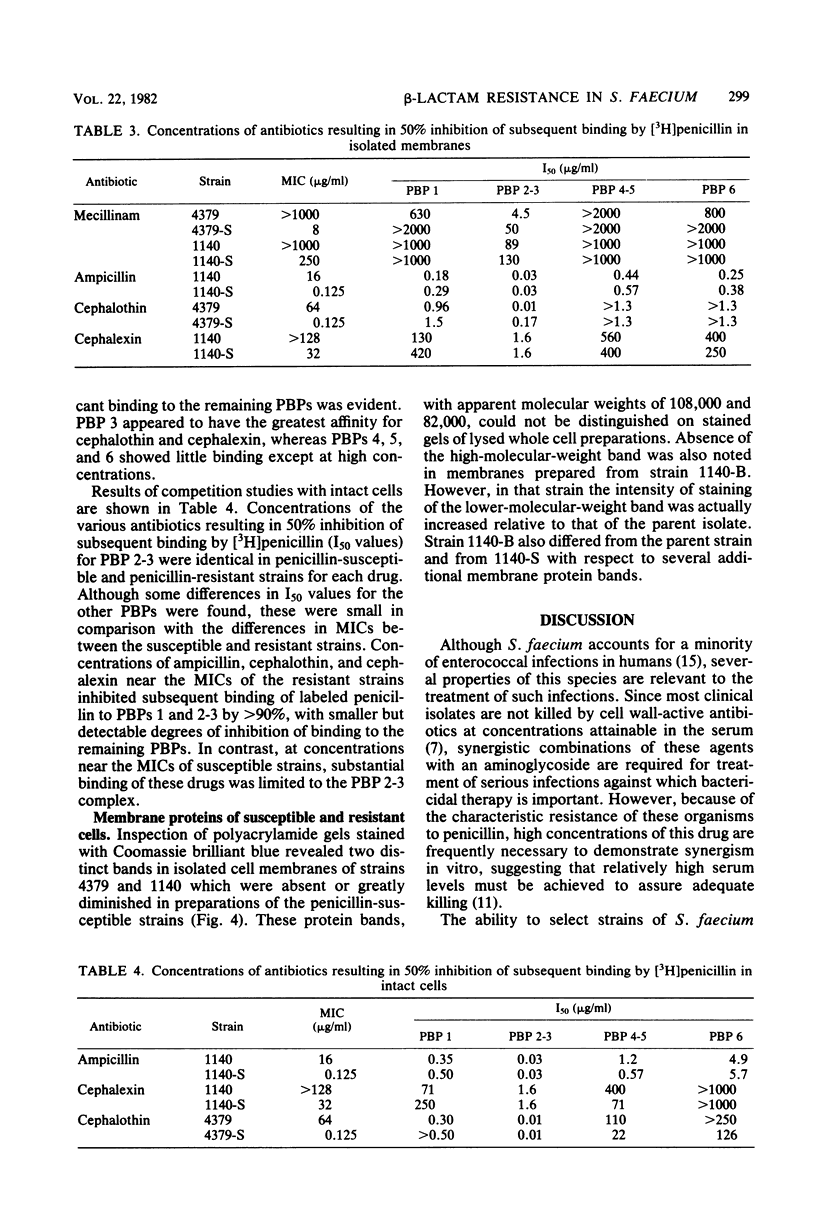
Clinical isolates of Streptococcus faecium are characteristically resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. Two strains, selected for hypersusceptibility to penicillin, were derived from normally resistant isolates treated with novobiocin. These strains were also found to be hypersusceptible to other beta-lactams. Differences in beta-lactam susceptibility between the original isolates and the hypersusceptible strains could not be attributed to alterations in penicillin-binding protein affinities, and no evidence of a relative permeability barrier was found in the resistant strains. Isolated cell membranes prepared from resistant strains were found to possess two protein bands which were absent or greatly diminished in the membranes of susceptible strains. Hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics in these strains may be due to the absence or alteration of one or more cell membrane proteins distinct from the penicillin-binding proteins of these organisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C. The involvement of DNA topoisomerases in DNA repair and mutagenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(2):157–160. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Tarpay M., Tomasz A. Multiple changes of penicillin-binding proteins in penicillin-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):364–371. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B., Tomasz A. Altered penicillin-binding proteins in methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):726–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Petrullo L. A., Rosenkranz H. S. Non-mutagenic genotoxicants: novobiocin and nalidixic acid, 2 inhibitors of DNA gyrase. Mutat Res. 1980 Sep;79(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(80)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Wennersten C. B. Species-specific resistance to antimocrobial synergism in Streptococcus faecium and Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percheson P. B., Bryan L. E. Penicillin-binding components of penicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):390–396. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm D. R., Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Inhibition of the Bacillus subtilis membrane-bound D-alanine carboxypeptidase by 6-aminopenicillanic acid covalently coupled to sepharose. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):783–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.783-785.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zighelboim S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of multiply antibiotic-resistant South African strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):434–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]