Abstract
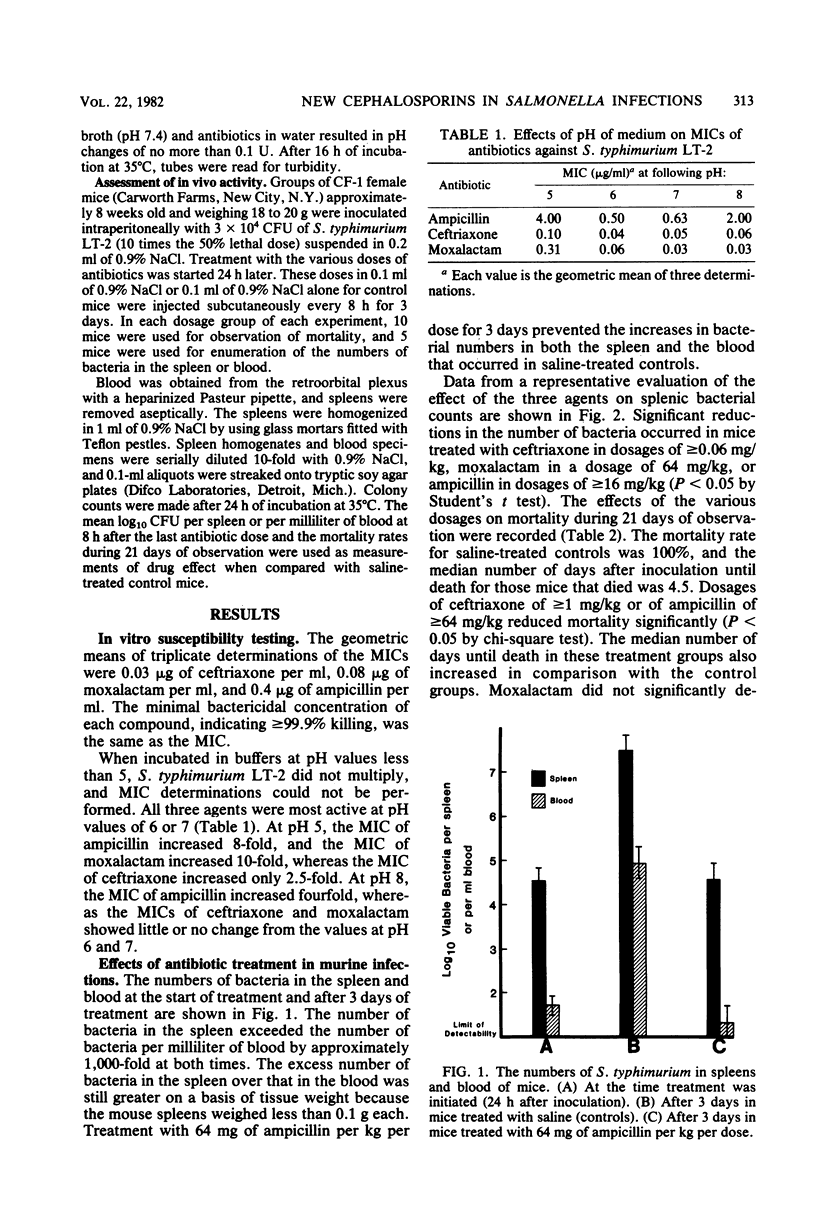
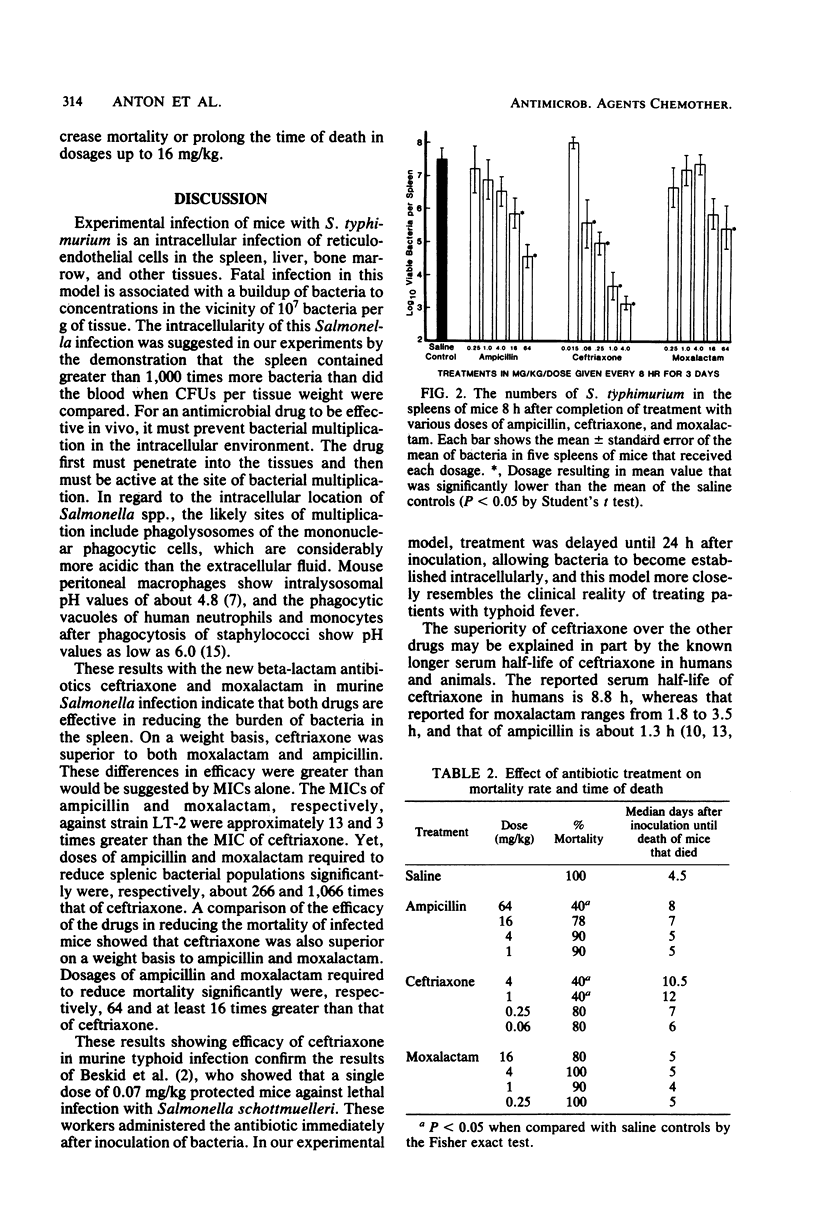
The activities of ceftriaxone, moxalactam, and ampicillin against Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 were compared in culture media at pH 5, 6, 7 and 8 and in mice inoculated intraperitoneally. The minimal inhibitory concentrations for strain LT-2 in Mueller-Hinton broth were 0.03 microgram of ceftriaxone per ml, 0.08 microgram of moxalactam per ml, and 0.4 microgram of ampicillin per ml. A comparison of minimal inhibitory concentrations in buffered broth at pH 5 with those in media at higher pH values showed that ceftriaxone was more acid stable than the other antibiotics. Groups of CF-1 female mice inoculated intraperitoneally with 3 X 10(4) colony-forming units received saline or each drug in fourfold decremental doses by the subcutaneous route every 8 h for 3 days, beginning at 24 h after challenge. The mean log 10 colony-forming units of S. typhimurium per spleen at the end of treatment and the mortality rates at 21 days after inoculation were measured for each treatment group. The mean log 10 colony-forming units per spleen was significantly reduced from that of the saline control by dosages of greater than or equal to 0.06 mg of ceftriaxone per kg, 64 mg of moxalactam per kg, or greater than or equal to 16 mg of ampicillin per kg (P less than 0.05). Mortality rates of infected mice were significantly reduced by dosages of greater than or equal to 1 mg of ceftriaxone per kg or greater than or equal to 64 mg of ampicillin per kg (P less than 0.05), whereas moxalactam in dosages as high as 16 mg/kg did not significantly reduce mortality rate. These results demonstrate the superiority of ceftriaxone to the other tested antibiotics on a weight basis in this model of experimental Salmonella infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angehrn P., Probst P. J., Reiner R., Then R. L. Ro 13-9904, a long-acting broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):913–921. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beskid G., Christenson J. G., Cleeland R., DeLorenzo W., Trown P. W. In vivo activity of ceftriaxone (Ro 13-9904), a new broad-spectrum semisynthetic cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):159–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Shuster C. W., Dixon P. Treatment of experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection with mecillinam and ampicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):328–331. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Shuster C. W., Franco A. Effect of a Salmonella group H1 R factor on virulence and response of infections to antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):478–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Ng W. S., Ling J., Arnold K. In vitro susceptibility of Salmonella to various antimicrobial agents, including a new cephalosporin, Ro 13-9904. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):8–11. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. M., Zemcov S. J. Ro 13-9904 and GR 20263, two new cephalosporins with broad-spectrum activity: an in vitro comparison with other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 May;7(5):515–520. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Fu K. P., Aswapokee P. Antibacterial activity of a new 1-oxa cephalosporin compared with that of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Meropol N. J., Fu K. P. Antibacterial activity of ceftriaxone (Ro 13-9904), a beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):414–423. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. N., Romano J. M., Levison M. E. Pharmacology of a new 1-oxa-beta-lactam (LY127935) in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):226–228. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner R., Weiss U., Brombacher U., Lanz P., Montavon M., Furlenmeier A., Angehrn P., Probst P. J. Ro 13-9904/001, a novel potent and long-acting parenteral cephalosporin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Jul;33(7):783–786. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loock C. A., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriologic efficacy of moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, and rocephin in experimental bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):156–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Spyker D. A., Donowitz G. R., Bolton W. K., Sande M. A. Moxalactam and cefazolin: comparative pharmacokinetics in normal subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):613–619. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon M., Wise R., Gillett A. P., Livingston R. Pharmacokinetics of Ro 13-9904, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):240–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Geisow M., Garcia R., Harper A., Miller R. The respiratory burst of phagocytic cells is associated with a rise in vacuolar pH. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):406–409. doi: 10.1038/290406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton S., Nelson J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr In vitro susceptibility of gram-negative bacilli from pediatric patients to moxalactam, cefotaxime, Ro 13-9904, and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):476–479. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Bedford K. A. LY127935, a novel oxa-beta-lactam: an in vitro comparison with other beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):341–345. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


