Abstract
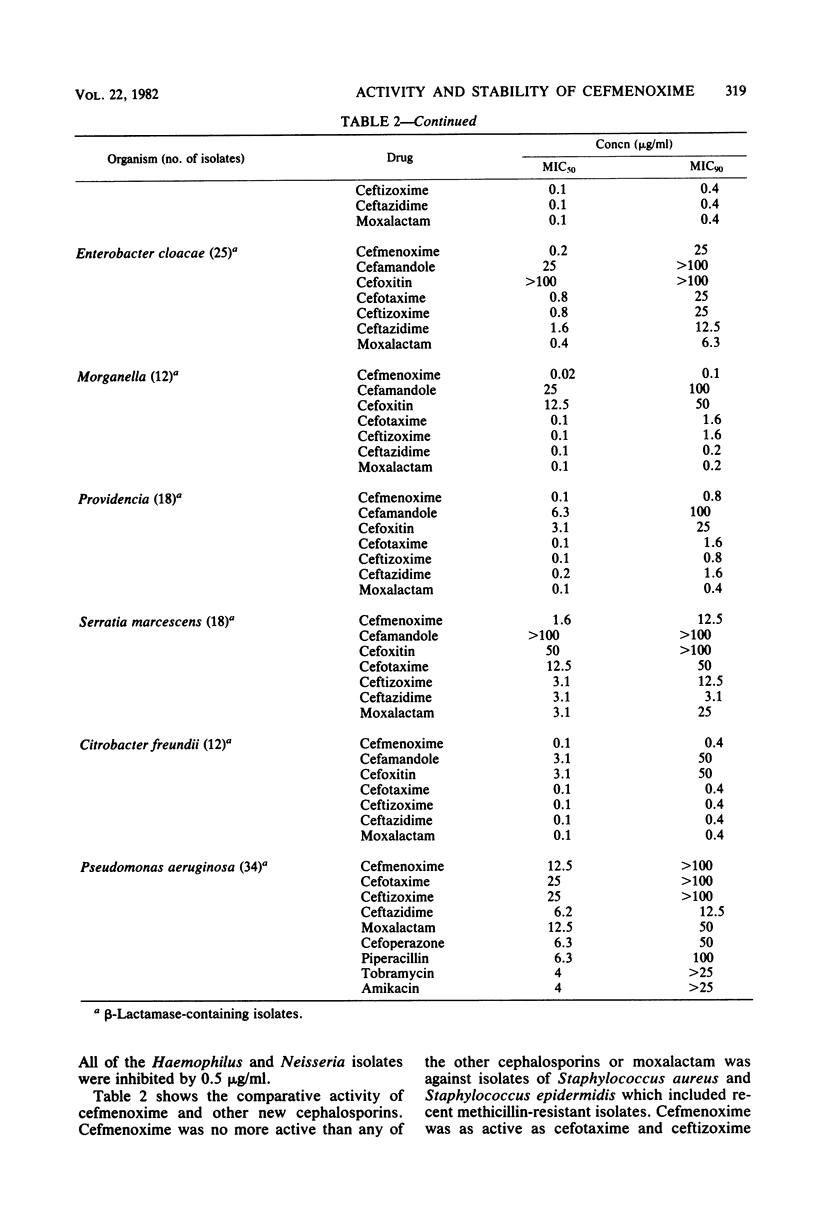
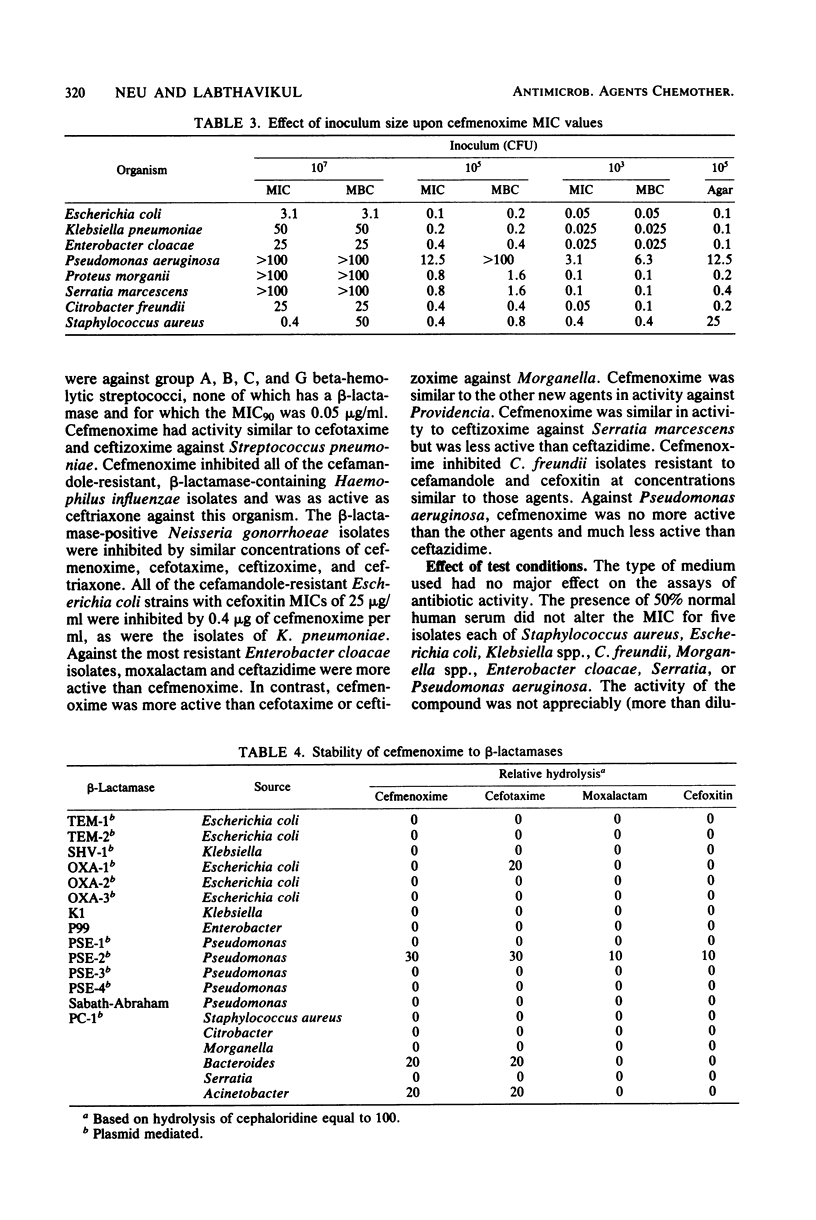
The activity of cefmenoxime, an aminothiazolyl cephalosporin, was studied against 650 bacteria. It was slightly less active than cefotaxime and more active than moxalactam against staphylococci. It had activity similar to that of cefotaxime and ceftizoxime against group A and B streptococci and Streptococcus pneumoniae. It did not inhibit Streptococcus faecalis or Listeria spp. Cefmenoxime had activity similar to that of cefotaxime, ceftizoxime, ceftazidime, and moxalactam against Escherichia coli, Citrobacter diversus, Klebsiella, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella, and Shigella. It inhibited beta-lactamase-positive and -negative isolates at less than or equal to 0.4 microgram/ml. Cefmenoxime was somewhat less active than moxalactam or ceftizoxime against Enterobacter cloacae, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Enterobacter agglomerans, but was more active than cefotaxime, ceftizoxime, or ceftazidime against Morganella (minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of isolates, 0.1 microgram/ml.), Proteus vulgaris and Providencia spp. It was as active as ceftizoxime was against Serratia. Pseudomonas spp. and Bacteroides spp. were relatively resistant (minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of isolates, greater than 100 micrograms/ml). The compound was stable to the common plasmid beta-lactamases, such as that of TEM. It was stable to most chromosomally mediated beta-lactamases, which act primarily as cephalosporinases, but was hydrolyzed by Bacteroides and Acinetobacter.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. The comparative beta-lactamase resistance and inhibitory activity of 1-oxa cephalosporin, cefoxitin and cefotaxime. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Sep;32(9):909–914. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. beta-lactamase stability of HR 756, a novel cephalosporin, compared to that of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):322–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Synergy of azlocillin and mezlocillin combined with aminoglycoside antibiotics and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):813–819. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okonogi K., Kuno M., Kida M., Mitsuhashi S. Beta-lactamase stability and antibacterial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):171–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm J. M., Girolami R. L., Shipkowitz N. L., Bower R. R. Antimicrobial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):454–460. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kondo M., Kida M., Nakao M., Iwahi T., Nishi T., Noji Y., Takeuchi M., Nozaki Y. Cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):56–65. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterworth P. M., Emmerson A. M. Dissociated resistance among cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T. Structural requirements for antibacterial activity and beta-lactamase stability of 7 beta-arylmalonylamino-7 alpha-methoxy-1-oxacephems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):231–237. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


