Abstract
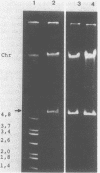
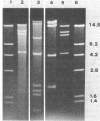
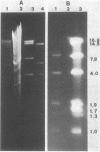
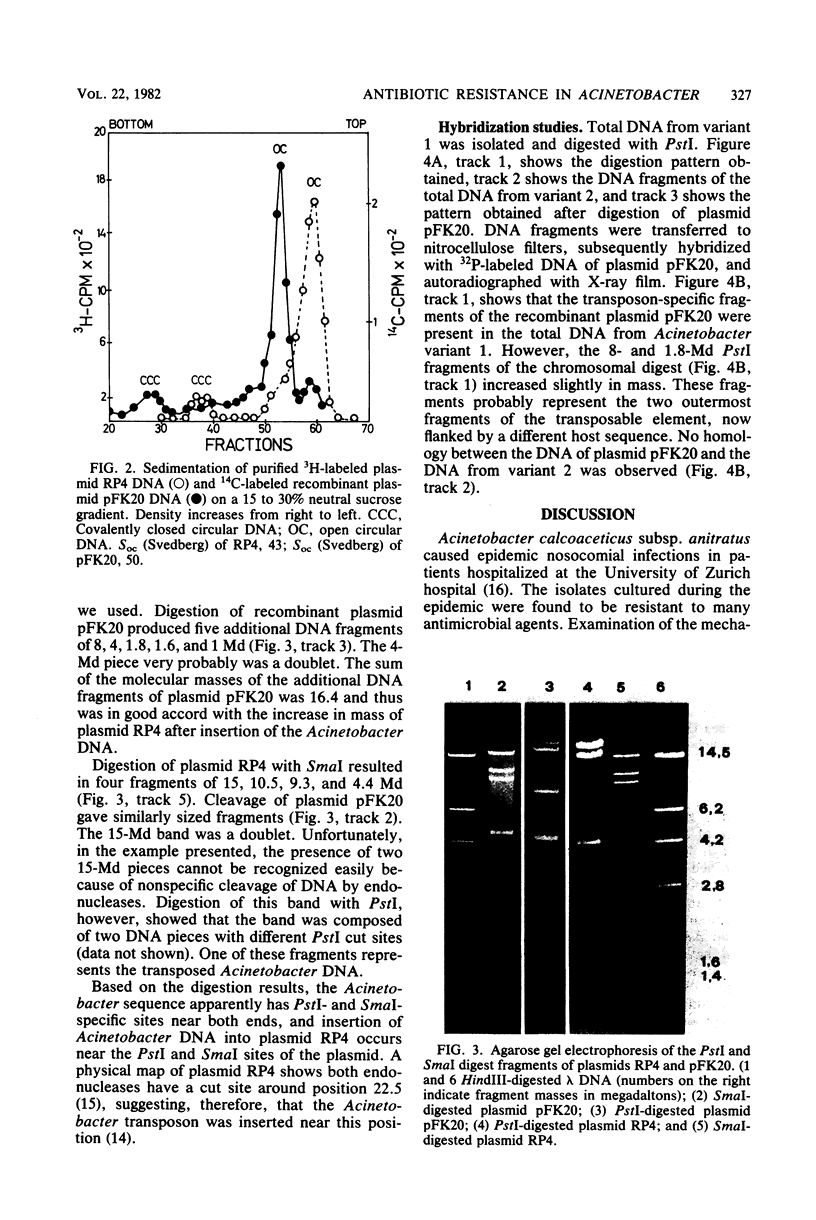
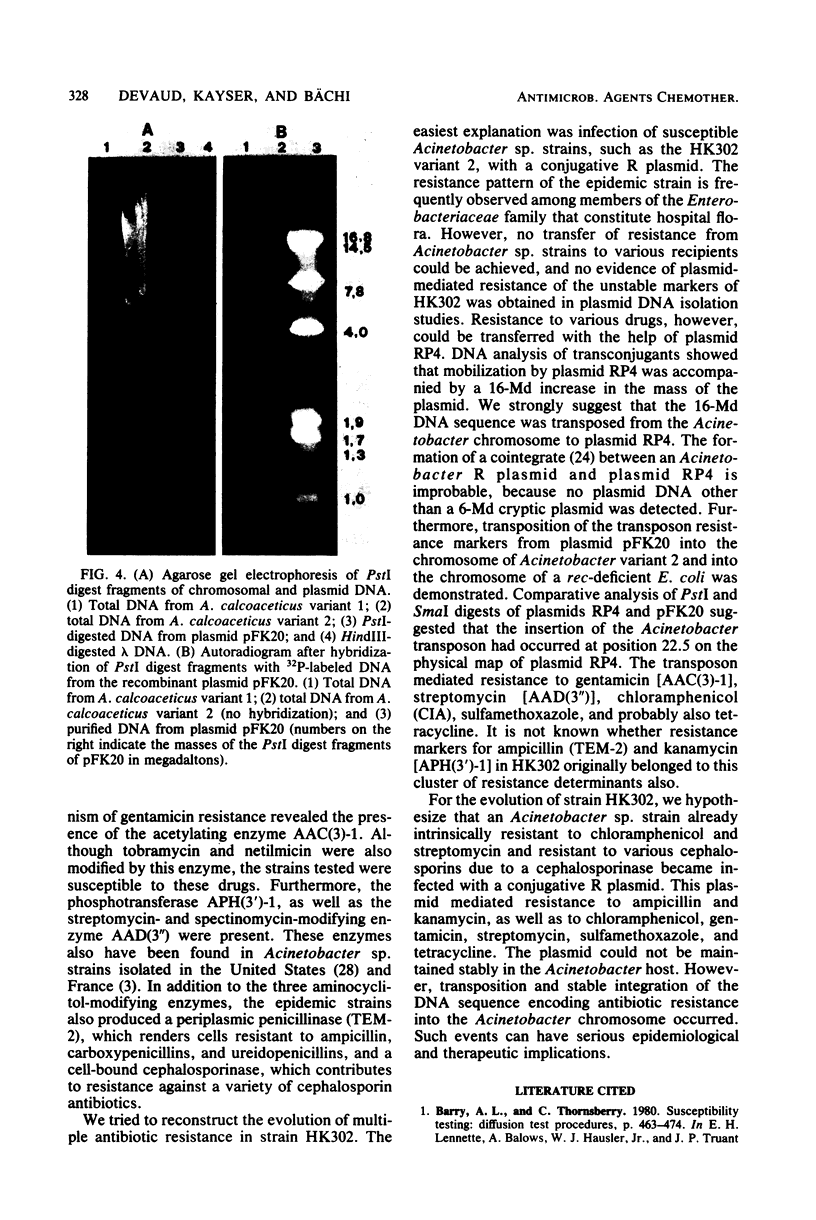
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus subsp. anitratus, which is unusually resistant to multiple antibiotics, was the cause of an epidemic of respiratory tract infections in patients in an intensive care unit. A representative isolate of the epidemic strain was found to contain the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes 3-N-acetyltransferase, 3'-phosphotransferase, and 3"-adenylyltransferase, which confer resistance to gentamicin, kanamycin, and streptomycin, respectively. In addition, the strain produced a cephalosporinase and was resistant to penicillins due to the production of a TEM-2 beta-lactamase. The bacterial isolate also exhibited resistance to chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and sulfonamides. The resistant phenotype of this strain was similar to resistance patterns frequently observed in endemic hospital flora, suggesting that the transfer of an R plasmid into Acinetobacter sp. may have occurred. However, antibiotic resistance could not be transferred to any recipient by various mating procedures. After plasmid RP4 was transferred into an ampicillin- and kanamycin-susceptible derivative of the epidemic strain, mobilization of resistance to chloramphenicol, gentamicin, streptomycin, sulfonamides, and possibly tetracycline could be achieved. This mobilization was due to the transposition of a 16-megadalton DNA sequence from the Acinetobacter chromosome into plasmid RP4. Insertion of the transposable sequence occurred near the PstI and SmaI sites around position 22.5 on the physical map of plasmid RP4. We suggest that a plasmid resistant to multiple antibiotics was transferred from the hospital flora into Acinetobacter sp. but could not be maintained stably in this host. Instead, a multiply resistant DNA sequence was transposed and stably integrated into the Acinetobacter chromosome. The occurrence of such multiply resistant transposons on conjugative plasmids contributes greatly to the genetic variability of bacteria and may sometimes have serious epidemiological and therapeutic consequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddlecome S., Haas M., Davies J., Miller G. H., Rane D. F., Daniels P. J. Enzymatic modification of aminoglycoside antibiotics: a new 3-N-acetylating enzyme from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):951–955. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Pardee A. B. Thymidine and thymine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid: inhibition and repression by uridine of thymidine phosphorylase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1546–1550. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1546-1550.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton A. E., Anderson R. L., Werdegar D., Atlas E. Nosocomial respiratory tract infection and colonization with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Epidemiologic characteristics. Am J Med. 1978 Sep;65(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90777-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Warren G. J. Conjugal transmission of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:99–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., Oishi M. Genetic transformation in Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):84–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Smith D. I. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial agents. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:469–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., De Block M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Schell J. IS-like element IS8 in RP4 plasmid and its involvement in cointegration. Gene. 1980 Sep;10(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaud M., Kayser F. H., Huber U. Resistance of bacteria to the newer aminoglycoside antibiotics: an epidemiological and enzymatic study. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Aug;30(8):655–664. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J. Infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (Herellea vaginicola): clinical and laboratory studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):79–97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinter N. J., Barth P. T. Characterization of SmSu plasmids by restriction endonuclease cleavage and compatibility testing. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):394–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.394-400.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B., Clayton D. A., Vinograd J. Complex mitochondrial DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:435–442. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack G. W., Richmond M. H. A comparative study of eight distinct beta-lactamases synthesized by gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):43–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Recombination between plasmids of incompatibility groups P-1 and P-2. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1278-1285.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Relaxation complexes of plasmid DNA and protein. II. Characterization of the proteins associated with the unrelaxed and relaxed complexes of plasmid ColE1. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8790–8795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Moellering R. C., Jr Evidence of plasmid-mediated production of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes not previously described in Acinetobacter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):30–36. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E. Phage lambda receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments made with restriction endonuclease III of Haemophilus influenzae and restriction endonuclease I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes by osmotic shock from Escherichia coli in exponential phase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Benveniste R., Tipper D., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics: inactivation by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli carrying R factors. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1144–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1144-1146.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasawa S., Utahara R., Okanishi M., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Studies on adenylylstreptomycin, a product of streptomycin inactivation by E. coli carrying the R-factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Aug;21(8):477–484. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towner K. J., Vivian A. RP4-mediated conjugation in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):355–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]