Abstract
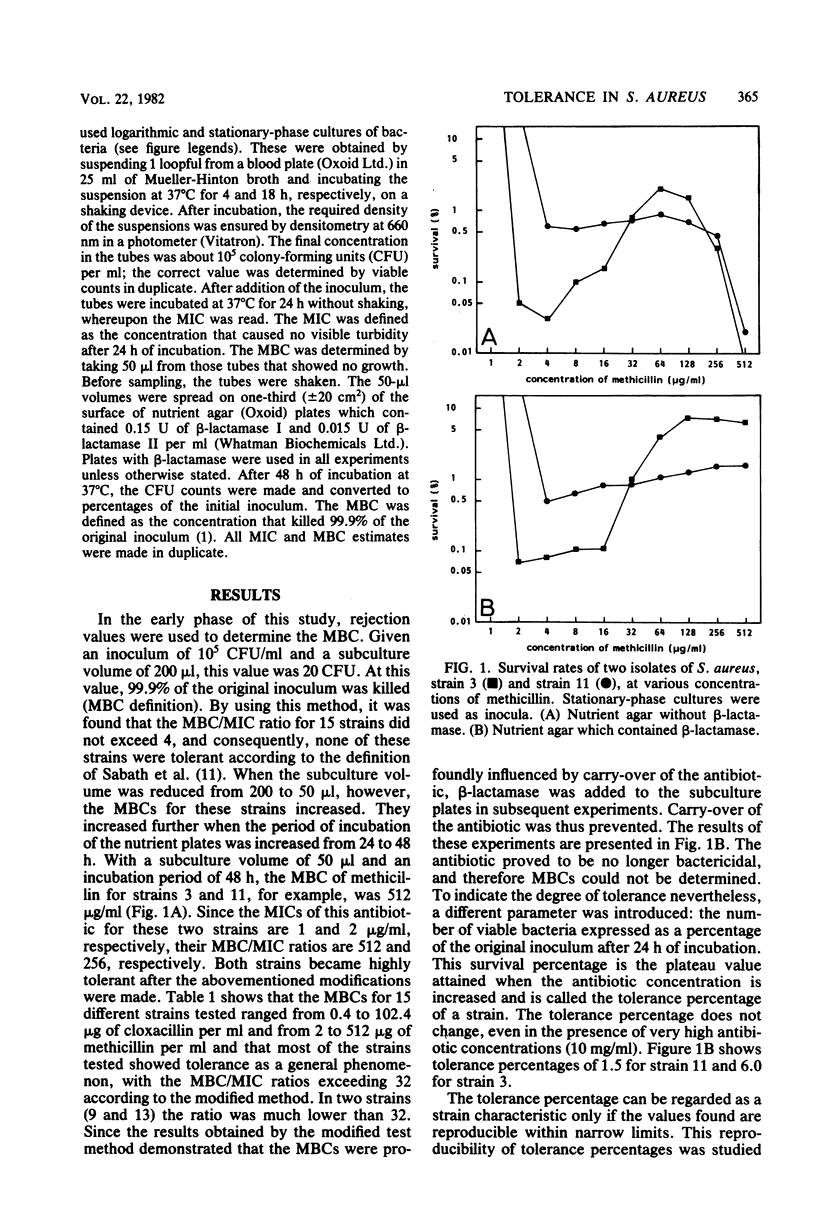
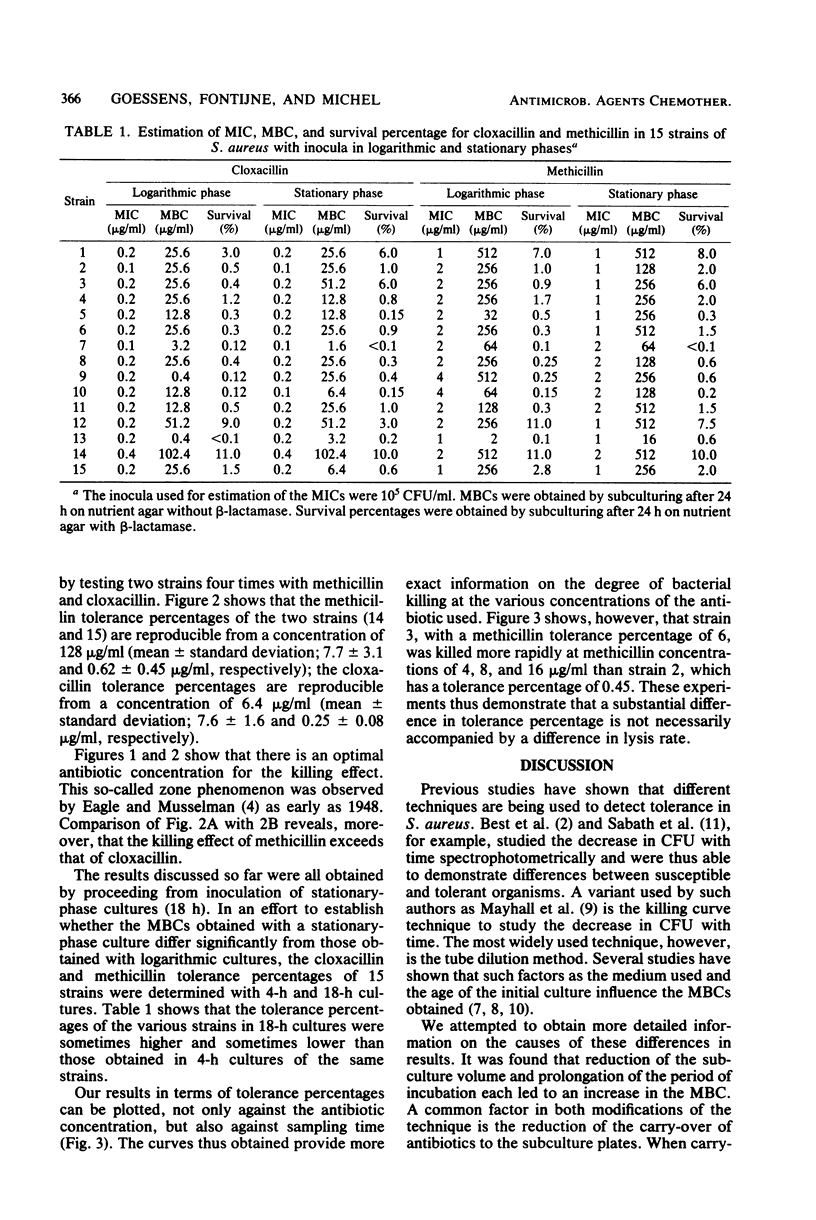
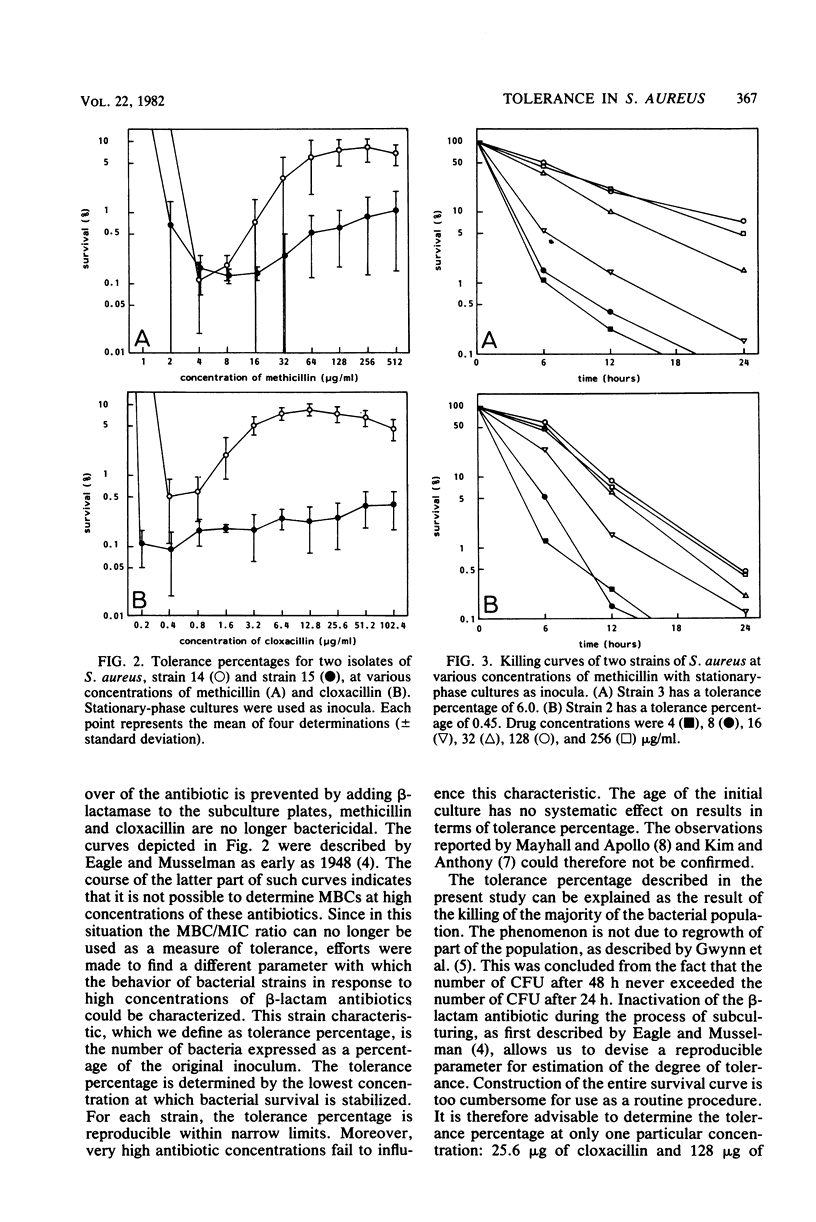
The phenomenon of tolerance to cloxacillin and methicillin was studied in Staphylococcus aureus. It was demonstrated that the minimal bactericidal concentrations showed marked differences, depending on the method of detection used. These differences resulted from carry-over of the antibiotic to the subculture plates. When carry-over of the antibiotic was prevented by the addition of beta-lactamase to the nutrient medium, the antibiotics were no longer bactericidal. At a certain antibiotic concentration and at higher concentrations, however, each strain showed a certain survival percentage after 24 h. The tolerance percentage was determined for 15 strains. The values found for the individual strains ranged from less than 0.1 to 11% for cloxacillin and methicillin. since these percentages were reproducible within narrow limits, they could be regarded as a characteristic of the strains. The tolerance percentage was independent of the growth phase of the initial cultures.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best G. K., Best N. H., Koval A. V. Evidence for participation of autolysins in bactericidal action of oxacillin on Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):825–830. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny A. E., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N., Hall W. H. Serious staphylococcal infections with strains tolerant to bactericidal antibiotics. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Sep;139(9):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynn M. N., Webb T. L., Rolinson G. N. Regrowth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria after the bactericidal action of carbenicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):263–269. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilty M. D., Venglarcik J. S., Best G. K. Oxacillin-tolerant staphylococcal bacteremia in children. J Pediatr. 1980 Jun;96(6):1035–1037. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80633-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Anthony B. F. Importance of bacterial growth phase in determining minimal bactericidal concentrations of penicillin and methicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1075–1077. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhall C. G., Apollo E. Effect of storage and changes in bacterial growth phase and antibiotic concentrations on antimicrobial tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):784–788. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhall C. G., Medoff G., Marr J. J. Variation in the susceptibility of strains of Staphylococcus aureus to oxacillin, cephalothin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):707–712. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N., Hall W. H., Schierl E. A. Medium-dependent variation in bactericidal activity of antibiotics against susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):665–668. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The role of autolysins in cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):439–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


