Abstract
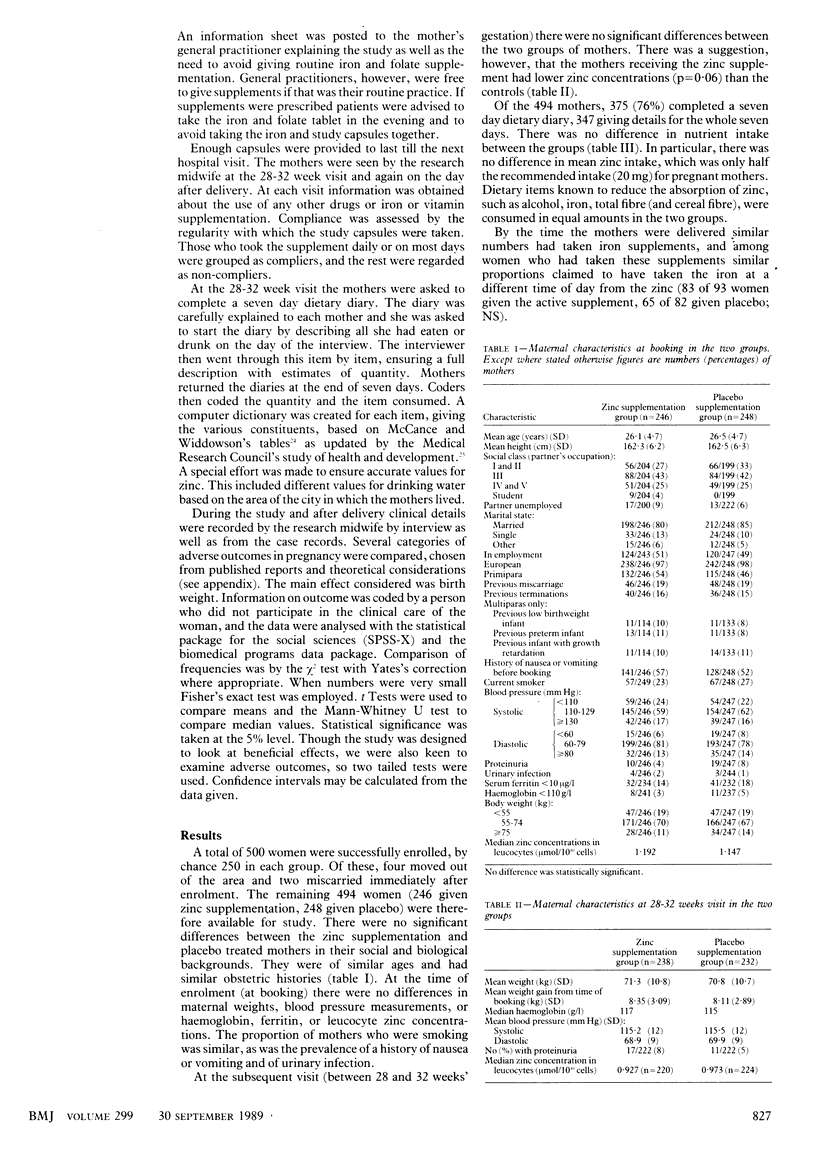
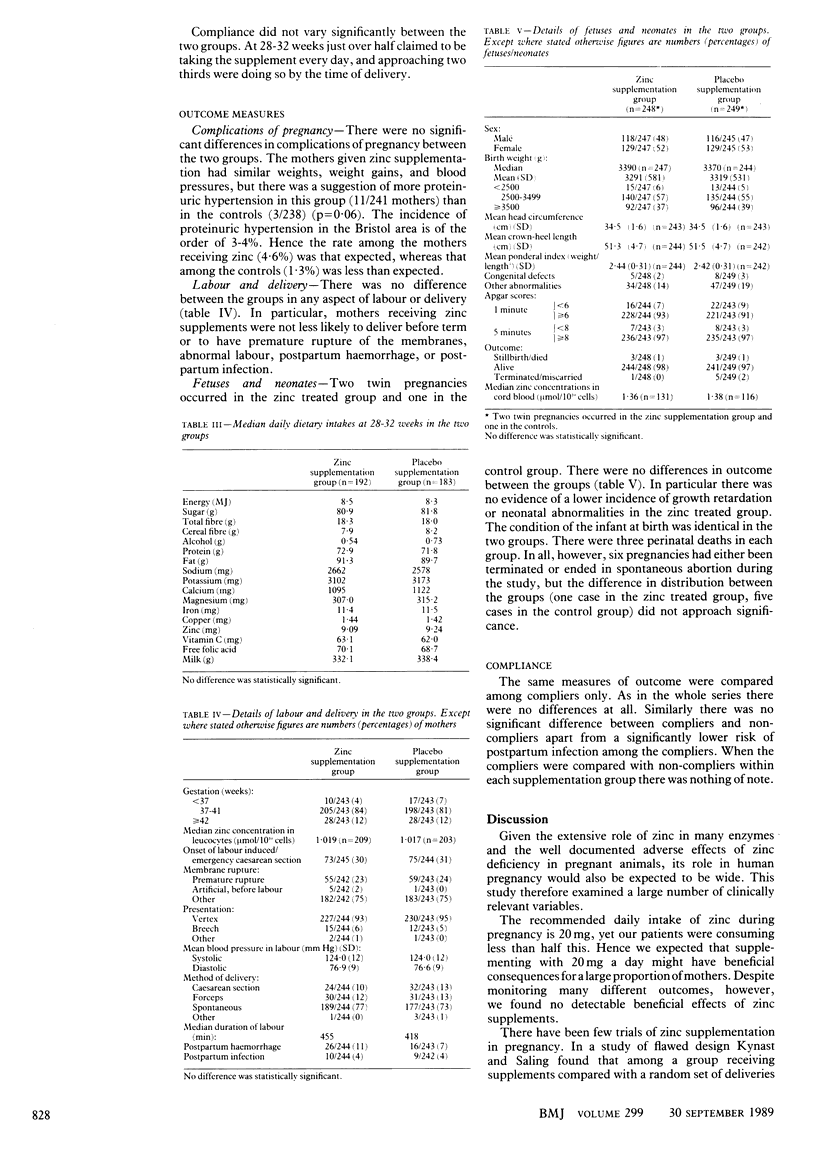
OBJECTIVE--To see whether zinc supplementation during pregnancy improves maternal and fetal outcome. DESIGN--Prospective study started at booking and continued till discharge of mother and baby from the maternity hospital. Mothers were randomly assigned to receive zinc supplementation or placebo in a double blind trial. SETTING--Mothers booking at one hospital. PATIENTS--Women booking before 20 weeks of gestation who agreed to take part in the study. 494 Mothers were followed up till the end of pregnancy. There was no difference between the groups given zinc and placebo in their social or medical backgrounds. INTERVENTIONS--Mothers in the active treatment group received one capsule of 20 mg elemental zinc daily and those in the placebo treated group a capsule identical in appearance and taste with the active capsule but which contained inert substances. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE--Various adverse outcomes were tested, including maternal bleeding, hypertension, complications of labour and delivery, gestational age, Apgar scores, and neonatal abnormalities. The main outcome measure was birth weight. RESULTS--There were no differences whatsoever between mothers given a zinc supplement and those given a placebo. CONCLUSION--Zinc supplementation in pregnancy in the United Kingdom does not seem to offer any benefits to the mother or her fetus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apgar J. Effect of zinc deficiency on maintenance of pregnancy in the rat. J Nutr. 1970 Apr;100(4):470–476. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.4.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atinmo T., Mbofung C., Osinusi B. O. Relationship of zinc and copper concentrations in maternal and cord blood and birth weight. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1980;18(6):452–454. doi: 10.1002/j.1879-3479.1980.tb00540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddon F. E., Wadsworth M. E., Davies J. M., Cripps H. A. Social and regional differences in food and alcohol consumption and their measurement in a national birth cohort. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1988 Dec;42(4):341–349. doi: 10.1136/jech.42.4.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry F. F., Bennett E. A., Bazzano G. S., Johnson L. K., Fosmire G. J., Batson H. K. Plasma zinc in hypertension/toxemia and other reproductive variables in adolescent pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Nov;34(11):2367–2375. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.11.2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Fong L. Y., Wan C. W., Liang S. T., Woo J. S., Wong V. Zinc deficiency is not a cause for abortion, congenital abnormality and small-for-gestational age infant in Chinese women. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Sep;92(9):886–891. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt I. F., Murphy N. J., Cleaver A. E., Faraji B., Swendseid M. E., Coulson A. H., Clark V. A., Browdy B. L., Cabalum T., Smith J. C., Jr Zinc supplementation during pregnancy: effects on selected blood constituents and on progress and outcome of pregnancy in low-income women of Mexican descent. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Sep;40(3):508–521. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/40.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiilholma P., Erkkola R., Pakarinen P., Grönroos M. Trace metals in postdate pregnancy. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1984;18(1):45–48. doi: 10.1159/000299047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiilholma P., Grönroos M., Erkkola R., Pakarinen P., Näntö V. The role of calcium, copper, iron and zinc in preterm delivery and premature rupture of fetal membranes. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1984;17(4):194–201. doi: 10.1159/000299148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kynast G., Saling E. Effect of oral zinc application during pregnancy. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1986;21(3):117–123. doi: 10.1159/000298940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., Fosmire G. J., Sandstead H. H. Zinc deficiency during the latter third of pregnancy: effects on fetal rat brain, liver, and placenta. J Nutr. 1975 Nov;105(11):1466–1475. doi: 10.1093/jn/105.11.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Dreosti I. E., Gibson G. T., Hartshorne J. M., Buckley R. A., Colley D. P. A prospective study of serial maternal serum zinc levels and pregnancy outcome. Early Hum Dev. 1982 Oct;7(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(82)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcoff J., Costiloe J. P., Crosby W., Bentle L., Seshachalam D., Sandstead H. H., Bodwell C. E., Weaver F., McClain P. Maternal nutrition and fetal outcome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Apr;34(Suppl 4):708–721. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.4.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee M. D., Sandstead H. H., Ratnaparkhi M. V., Johnson L. K., Milne D. B., Stelling H. P. Maternal zinc, iron, folic acid, and protein nutriture and outcome of human pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Sep;40(3):496–507. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/40.3.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad L. S., Ganguly S. K., Vasuki K. Role of zinc in foetal nutrition. Indian Pediatr. 1974 Dec;11(12):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prema K. Predictive value of serum copper and zinc in normal and abnormal pregnancy. Indian J Med Res. 1980 Apr;71:554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomons N. W. On the assessment of zinc and copper nutriture in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Apr;32(4):856–871. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.4.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle S., Aggett P. J., Campbell D., MacGillivray I. Zinc and copper nutrition in human pregnancy: a longitudinal study in normal primigravidae and in primigravidae at risk of delivering a growth retarded baby. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 May;41(5):1032–1041. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/41.5.1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verburg D. J., Burd L. I., Hoxtell E. O., Merrill L. K. Acrodermatitis enteropathica and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Aug;44(2):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. L., James D. K., Luxton R., Pennock C. A. Maternal leucocyte zinc deficiency at start of third trimester as a predictor of fetal growth retardation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Apr 25;294(6579):1054–1056. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6579.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


