Abstract
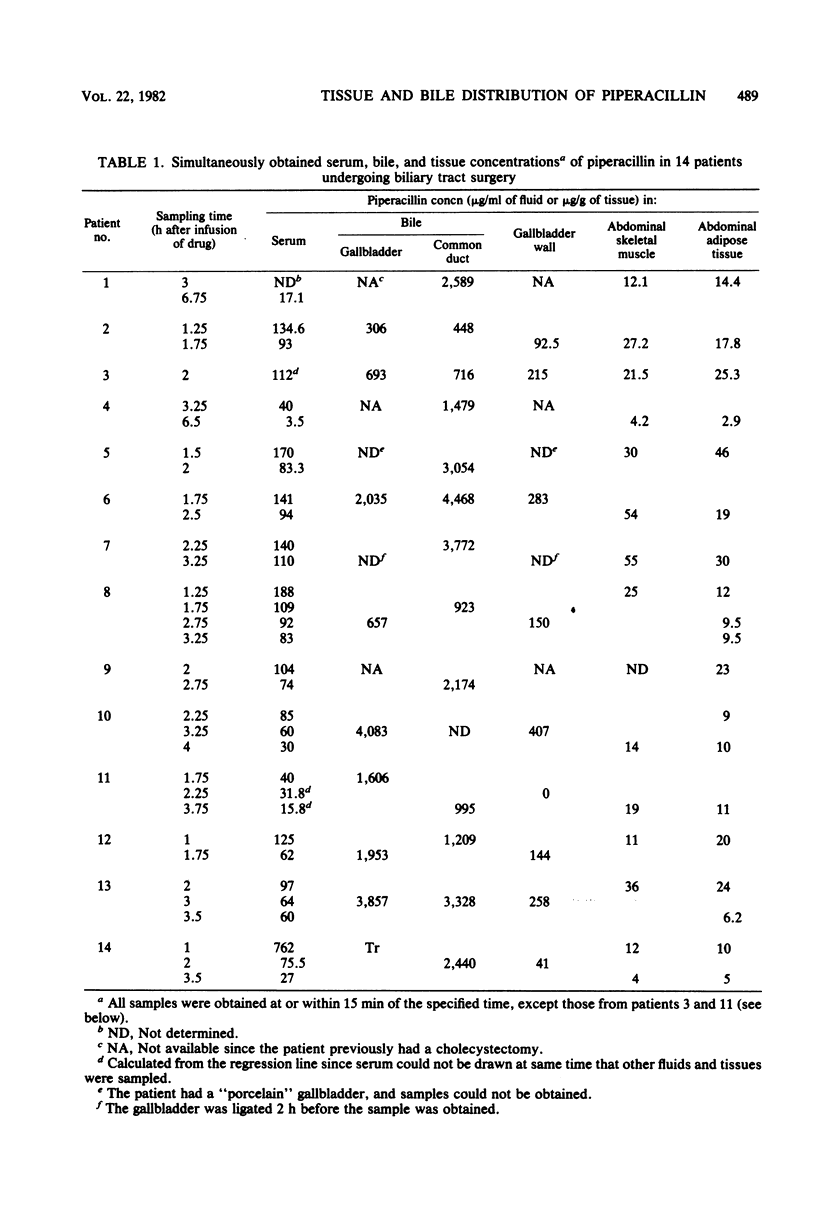
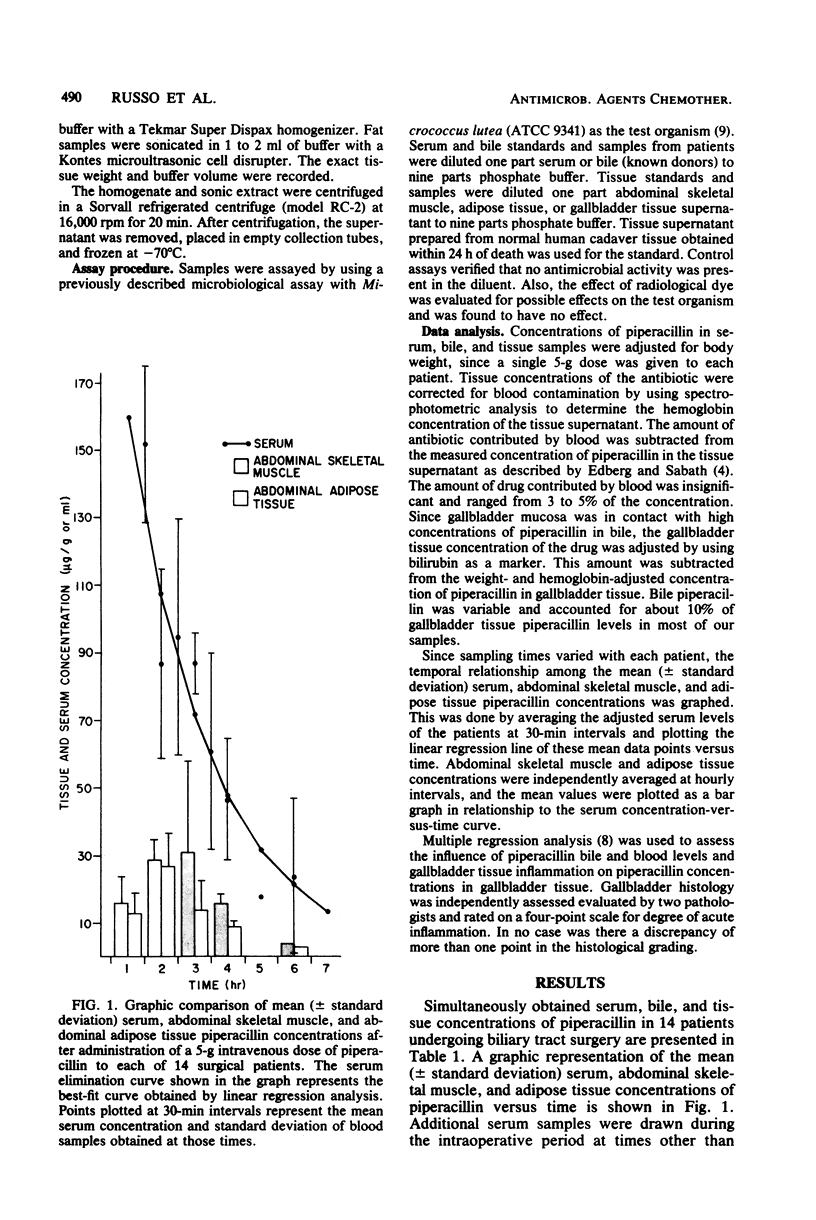
The concentrations of piperacillin in serum, bile, gallbladder wall, abdominal skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue were measured simultaneously at various times after the intravenous administration of a single 5-g dose to each of 14 patients undergoing biliary tract surgery. Piperacillin concentrated in the bile with peak levels exceeding 4,000 micrograms/ml. In a single patient with cystic duct obstruction, trace gallbladder bile piperacillin levels were measured. Gallbladder wall concentrations of piperacillin tended to be higher than corresponding serum concentrations, with a correlation observed between tissue values and the degree of acute gallbladder inflammation and gallbladder bile piperacillin concentrations. Mean peak muscle and adipose tissue piperacillin concentrations of 31 and 27 micrograms/g, respectively, were reached at between 2 and 3 h after the start of infusion. These concentrations exceeded the minimum inhibitory concentration for a majority of susceptible organisms. A single 5-g dose of piperacillin achieved therapeutic levels in gallbladder wall, intraabdominal skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue and concentrated in the bile of patients with patent biliary tracts.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogard J. M., Kopferschmitt J., Arnaud J. P., Dorner M., La Villaureix J. Biliary elimination of mezlocillin: an experimental and clinical study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):69–76. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson G. M., Cleary T. J., Hoffman T. A. Comparative evaluation of piperacillin in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):919–921. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gengo F. M., Schentag J. J. Methicillin distribution in serum and extravascular fluid and its relevance to normal and damaged heart valves. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):836–841. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. R., Mackie D. B., Haynes S. Ampicillin levels in human bile in the presence of biliary tract disease. Br Med J. 1969 Jul 12;3(5662):88–89. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5662.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. I., Russo M. E., Matsen J. M., Atkin-Thor E. Piperacillin pharmacokinetics in subjects with chronic renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):450–453. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman N. G., Kastan L. B. Interstitial fluid and serum antibiotic concentrations. Arch Surg. 1972 Aug;105(2):192–196. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180080046008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


