Abstract
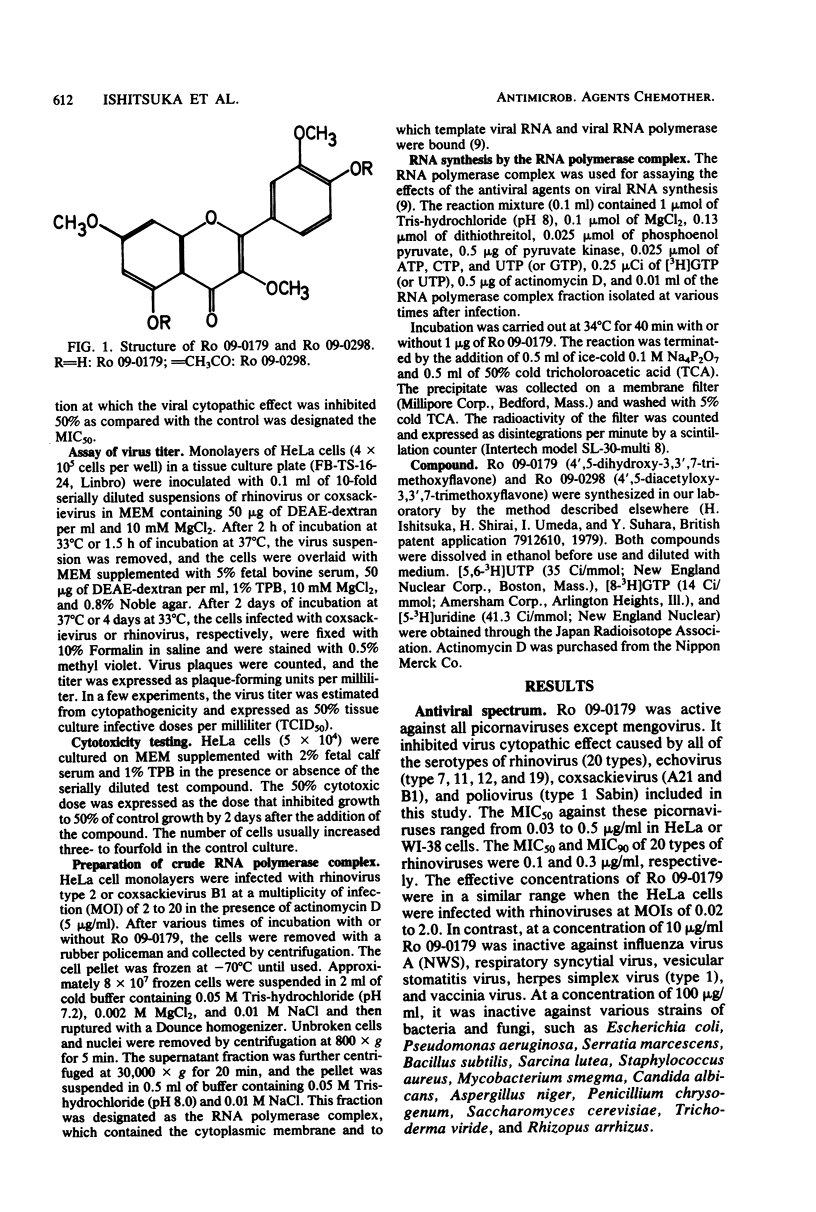
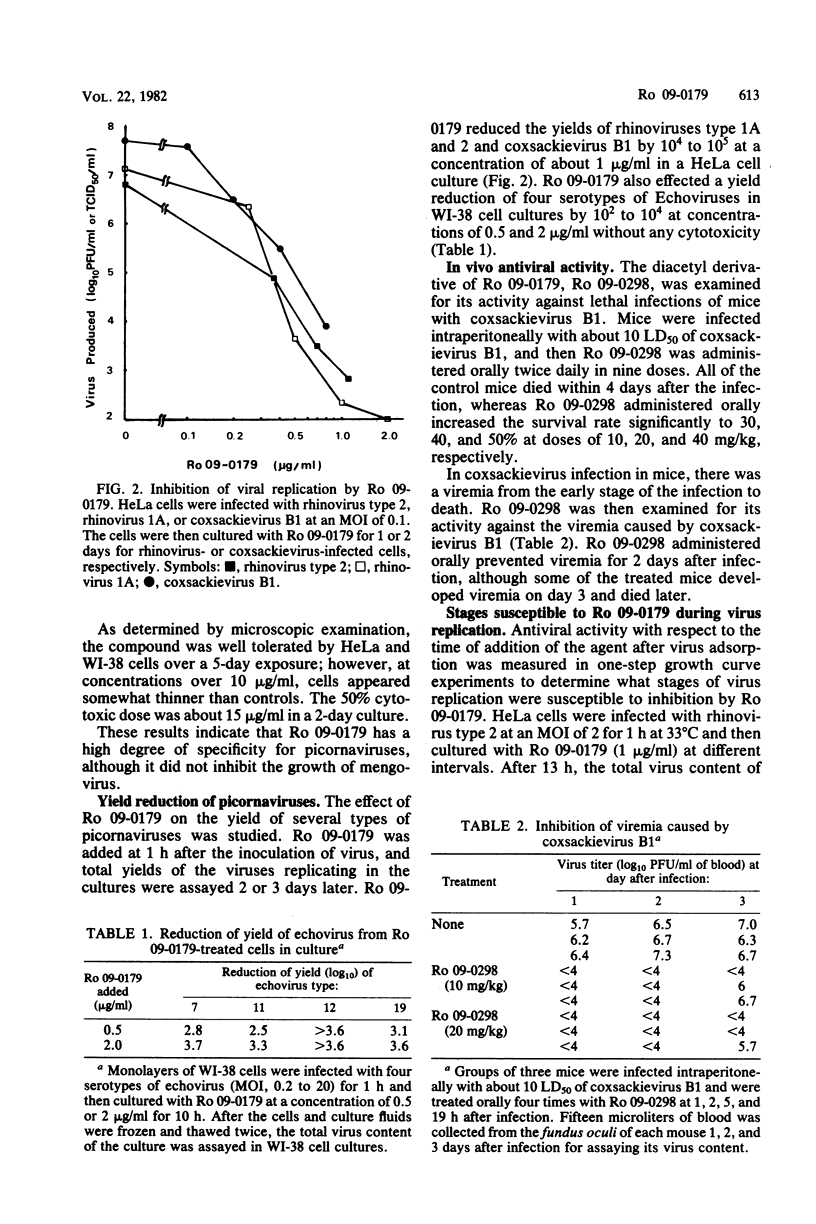
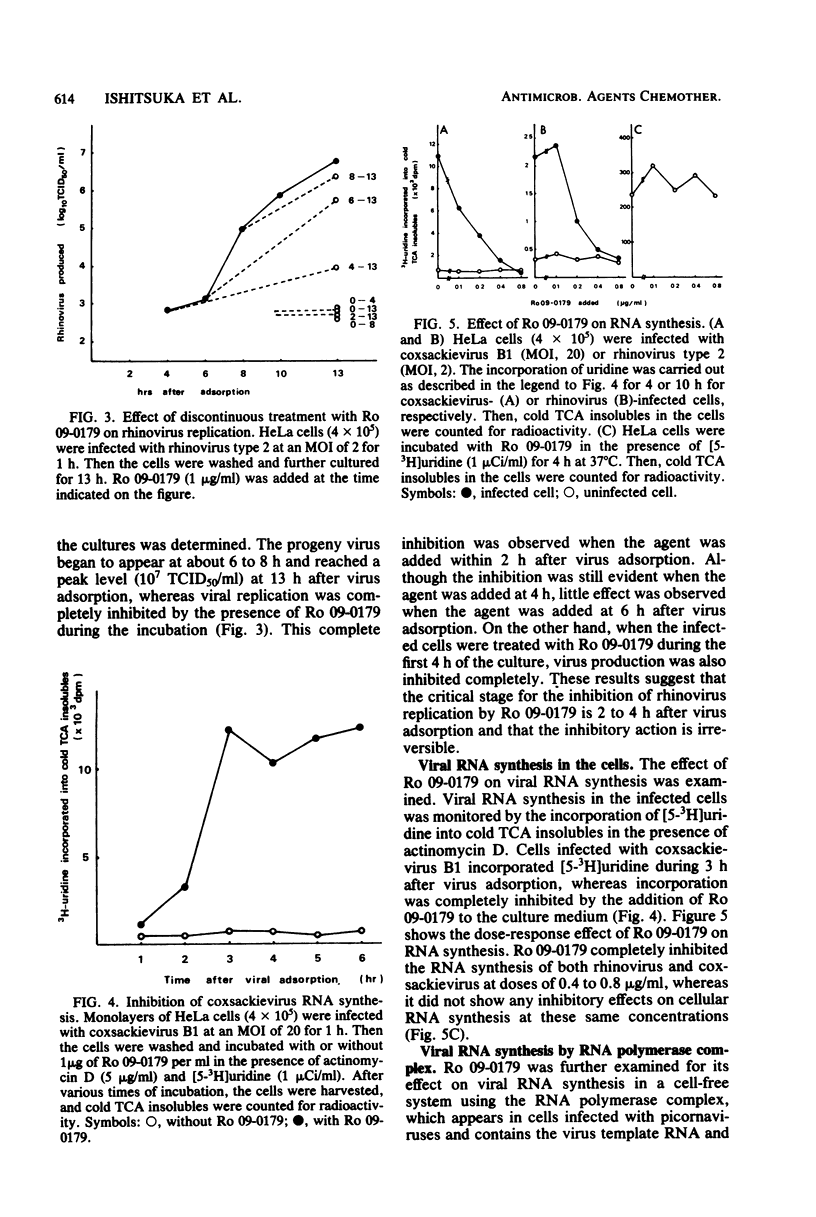
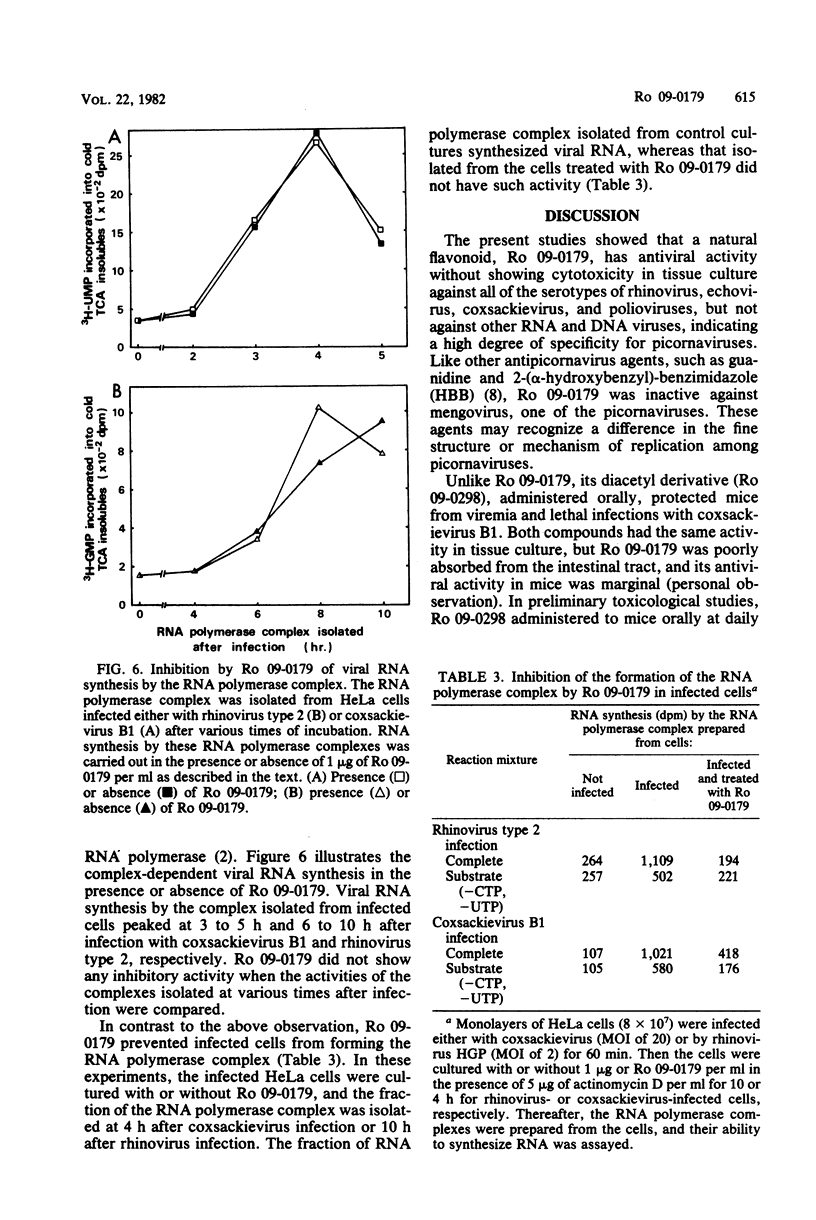
Ro 09-0179 (4',5-dihydroxy-3,3',7-trimethoxyflavone), isolated from a Chinese medicinal herb, was found to have potent antiviral activity. It selectively inhibited the replication of human picornaviruses, such as rhinoviruses and coxsackieviruses in tissue culture, but not other DNA and RNA viruses. Ro 09-0298 (4',5-diacetyloxy-3,3',7-trimethoxyflavone), an orally active derivative of Ro 09-0179, prevented coxsackievirus (B1) infection in mice. The critical time for the inhibition of rhinovirus replication by Ro 09-0179 was 2 to 4 h after virus adsorption, i.e., in the early stages of virus replication. It markedly inhibited coxsackievirus and rhinovirus RNA synthesis in infected HeLa cells, but not in a cell-free system using the RNA polymerase complex isolated from the infected cells. In the infected cells, the RNA polymerase complex was not formed in the presence of Ro 09-0179. Therefore, it is suggested that Ro 09-0179 interferes with some process of viral replication which occurs between viral uncoating and the initiation of viral RNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. Preliminary data on a virus-specific enzyme system responsible for the synthesis of viral RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Nov 27;9:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer D. J., Selway J. W., Batchelor J. F., Tisdale M., Caldwell I. C., Young D. A. 4',6-Dichloroflavan (BW683C), a new anti-rhinovirus compound. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):369–370. doi: 10.1038/292369a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béládi I., Pusztai R., Mucsi I., Bakay M., Gábor M. Activity of some flavonoids against viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:358–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., EGGERS H. J. SPECIFIC INHIBITION OF REPLICATION OF ANIMAL VIRUSES. Science. 1963 Oct 4;142(3588):24–33. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3588.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



