Abstract
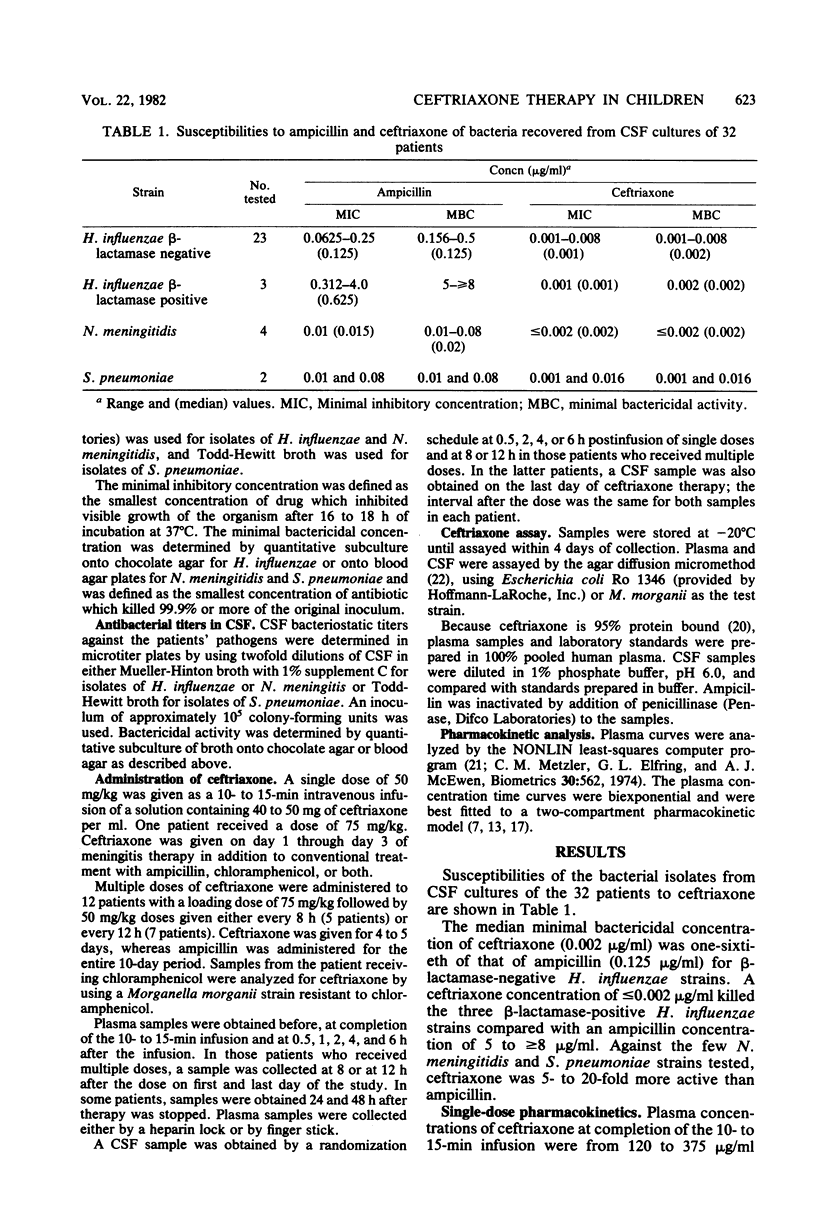
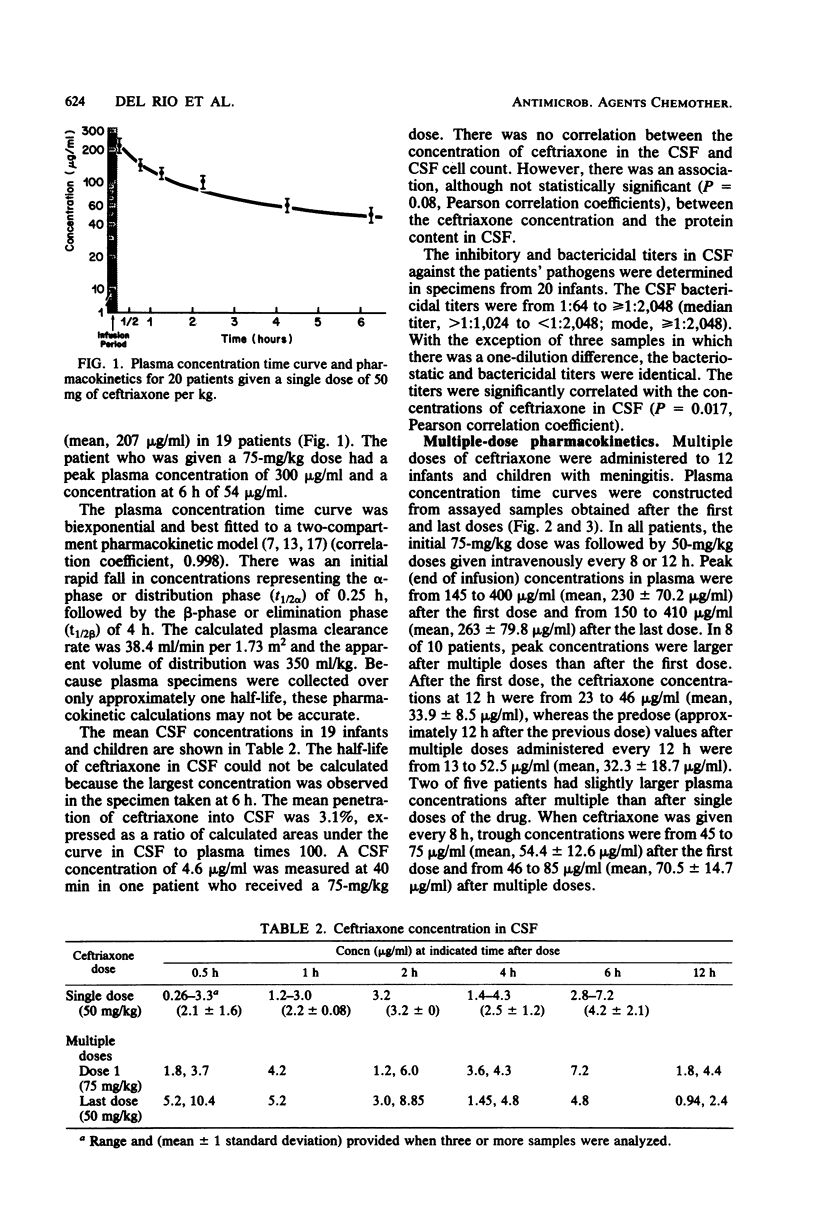
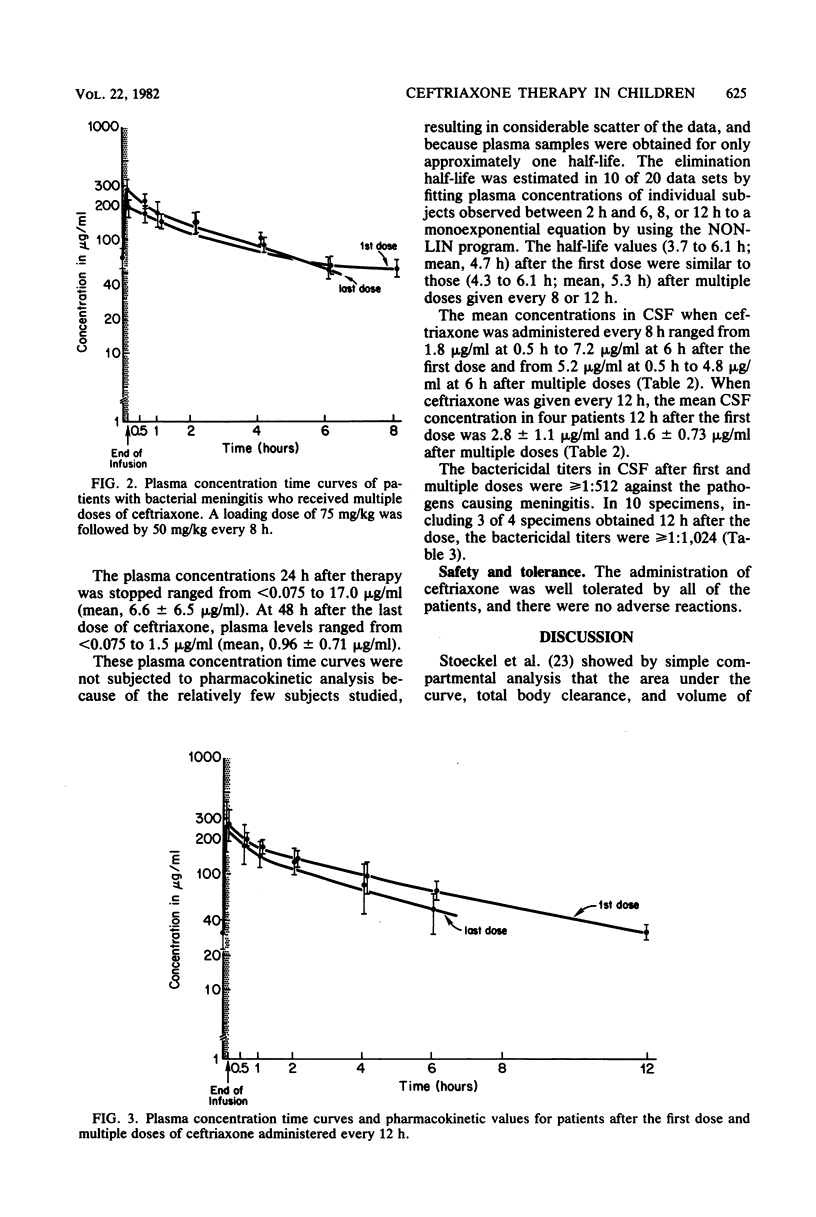
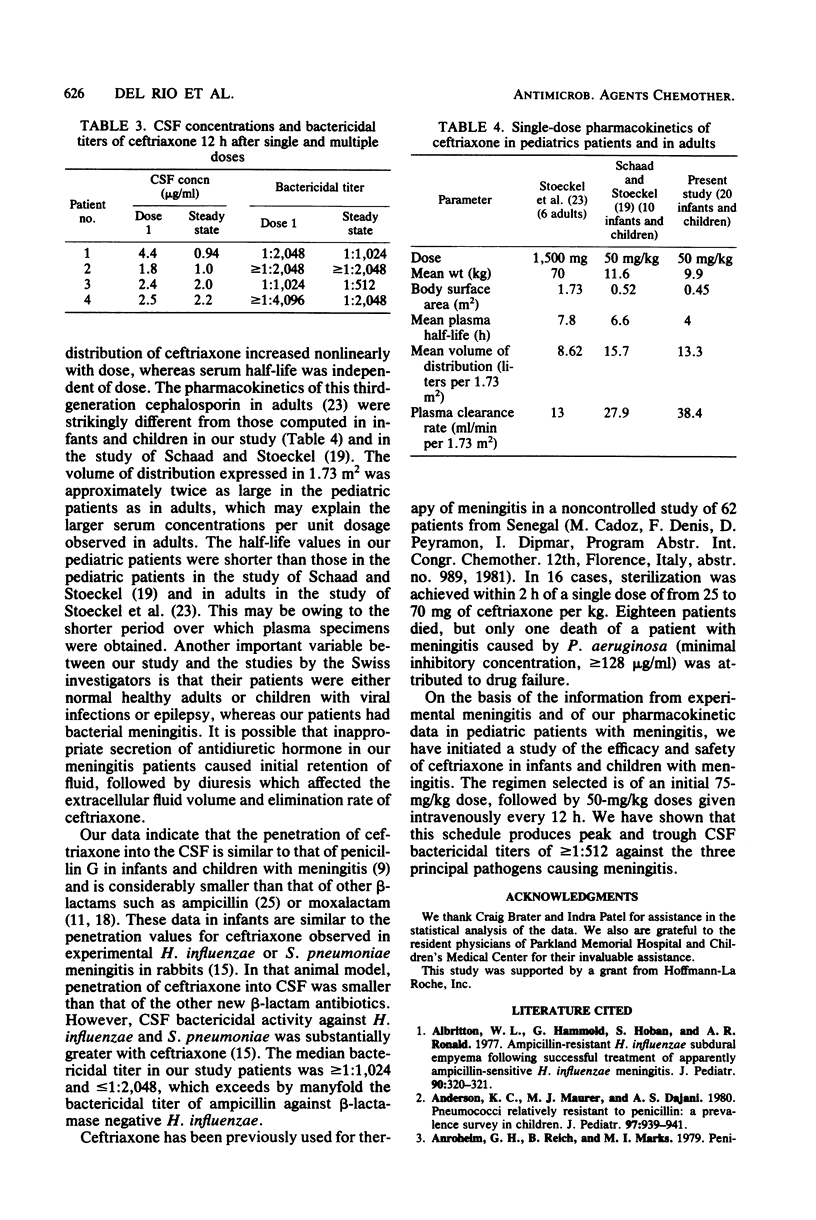
Single-dose pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone were determined in 19 patients with proven bacterial meningitis. The dosage was 50 mg of ceftriaxone per kg. The plasma concentration time curve declined in a biexponential manner. The mean peak plasma concentration was 207 micrograms/ml, and the elimination half-life was 4 h. In 12 patients, multiple-dose pharmacokinetics were determined after a loading dose of 75 mg of ceftriaxone per kg, followed by 50-mg/kg doses every 8 h in 5 patients or every 12 h in 7 patients. The mean peak plasma concentration was 230 micrograms/ml after the first dose and 263 micrograms/ml after the last dose. Of 12 patients, 5 had trough values that were larger after multiple doses than after a single dose. Mean penetration of ceftriaxone into cerebrospinal fluid was 3.1%. The median cerebrospinal fluid bactericidal titer against the patients pathogens was greater than 1:1,024 and less than 1:2,048. The drug was well tolerated without adverse effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahronheim G. A., Reich B., Marks M. I. Penicillin-insensitive pneumococci. Case report and review. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Feb;133(2):187–191. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130020079017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton W. L., Hammond G., Ronald A. R., Hoban S. Ampicillin-resistant H. influenzae subdural empyemia following successful treatment of apparently ampicillin-sensitive H. influenzae meningitis. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):320–321. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80664-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. C., Maurer M. J., Dajani A. S. Pneumococci relatively resistant to penicillin: a prevalence survey in children. J Pediatr. 1980 Dec;97(6):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delage G., DeClerck Y., Lescop J., Bery P., Shareck F. Hemophilus influenzae type b infections: recurrent disease due to ampicillin-resistant strains. J Pediatr. 1977 Feb;90(2):319–320. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieber J. P., Nelson J. D. A pharmacologic evaluation of penicillin in children with purulent meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 25;297(8):410–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708252970802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Mason E. O., Jr, Garcia H., Kvernland S. J., Loiselle E. M., Anderson D. C., Mintz A. A., Feigin R. D. Pharmacokinetics and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of moxalactam in children with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):152–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80562-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Isburg C. D., Michaels R. H. Meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae type b resistant to both ampicillin and chloramphenicol. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):14–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughnan P. M., Sitar D. S., Ogilvie R. I., Neims A. H. The two-compartment open-system kinetic model: a review of its clinical implications and applications. J Pediatr. 1976 May;88(5):869–873. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D., Grimm L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of cefoperazone, ceftriaxone, and moxalactam in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel I. H., Miller K., Weinfeld R., Spicehandler J. Multiple intravenous dose pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in man. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):47–56. doi: 10.1159/000238029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N., Thomas M. L. Clinical evaluation of a new broad-spectrum oxa-beta-lactam antibiotic, moxalactam, in neonates and infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80559-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., Stoeckel K. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in infants and young children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon M., Wise R., Gillett A. P., Livingston R. Pharmacokinetics of Ro 13-9904, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):240–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman A. J., Wagner J. G. CSTRIP, a fortran IV computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci. 1976 Jul;65(7):1006–1010. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., McNamara P. J., Brandt R., Plozza-Nottebrock H., Ziegler W. H. Effects of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding on ceftriaxone kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):650–657. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama N., Greene G. R., Kitts D. B., Thrupp L. D. Meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae type b resistant to ampicillin and chloramphenicol. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):421–424. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. D., Haltalin K. C. Ampicillin in Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Clinicopharmacologic evaluation of intramuscular vs intravenous administration. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Feb;129(2):208–215. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120390042009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


