Abstract
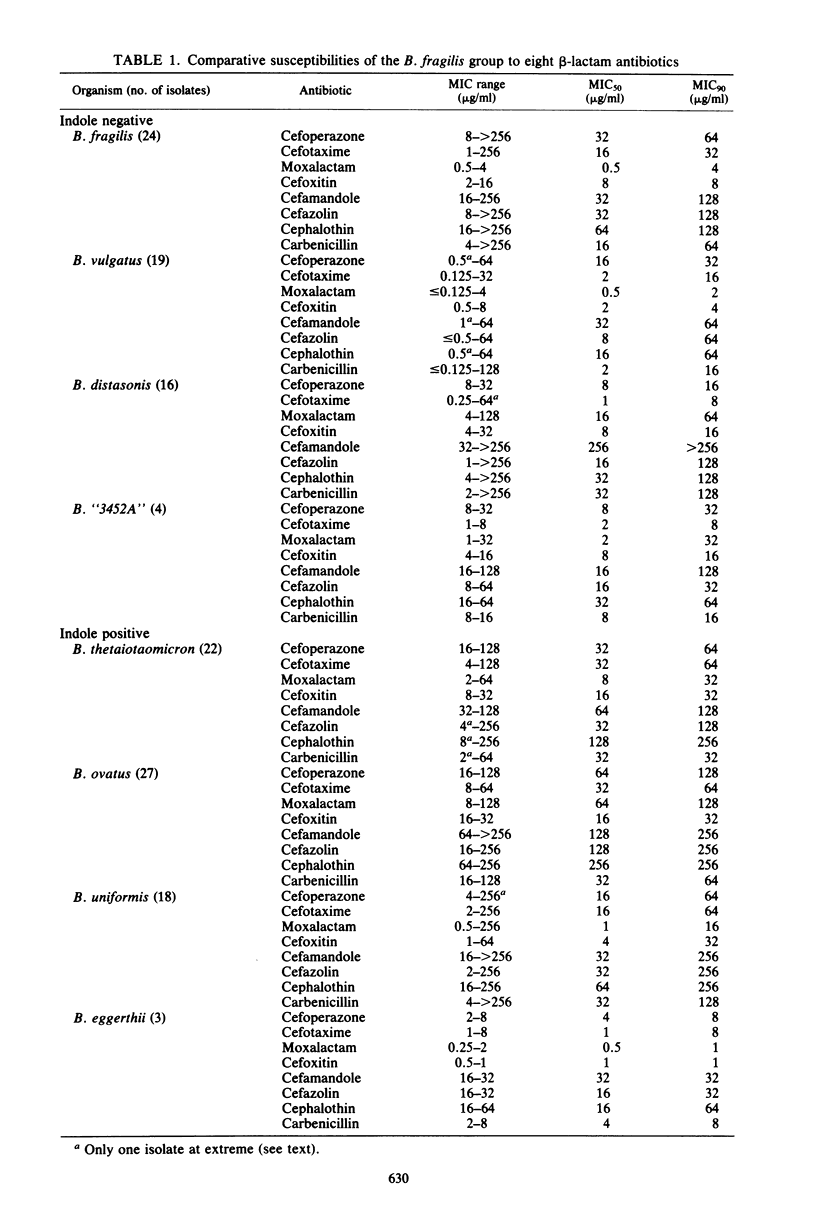
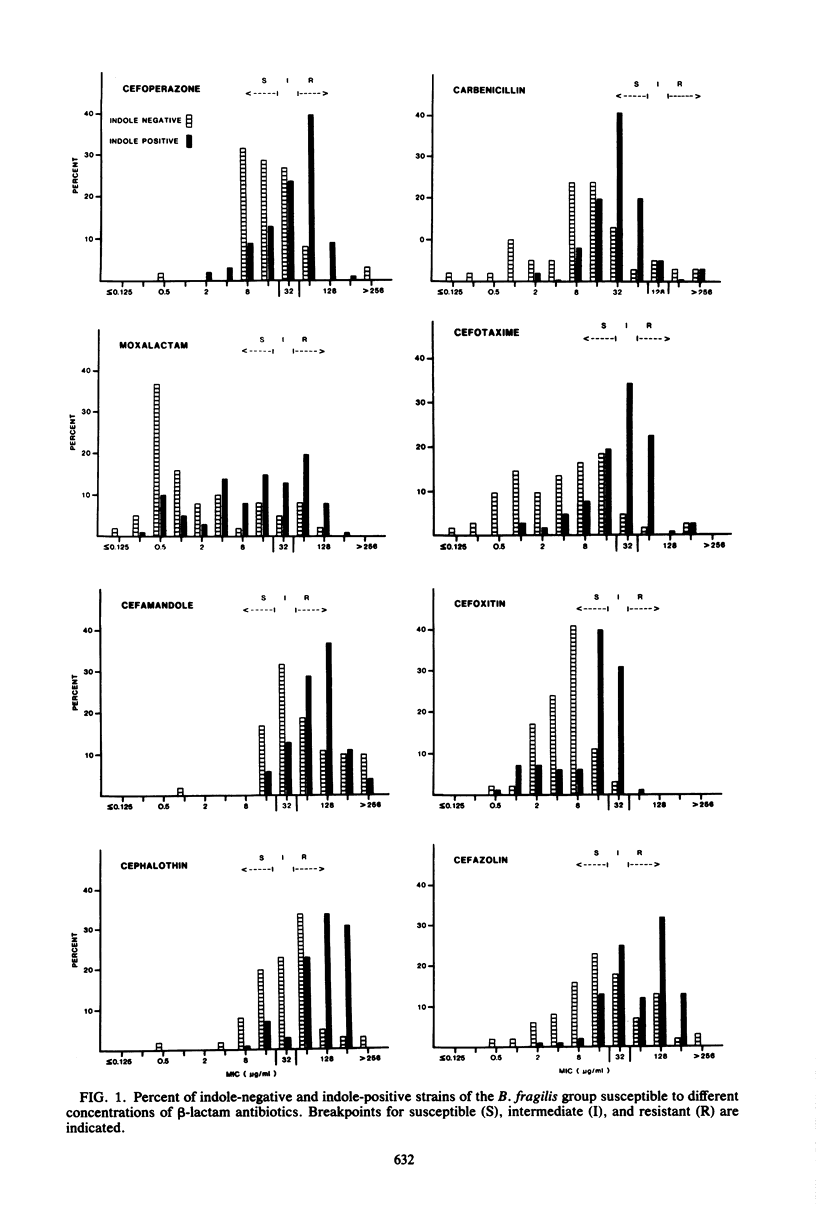
Clinical isolates of the members of the Bacteroides fragilis group differ markedly in their susceptibilities to a variety of beta-lactam antibiotics, including cefoperazone, moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole, cephalothin, cefazolin, and carbenicillin, as determined by dilution techniques. The minimum concentrations required to inhibit at least 50% of the strains tested (MIC50) for the entire B. fragilis group were lowest with moxalactam and cefoxitin, 4 and 8 micrograms/ml, respectively, whereas the MIC90S of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, moxalactam, cefoxitin, and carbenicillin were equivalent (64 micrograms/ml); the MIC90S of cefamandole, cephalothin, and cefazolin were higher. Indole-positive members of the group (B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, and B. uniformis) were significantly more resistant to every antibiotic tested than were indole-negative members (B. fragilis, B. distasonis, and B. vulgatus). In a 6-month survey of clinical laboratory data, indole-positive strains comprised 40% of the B. fragilis group isolates and 22% of all Bacteroides isolates; B. fragilis was the most common species isolated (23%). The increased use of second-generation and the introduction of third-generation cephalosporins may dictate that clinical microbiology laboratories routinely identify members of the B. fragilis group as to species or, alternatively, test for indole production in addition to performing more extensive susceptibility testing.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Del Bene V. E., Collins C. D. In vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin, moxalactam, and other new beta-lactam agents against Bacteroides fragilis: contribution of beta-lactamase to resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):248–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Nord C. E., Olsson-Liljeqvist B. Antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria with special reference to Bacteroides fragilis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1979;(19):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drulak M. W., Chow A. W. Comparative in vitro activity of ceftizoxime, cefoperazone, and cefoxitin against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):683–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C., Ehret J. Comparative in vitro studies of Ro 13-9904, a new cephalosporin derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):435–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):503–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. L. Variation in susceptibility patterns of species within the Bacteroides fragilis group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):686–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Kobasa W., Kaye K. Susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria to cefoperazone and other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):957–960. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane E. V., Swantee C. A., Kerr E. A. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to nine antimicrobial agents and demonstration of decreased susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):51–55. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasu M., Maskell J. P., Williams R. J., Williams J. D. In vitro activity of MK0787 (N-formimidoyl thienamycin) and other beta-lactam compounds against Bacteroides spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):433–436. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Meropol N. J., Fu K. P. Antibacterial activity of ceftriaxone (Ro 13-9904), a beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):414–423. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe R. D., Finegold S. M. Comparative in vitro activity of new beta-lactam antibiotics against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):600–609. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Barry A. L., Wilkins T. D., Zabransky R. J. Collaborative evaluation of a proposed reference dilution method of susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y. Y. Factors affecting the in vitro activity of cefoperazone against the Bacteroides fragilis group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):723–725. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Vaspar broth-disk procedure for antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):288–291. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Chalgren S. Medium for use in antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):926–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


