Abstract
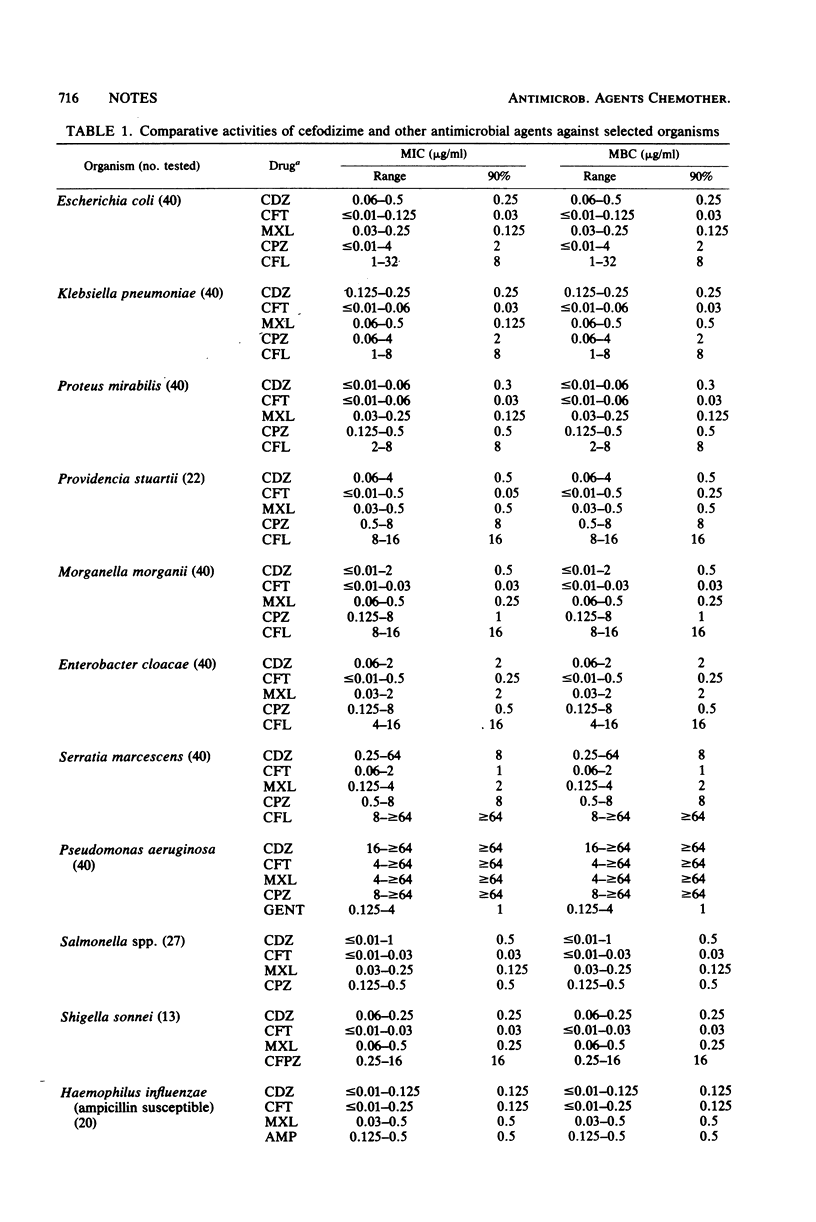
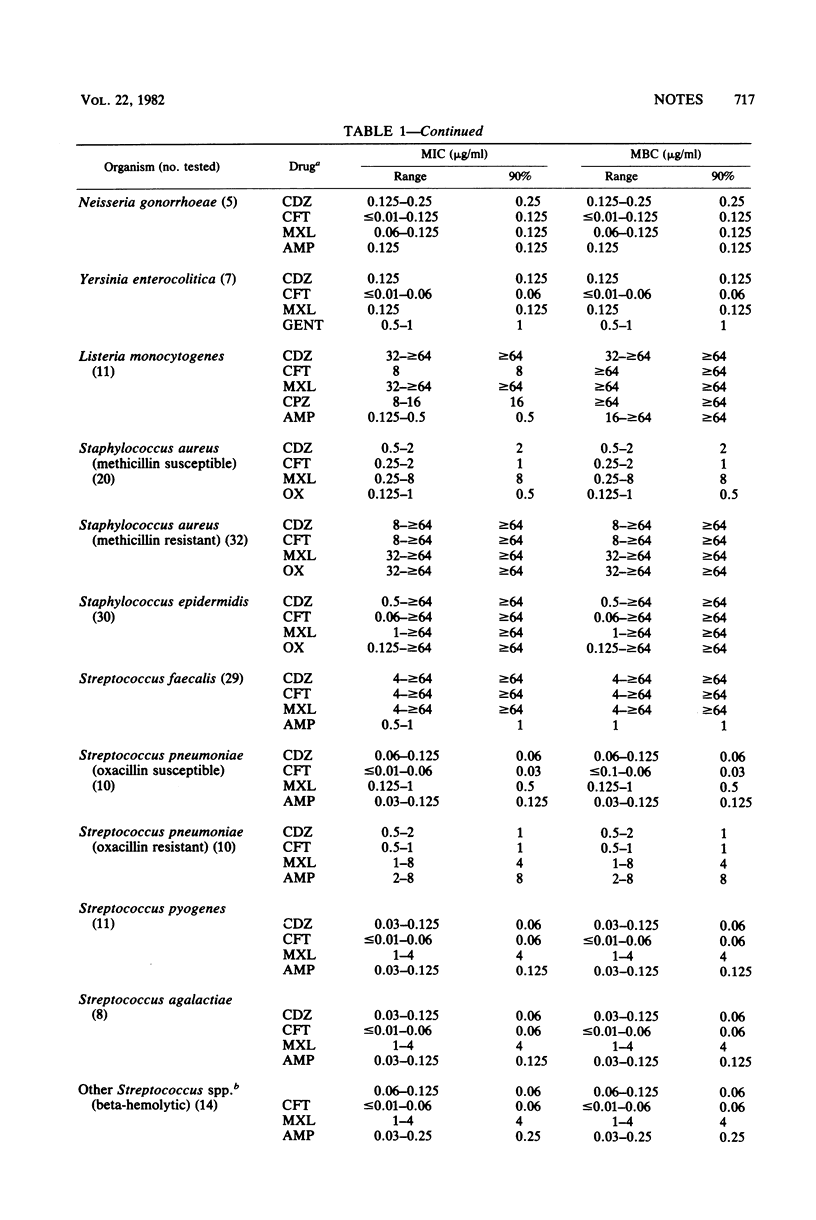
The in vitro activity of cefodizime (HR-221), a new cephalosporin antibiotic, was compared with the activities of selected antimicrobial agents against a broad spectrum of aerobic bacteria. Cefodizime concentrations of 2 micrograms/ml inhibited about 90% of Enterobacteriaceae studied. Serratia marcescens required 8 micrograms/ml to inhibit 90% of strains. Among gram-positive cocci, 50% of strains were inhibited by 2 micrograms/ml of cefodizime (including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus faecalis, and penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae). Pseudomonas aeruginosa was less susceptible to cefodizime. Cefotaxime, an antibiotic closely related to cefodizime structurally, was about fourfold more active.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahonkhai V. I., Cherubin C. E., Shulman M. A., Bancroft U. Comparative in vitro activities of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365) and newer cephalosporin derivatives of clinical utility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):999–1002. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C., Wilson H. W. In vitro antimicrobial activity evaluation of cefodizime (HR221), a new semisynthetic cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):760–768. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okonogi K., Kuno M., Kida M., Mitsuhashi S. Beta-lactamase stability and antibacterial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):171–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


