Full text
PDF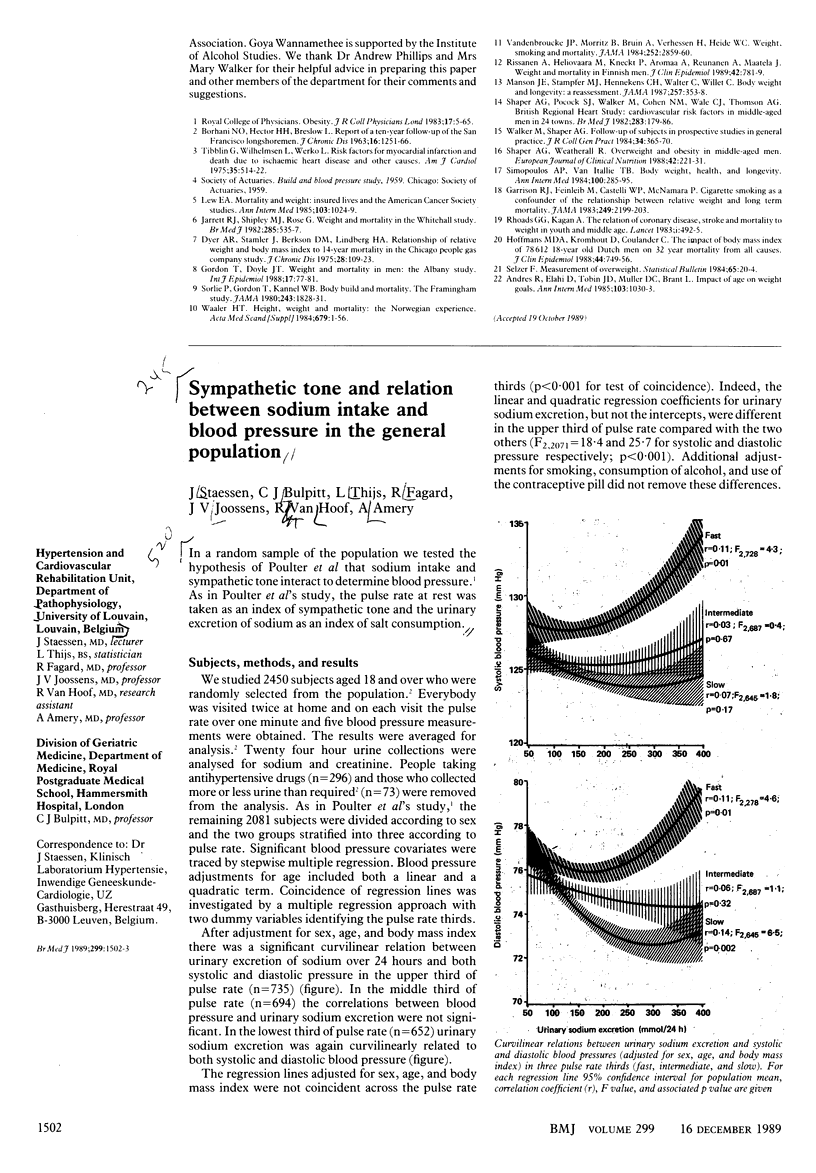

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Light K. C., Koepke J. P., Obrist P. A., Willis P. W., 4th Psychological stress induces sodium and fluid retention in men at high risk for hypertension. Science. 1983 Apr 22;220(4595):429–431. doi: 10.1126/science.6836285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J., Bulpitt C. J., Fagard R., Joossens J. V., Lijnen P., Amery A. Salt intake and blood pressure in the general population: a controlled intervention trial in two towns. J Hypertens. 1988 Dec;6(12):965–973. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198812000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


