Abstract
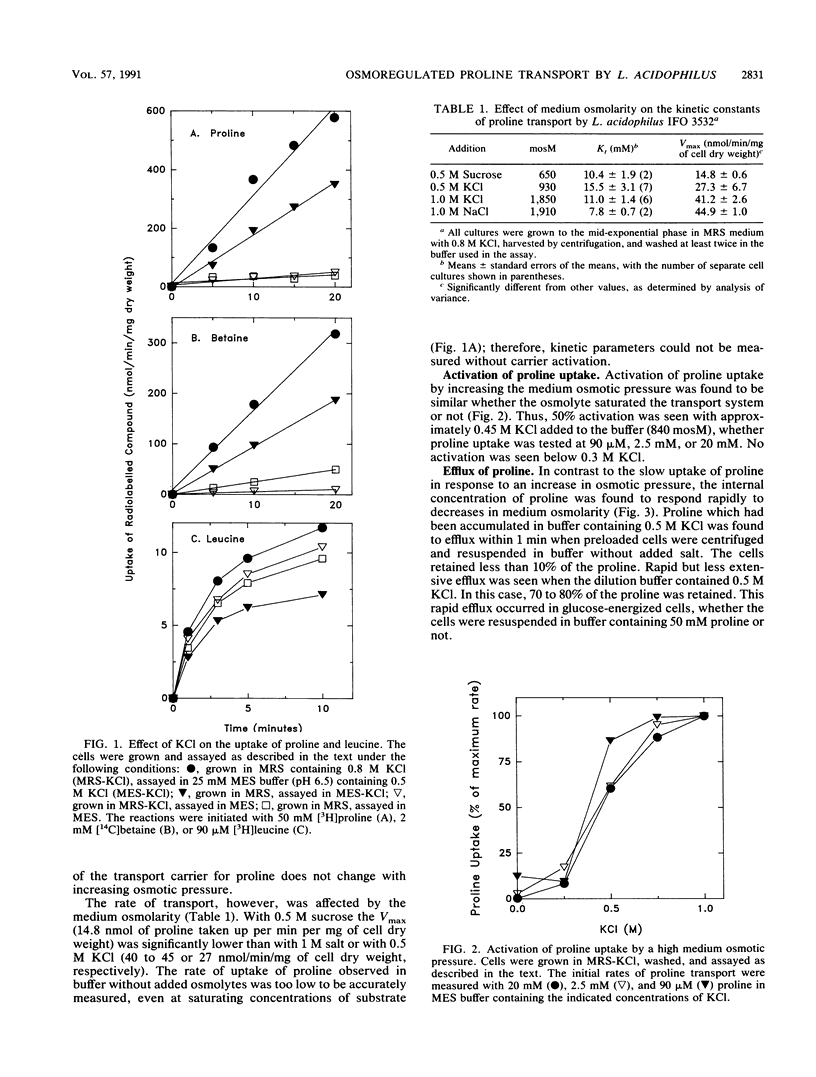
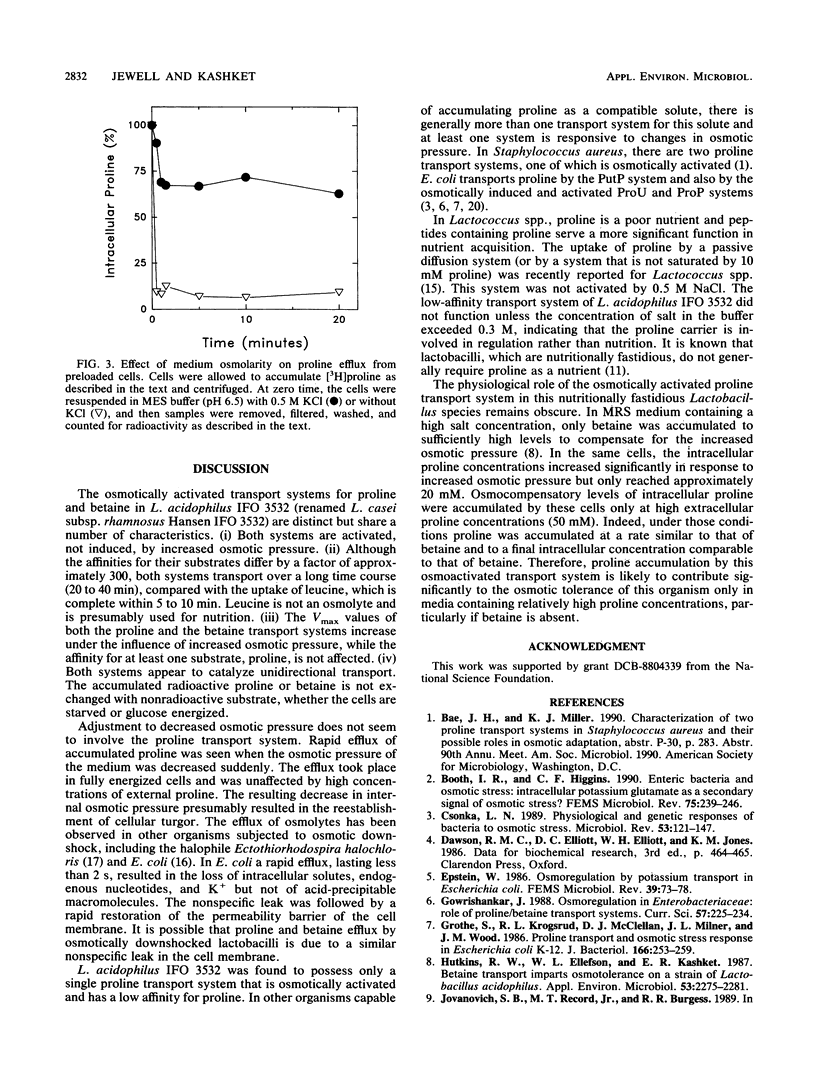
We reported previously that, when exposed to high osmotic pressure, Lactobacillus acidophilus IFO 3532 cells accumulated N,N,N-trimethylglycine (glycine betaine), which serves as a compatible intracellular solute. When grown in medium with high osmotic pressure, these cells also accumulated one amino acid, proline. The uptake of [3H]proline by resting, glucose-energized cells was stimulated by increasing the osmotic pressure of the assay medium with 0.5 to 1.0 M KCl, 1.0 M NaCl, or 0.5 M sucrose. The accumulated [3H]proline was not metabolized further. In contrast, there was no osmotic stimulation of [3H]leucine uptake. The uptake of proline was activated rather than induced by exposure of the cells to high osmotic pressure. Only one proline transport system could be discerned from kinetics plots. The affinity of the carrier for proline remained constant over a range of osmotic pressures from 650 to 1,910 mosM (Kt, 7.8 to 15.5 mM). The Vmax, however, increased from 15 nmol/min/mg of dry weight in 0.5 M sucrose to 27 and 40 nmol/min/mg of dry weight in 0.5 M KCl and in 1.0 M KCl or NaCl, respectively. The efflux of proline from preloaded cells occurred rapidly when the osmotic pressure of the suspending buffer was lowered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Enteric bacteria and osmotic stress: intracellular potassium glutamate as a secondary signal of osmotic stress? FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;6(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):121–147. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.121-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe S., Krogsrud R. L., McClellan D. J., Milner J. L., Wood J. M. Proline transport and osmotic stress response in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):253–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.253-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutkins R. W., Ellefson W. L., Kashket E. R. Betaine Transport Imparts Osmotolerance on a Strain of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2275–2281. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2275-2281.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. L., Grothe S., Wood J. M. Proline porter II is activated by a hyperosmotic shift in both whole cells and membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14900–14905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita T., Deguchi Y., Yajima M., Sakurai T., Yura T. Multiple nutritional requirements of lactobacilli: genetic lesions affecting amino acid biosynthetic pathways. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):64–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.64-71.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perroud B., Le Rudulier D. Glycine betaine transport in Escherichia coli: osmotic modulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):393–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.393-401.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince W. S., Villarejo M. R. Osmotic control of proU transcription is mediated through direct action of potassium glutamate on the transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17673–17679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smid E. J., Konings W. N. Relationship between utilization of proline and proline-containing peptides and growth of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5286–5292. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5286-5292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsapis A., Kepes A. Transient breakdown of the permeability barrier of the membrane of Escherichia coli upon hypoosmotic shock. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatmore A. M., Chudek J. A., Reed R. H. The effects of osmotic upshock on the intracellular solute pools of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2527–2535. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M. Proline porters effect the utilization of proline as nutrient or osmoprotectant for bacteria. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(3):183–202. doi: 10.1007/BF01872157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


