Abstract
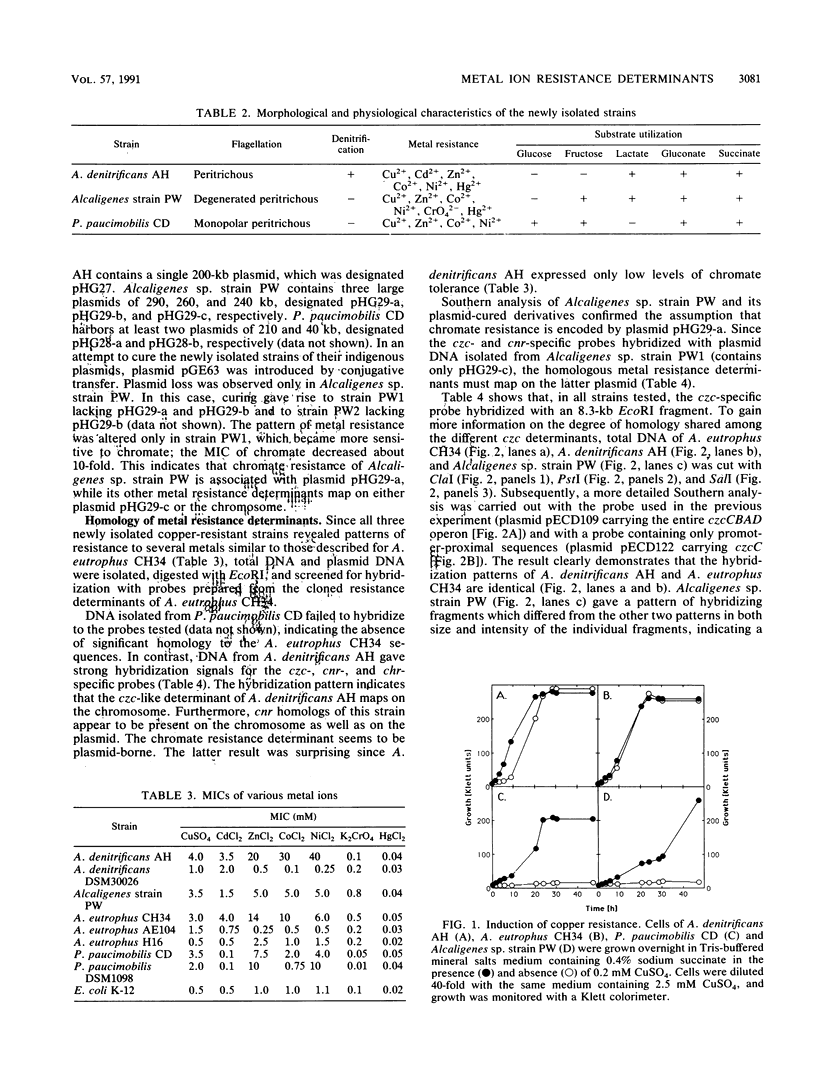
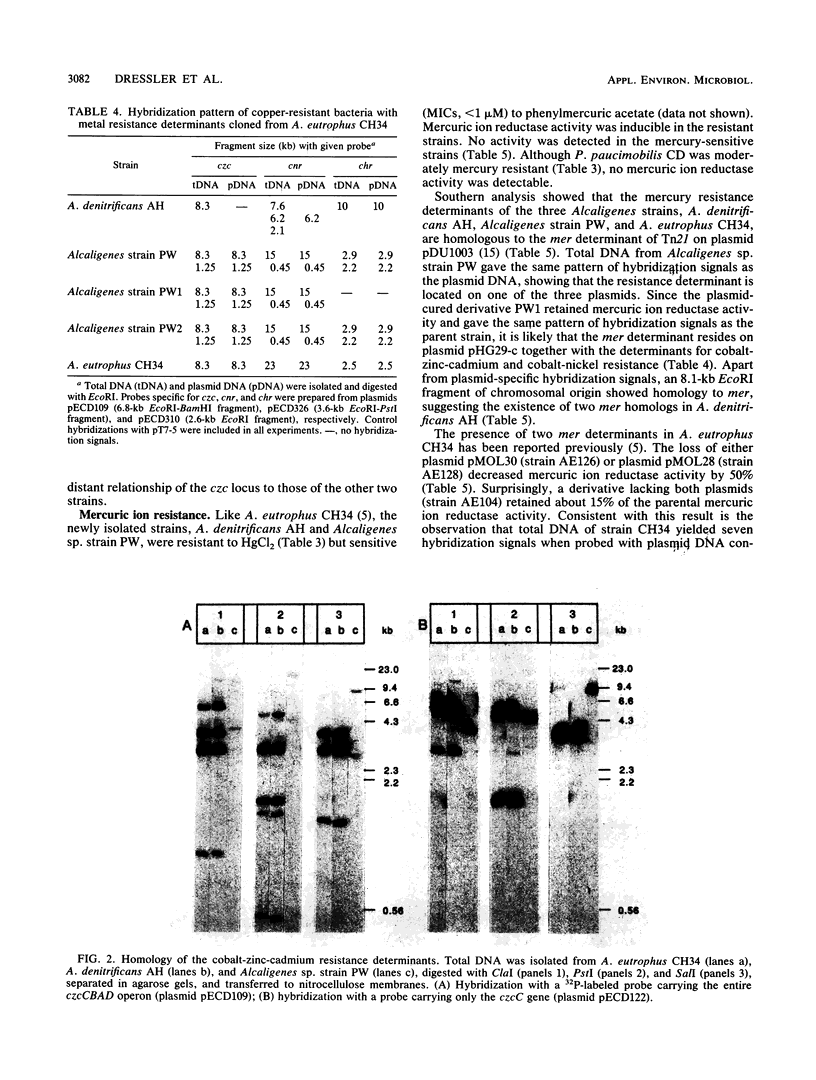
Three copper-resistant, gram-negative bacteria were isolated and characterized. Of the three strains, Alcaligenes denitrificans AH tolerated the highest copper concentration (MIC = 4 mM CuSO4). All three strains showed various levels of resistance to other metal ions. A. denitrificans AH contains sequences which cross-hybridized with the mer (mercury resistance) determinant of Tn21 and the czc (cobalt, zinc, and cadmium resistance), cnr (cobalt and nickel resistance), and chr (chromate resistance) determinants of A. eutrophus CH34. DNA-DNA hybridization with probes prepared from A. eutrophus CH34 and Tn21 revealed the presence of chr-, cnr-, and mer-like sequences on the 200-kb plasmid pHG27 and of czc, cnr, and mer homologs located on the chromosome. The second strain, classified as Alcaligenes sp. strain PW, carries czc, cnr, and mer homologs on the 240-kb plasmid pHG29-c and a chr determinant on the 290-kb plasmid pHG29-a; a third plasmid, the 260-kb large plasmid pHG29-b, is cryptic. In contrast to the Alcaligenes strains, which were isolated from metal-contaminated water, Pseudomonas paucimobilis CD was isolated from the air. This strain harbors two cryptic plasmids: the 210-kb large plasmid pHG28-a and the 40-kb plasmid pHG28-b. Southern analysis revealed no homology between the metal ion resistance determinants of A. eutrophus CH34 and P. paucimobilis CD.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender C. L., Cooksey D. A. Indigenous plasmids in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: conjugative transfer and role in copper resistance. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.534-541.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender C. L., Cooksey D. A. Molecular cloning of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):470–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.470-474.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A. Characterization of a Copper Resistance Plasmid Conserved in Copper-Resistant Strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):454–456. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.454-456.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diels L., Mergeay M. DNA probe-mediated detection of resistant bacteria from soils highly polluted by heavy metals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1485–1491. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1485-1491.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberz G., Friedrich B. Three trans-acting regulatory functions control hydrogenase synthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1845–1854. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1845-1854.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellano M. A., Cooksey D. A. Induction of the copper resistance operon from Pseudomonas syringae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4399–4401. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4399-4401.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellano M. A., Cooksey D. A. Nucleotide sequence and organization of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2879–2883. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2879-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Houba C., Gerits J. Extrachromosomal inheritance controlling resistance to cadmium, cobalt, copper and zinc ions: evidence from curing in a Pseudomonas [proceedings]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1978 May;86(2):440–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Nies D., Schlegel H. G., Gerits J., Charles P., Van Gijsegem F. Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy metals. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):328–334. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.328-334.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni'Bhriain N. N., Silver S., Foster T. J. Tn5 insertion mutations in the mercuric ion resistance genes derived from plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):690–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.690-703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A., Nies D. H., Silver S. Cloning and expression of plasmid genes encoding resistances to chromate and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5065–5070. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5065-5070.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A., Nies D. H., Silver S. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a plasmid-encoded chromate resistance determinant from Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5648–5653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H., Nies A., Chu L., Silver S. Expression and nucleotide sequence of a plasmid-determined divalent cation efflux system from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H., Silver S. Metal ion uptake by a plasmid-free metal-sensitive Alcaligenes eutrophus strain. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4073–4075. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4073-4075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D. H., Silver S. Plasmid-determined inducible efflux is responsible for resistance to cadmium, zinc, and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):896–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.896-900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies D., Mergeay M., Friedrich B., Schlegel H. G. Cloning of plasmid genes encoding resistance to cadmium, zinc, and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4865–4868. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4865-4868.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderle S. J., Booth J. E., Williams J. W. Mercuric reductase from R-plasmid NR1: characterization and mechanistic study. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):869–876. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D., Camakaris J., Lee B. T., Luke R. K. Inducible plasmid-mediated copper resistance in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):939–943. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui R. A., Benthin K., Schlegel H. G. Cloning of pMOL28-encoded nickel resistance genes and expression of the genes in Alcaligenes eutrophus and Pseudomonas spp. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5071–5078. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5071-5078.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K. Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:717–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetaz T. J., Luke R. K. Plasmid-controlled resistance to copper in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1263–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1263-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevors J. T. Copper resistance in bacteria. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Jan;4(1):29–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]