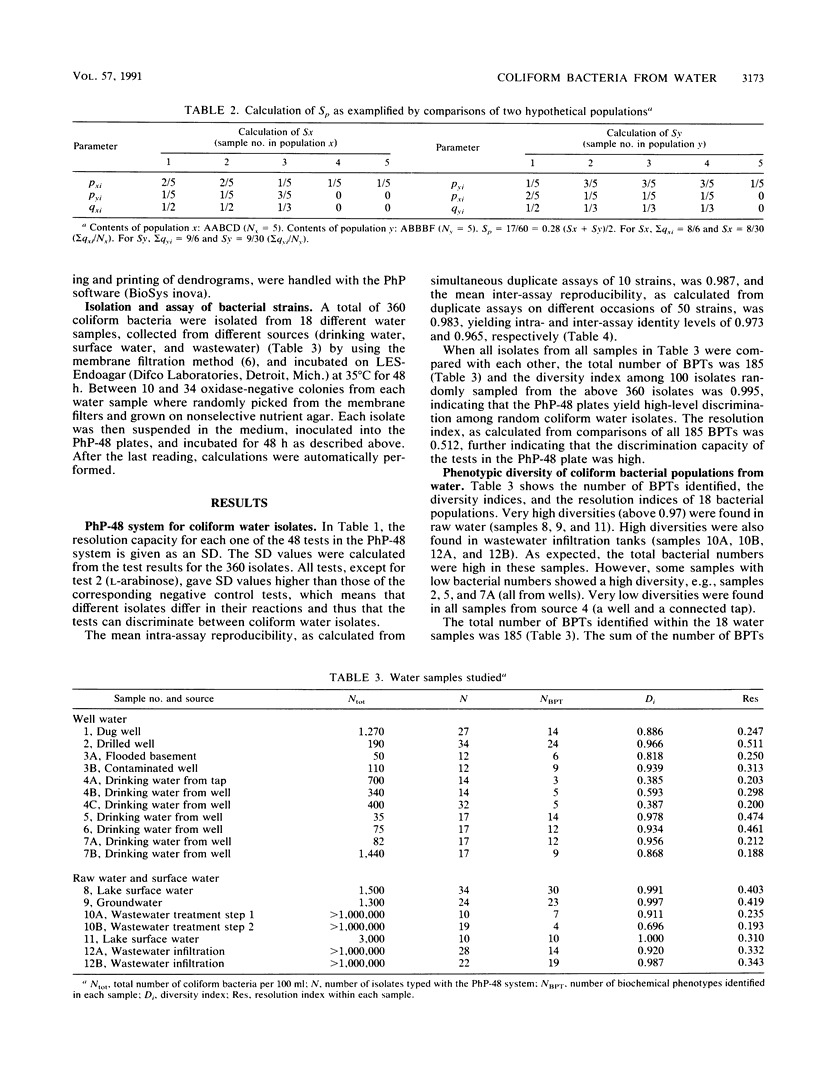
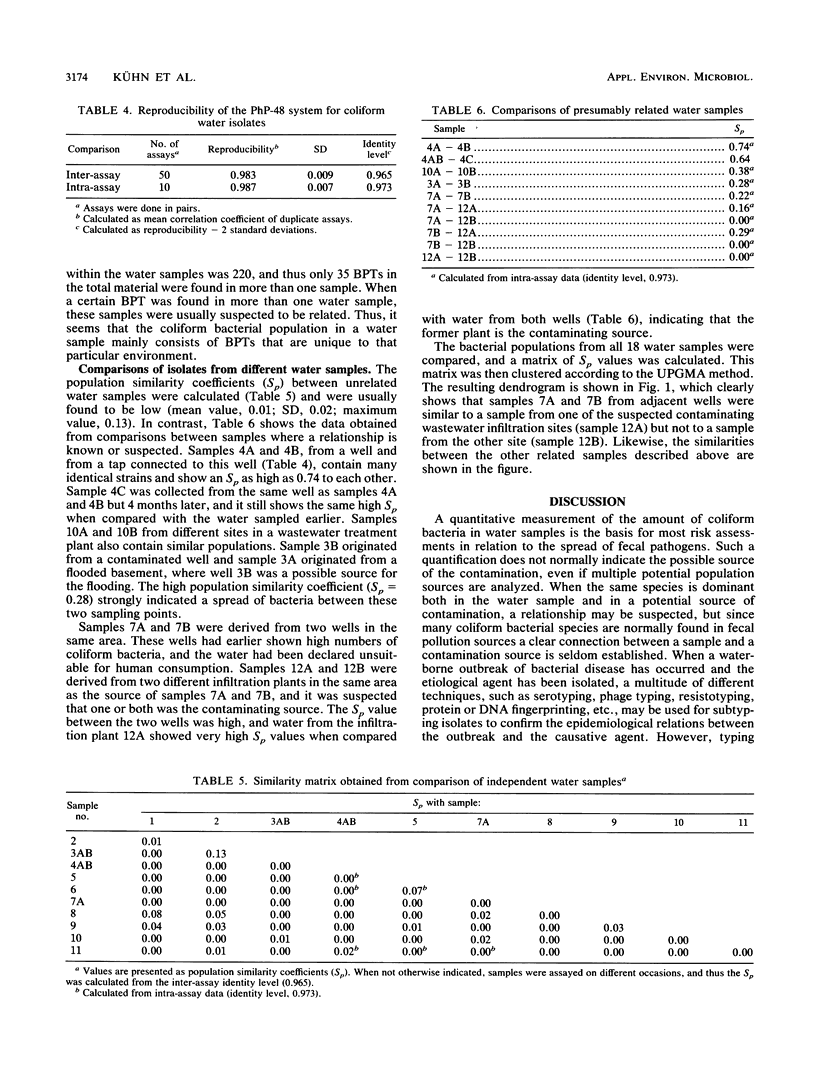
Abstract
A simple, automated microplate system for biochemical characterization of water isolates can be used to obtain fingerprints of the bacterial flora from various water samples. Mathematical models for calculating the diversities and similarities between bacterial populations are described for such fingerprints. The diversity may give information on whether an indigenous or allochthonous flora is present, and the similarities between bacterial populations, as calculated by using a population similarity coefficient (Sp), may indicate contaminations between different water samples. The system was demonstrated on coliform bacterial populations from various water samples, with or without suspected intercontamination. For unrelated water samples, the Sps were close to 0, whereas repeated samples of the same source showed Sps of 0.64 to 0.74. The Sp values from several water samples were also clustered to form a dendrogram, thus indicating the relative similarities between the bacterial populations to confirm suspected common sources of pollution.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkwill D. L., Fredrickson J. K., Thomas J. M. Vertical and horizontal variations in the physiological diversity of the aerobic chemoheterotrophic bacterial microflora in deep southeast coastal plain subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1058–1065. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1058-1065.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Balkwill D. L., Zachara J. M., Li S. M., Brockman F. J., Simmons M. A. Physiological diversity and distributions of heterotrophic bacteria in deep cretaceous sediments of the atlantic coastal plain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):402–411. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.402-411.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R., Gaston M. A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson's index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2465–2466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2465-2466.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R., Izsák J. Diversity studies of Salmonella incidents in some domestic livestock and their potential relevance as indicators of niche width. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Dec;105(3):501–510. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katouli M., Kühn I., Möllby R. Evaluation of the stability of biochemical phenotypes of Escherichia coli upon subculturing and storage. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Sep;136(9):1681–1688. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-9-1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn I., Brauner A., Möllby R. Evaluation of numerical typing systems for Escherichia coli using the API 50 CH and the PhP-EC systems as models. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Dec;105(3):521–531. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn I., Franklin A., Söderlind O., Möllby R. Phenotypic variations among enterotoxinogenic Escherichia coli from Swedish piglets with diarrhoea. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(3):119–130. doi: 10.1007/BF02298122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn I., Tullus K., Möllby R. Colonization and persistence of Escherichia coli phenotypes in the intestines of children aged 0 to 18 months. Infection. 1986 Jan-Feb;14(1):7–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01644802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. M., Lavoie M. C. Microcomputer package for statistical analysis of microbial populations. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Nov;3(4):309–312. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.4.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Cato E. P., Good I. J., Smith E. P., Ranney R. R., Palcanis K. G. Variation in periodontal floras. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):720–726. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.720-726.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik V., Salte K., Sørheim R., Goksøyr J. Comparison of phenotypic diversity and DNA heterogeneity in a population of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):776–781. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.776-781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullus K., Berglund B., Fryklund B., Kühn I., Burman L. G. Epidemiology of fecal strains of the family Enterobacteriaceae in 22 neonatal wards and influence of antibiotic policy. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1166–1170. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1166-1170.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vätänen P. Effects of Environmental Factors on Microbial Populations in Brackish Waters off the Southern Coast of Finland. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):48–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.48-54.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vätänen P. Factor analysis of the impact of the environment on microbial communities in the tvärminne area, southern coast of Finland. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.55-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


