Abstract
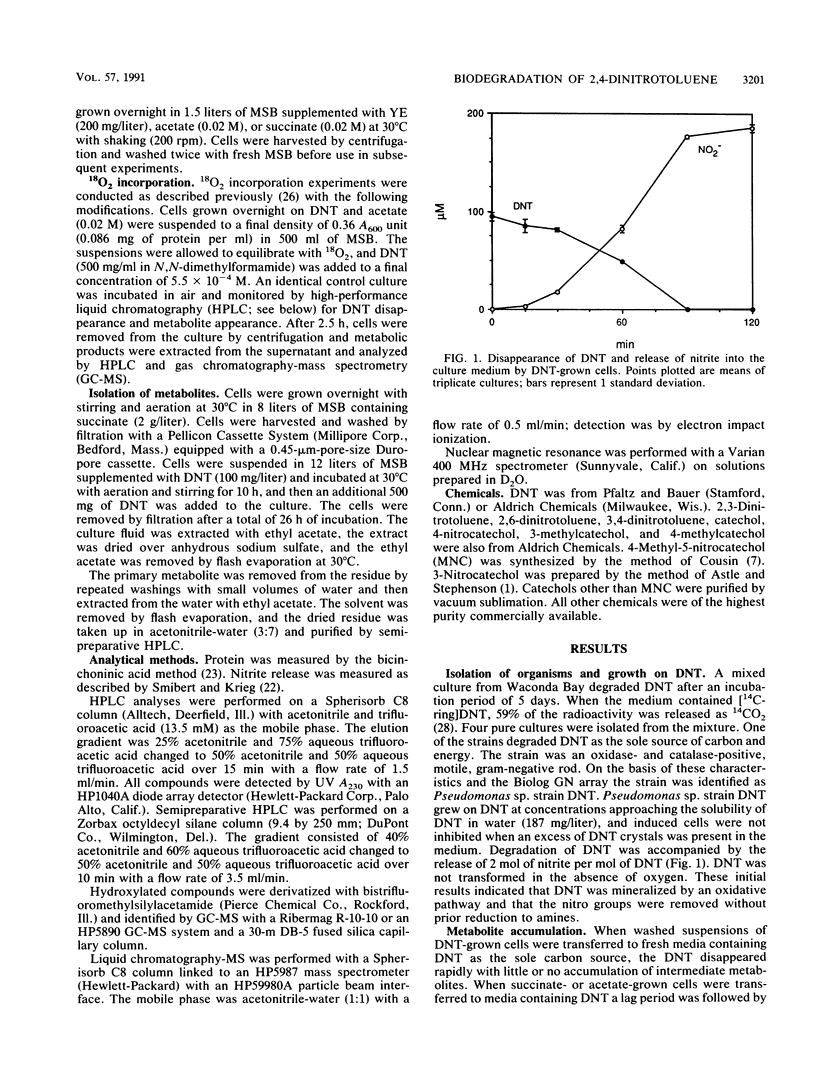
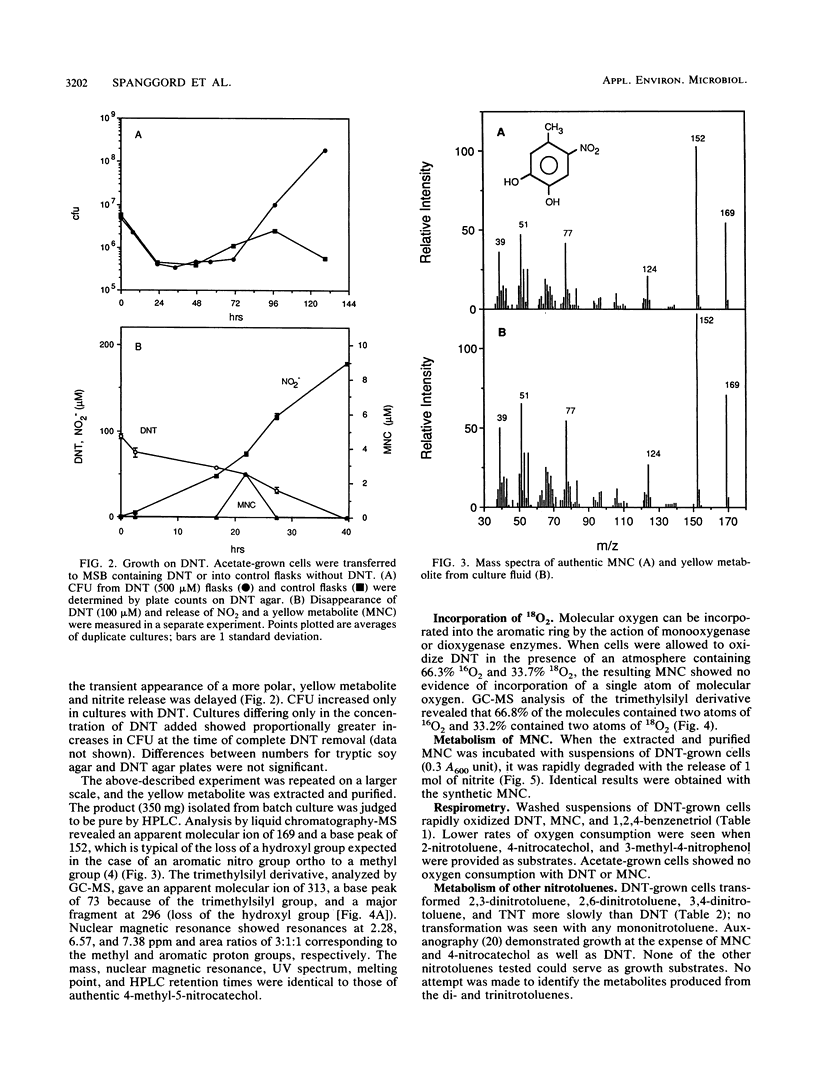
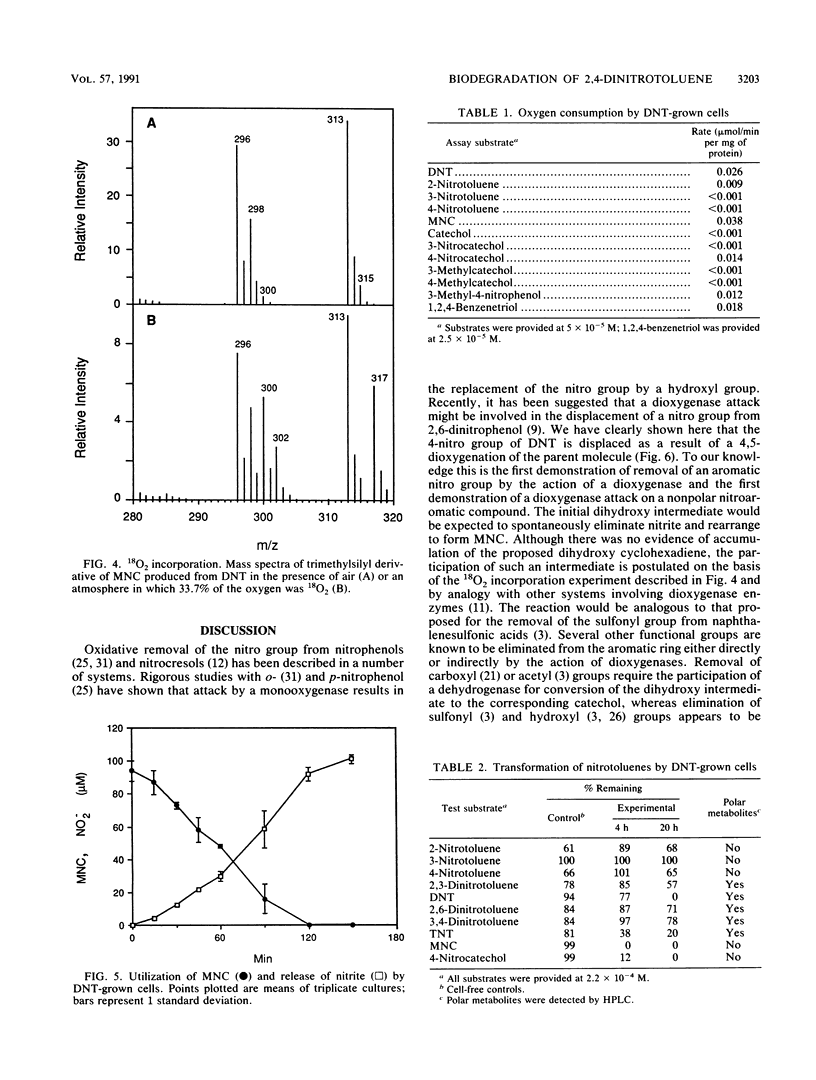
Previous studies of the biodegradation of nonpolar nitroaromatic compounds have suggested that microorganisms can reduce the nitro groups but cannot cleave the aromatic ring. We report here the initial steps in a pathway for complete biodegradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene (DNT) by a Pseudomonas sp. isolated from a four-member consortium enriched with DNT. The Pseudomonas sp. degraded DNT as the sole source of carbon and energy under aerobic conditions with stoichiometric release of nitrite. During induction of the enzymes required for growth on DNT, 4-methyl-5-nitrocatechol (MNC) accumulated transiently in the culture fluid when cells grown on acetate were transferred to medium containing DNT as the sole carbon and energy source. Conversion of DNT to MNC in the presence of 18O2 revealed the simultaneous incorporation of two atoms of molecular oxygen, which demonstrated that the reaction was catalyzed by a dioxygenase. Fully induced cells degraded MNC rapidly with stoichiometric release of nitrite. The results indicate an initial dioxygenase attack at the 4,5 position of DNT with the concomitant release of nitrite. Subsequent reactions lead to complete biodegradation and removal of the second nitro group as nitrite.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachofer R., Lingens F., Schäfer W. Conversion of aniline into pyrocatechol by a Nocardia sp.; incorporation of oxygen-18. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):288–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of Naphthalenesulfonic Acids by Pseudomonas sp. A3 and Pseudomonas sp. C22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.44-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN R. B. The microbial metabolism of nitro-aromatic compounds. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B. Utilization of anthranilic and nitrobenzoic acids by Nocardia opaca and a flavobacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):219–235. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando T., Bumpus J. A., Aust S. D. Biodegradation of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1666-1671.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallas L. E., Alexander M. Microbial transformation of nitroaromatic compounds in sewage effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1234-1241.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Thomson K., Anderson A. C. Identification of nitroso compounds from biotransformation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1295–1298. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1295-1298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Cornell J. H., Kaplan A. M. Identification of biotransformation products from 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):945–948. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.945-948.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Feeherry F. E., Levinson H. S. Microbial transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and other nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):949–958. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.949-958.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Metabolism of aromatic compounds in bacteria. Purification and properties of the catechol-forming enzyme, 3,5-cyclohexadiene-1,2-diol-1-carboxylic acid (NAD + ) oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):4960–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Zylstra G. J., Blake C. K., Gibson D. T. Monohydroxylation of phenol and 2,5-dichlorophenol by toluene dioxygenase in Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2648–2652. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2648-2652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



