Abstract
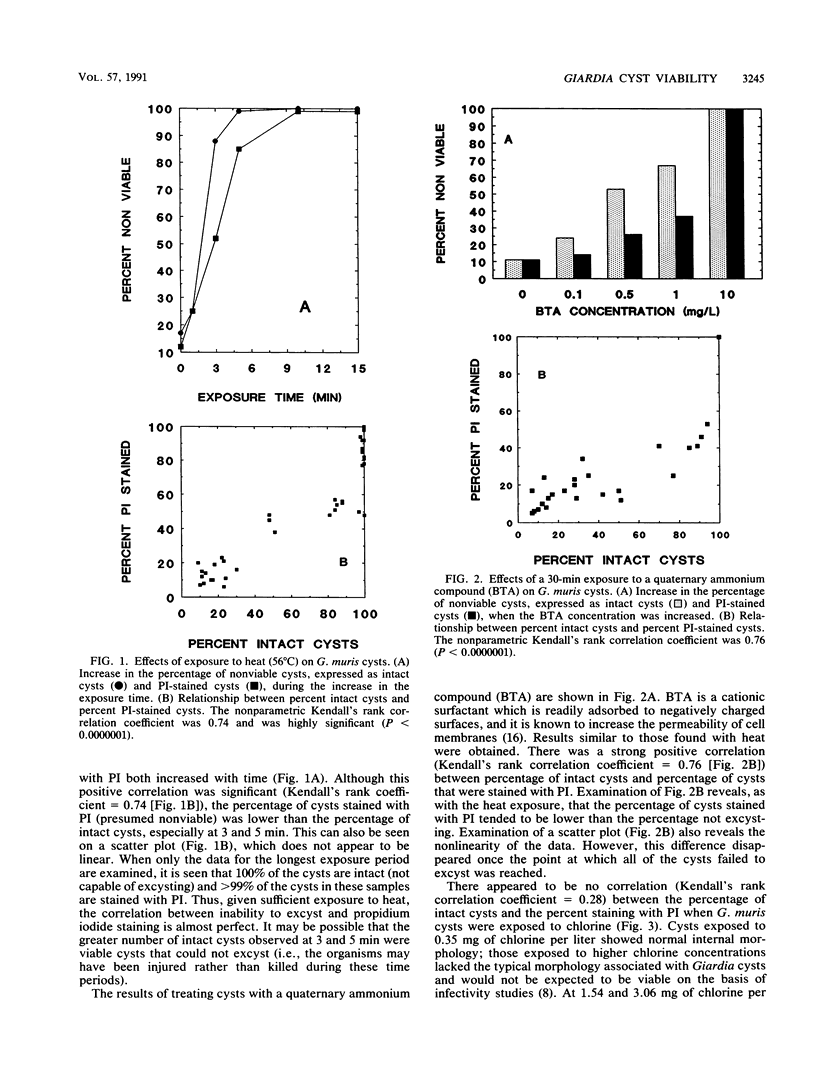
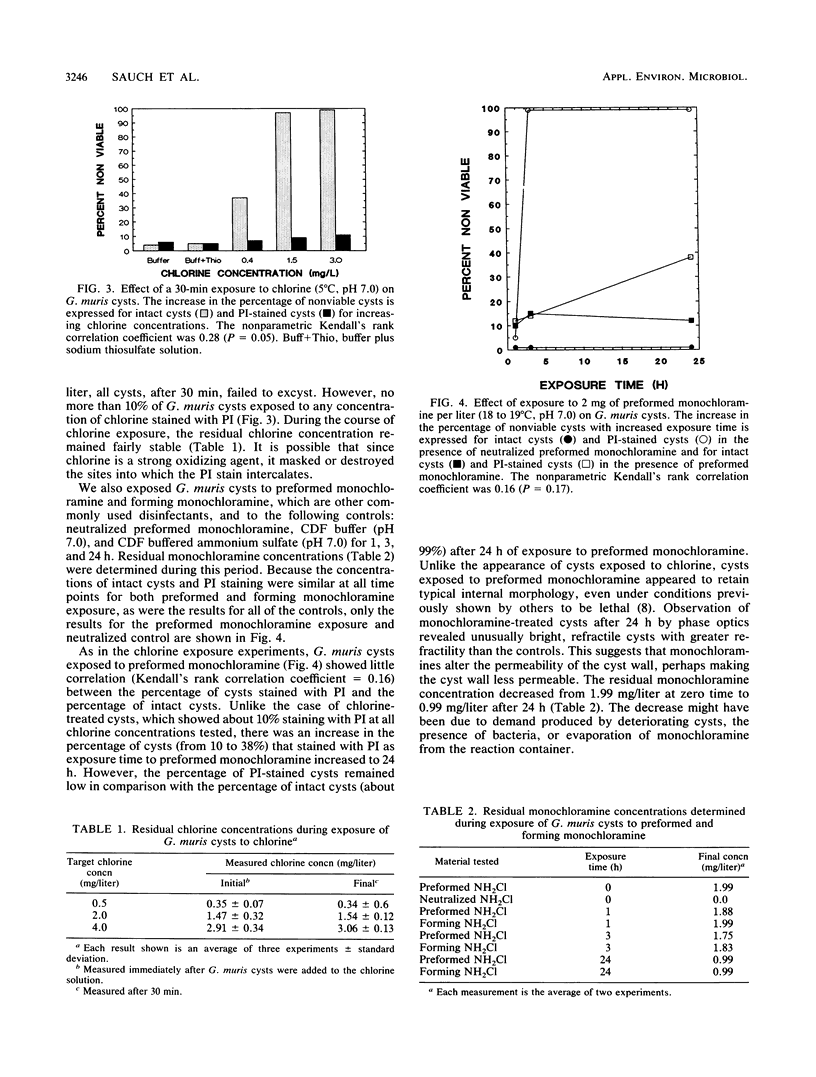
The use of propidium iodide, whose uptake indicates cell death or damage, was investigated to assess the viability of heat-inactivated and chemically inactivated Giardia muris cysts. This was done by comparing propidium iodide staining with excystation. We first determined that propidium iodide could be used with an immunofluorescence detection procedure by showing that the percentages of Giardia lamblia cysts stained with this dye before and after subjecting them to a fluorescence detection method were similar. G. muris cysts were then exposed to heat (56 degrees C), 0.5 to 4 mg of chlorine per liter (pH 7.0, 5 degrees C), 0.1 to 10 mg of a quaternary ammonium compound per liter, or 2 mg of preformed and forming monochloramine per liter (pH 7.2, 18 to 20 degrees C). A good positive correlation between percent propidium iodide-stained cysts and lack of excystation was demonstrated for G. muris cysts exposed either to heat or to the quaternary ammonium compound. However, no significant correlation between absence of excystation and propidium iodide staining was found for cysts exposed to chlorine or monochloramines. These results demonstrate that the propidium iodide staining procedure is not satisfactory for determining the viability of G. muris cysts exposed to these two commonly used drinking water disinfectants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belosevic M., Faubert G. M., MacLean J. D., Law C., Croll N. A. Giardia lamblia infections in Mongolian gerbils: an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):222–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D., Hoff J. C. Inactivation of simian rotavirus SA11 by chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and monochloramine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):317–323. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.317-323.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham A. K., Jarroll E. L., Jr, Meyer E. A., Radulescu S. Giardia sp.: physical factors of excystation in vitro, and excystation vs eosin exclusion as determinants of viability. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Apr;47(2):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff J. C., Rice E. W., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Comparison of animal infectivity and excystation as measures of Giardia muris cyst inactivation by chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1115–1117. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1115-1117.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. H., Senft J. A. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate-propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):77–79. doi: 10.1177/33.1.2578146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ongerth J. E., Johnson R. L., Macdonald S. C., Frost F., Stibbs H. H. Back-country water treatment to prevent giardiasis. Am J Public Health. 1989 Dec;79(12):1633–1637. doi: 10.2105/ajph.79.12.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Stevens D. P., Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S. Giardiasis in the mouse: an animal model. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauch J. F., Berman D. Immunofluorescence and morphology of Giardia lamblia cysts exposed to chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1573–1575. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1573-1575.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauch J. F. Purification of Giardia muris cysts by velocity sedimentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):454–455. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.454-455.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauch J. F. Use of immunofluorescence and phase-contrast microscopy for detection and identification of Giardia cysts in water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1434–1438. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1434-1438.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer F. W., 3rd, Rice E. W., Hoff J. C. Factors promoting in vitro excystation of Giardia muris cysts. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(6):795–800. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp D. G., Erlandsen S. L. A new method to determine Giardia cyst viability: correlation of fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide staining with animal infectivity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):704–707. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.704-707.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp D. G., Erlandsen S. L. Determination of Giardia muris cyst viability by differential interference contrast, phase, or brightfield microscopy. J Parasitol. 1987 Aug;73(4):723–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp D. G., Januschka M. M., Sherlock L. A., Stibbs H. H., Meyer E. A., Bemrick W. J., Erlandsen S. L. Production of viable Giardia cysts in vitro: determination by fluorogenic dye staining, excystation, and animal infectivity in the mouse and Mongolian gerbil. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith H. V. A comparison of fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide staining and in vitro excystation for determining Giardia intestinalis cyst viability. Parasitology. 1989 Dec;99(Pt 3):329–331. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000059035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. J., Hsi B. L., Faulk W. P. Propidium iodide as a nuclear marker in immunofluorescence. II. Use with cellular identification and viability studies. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deRegnier D. P., Cole L., Schupp D. G., Erlandsen S. L. Viability of Giardia cysts suspended in lake, river, and tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1223-1229.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


