Abstract
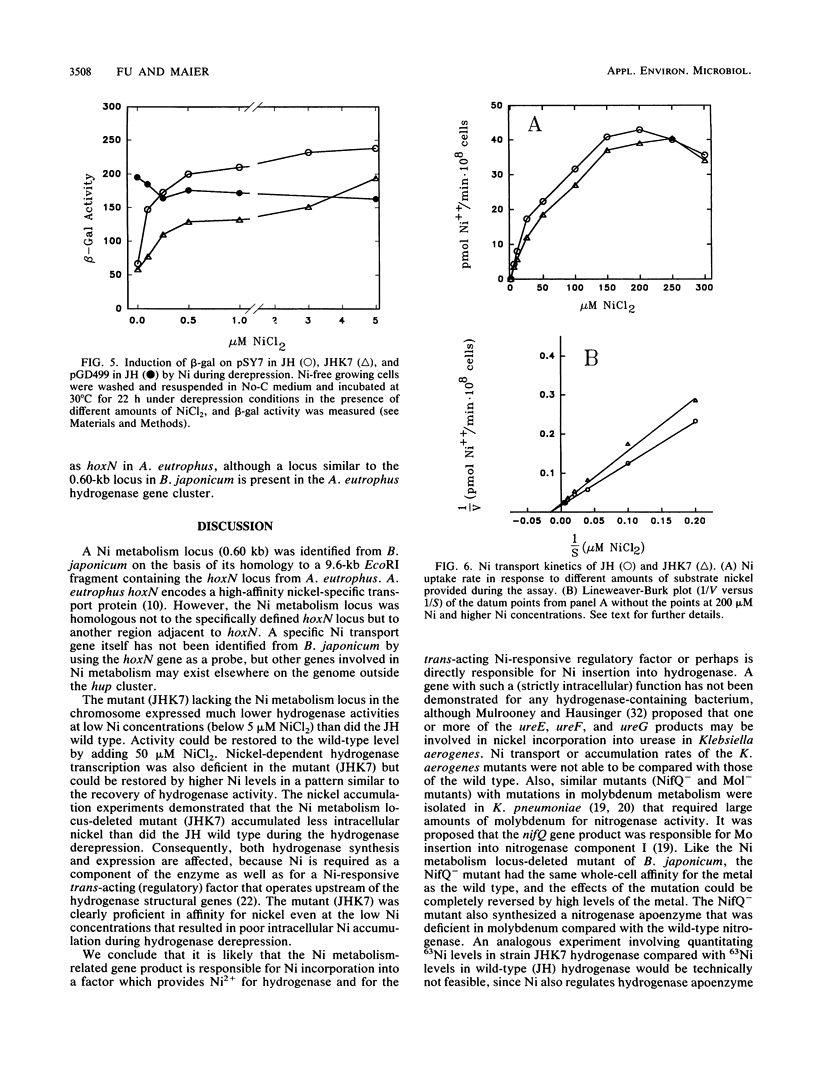
A 0.6-kb fragment of DNA involved in intracellular Ni metabolism was isolated and cloned from a cosmid containing 23.2 kb of hydrogenase-related genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. This locus is located 8.3 kb upstream of the hydrogenase structural genes. The hydrogenase activity of a mutant with a gene-directed mutation at this locus (strain JHK7) showed dependency on nickel provided during hydrogenase derepression. The hydrogenase activity was only 20% of that in the wild-type strain, JH, at a concentration of 0.5 microM NiCl2. The hydrogenase activity in JH reached its maximum at 3 microM NiCl2, whereas the mutant (JHK7) reached wild-type levels of hydrogenase activity when derepressed in 50 microM NiCl2. Studies with the hup-lacZ transcriptional fusion plasmid pSY7 in JHK7 showed that the mutant JHK7 expressed less promoter activity under low-nickel conditions than did strain JH. The mutant accumulated less nickel during a 45-h hydrogenase derepression period than did the wild type. However, both JHK7 and the JH wild-type strain had the same short-term Ni transport rates, and the KmS for Ni of both strains were about 62 microM. When incubated under non-hydrogenase-derepression conditions, the mutant accumulated Ni at the same rate as strain JH. However, this stored source of nickel was unable to restore hydrogenase expression ability of the mutant to wild-type levels during derepression without nickel. The results indicate that the locus identified in B. japonicum is not involved in nickel-specific transport; indeed, it was not at all homologous to the "nickel transporter" hoxN gene of Alcaligenes eutrophus.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp D. J. Rhizobium japonicum hydrogenase: purification to homogeneity from soybean nodules, and molecular characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barany F. Single-stranded hexameric linkers: a system for in-phase insertion mutagenesis and protein engineering. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):111–123. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberz G., Eitinger T., Friedrich B. Genetic determinants of a nickel-specific transport system are part of the plasmid-encoded hydrogenase gene cluster in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1340-1345.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitinger T., Friedrich B. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and heterologous expression of a high-affinity nickel transport gene from Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3222–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskew D. L., Welch R. M., Cary E. E. A simple plant nutrient solution purification method for effective removal of trace metals using controlled pore glass-8-hydroxyquinoline chelation column chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):103–105. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Xu L. S., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Some properties of the nickel-containing hydrogenase of chemolithotrophically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):850–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.850-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R. A., Cantrell M. A., Beaty J. S., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Characterization of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1006-1012.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Nickel utilization by microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):22–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.22-42.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton S. M., Dean D. Biogenesis of molybdenum cofactors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(3):169–188. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom S. S., Graham L. A., Maier R. J. Isolation of genes (nif/hup cosmids) involved in hydrogenase and nitrogenase activities in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):882–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.882-887.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom S. S., Uratsu S. L., Hoang F. Transposon Tn5-induced mutagenesis of Rhizobium japonicum yielding a wide variety of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):335–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.335-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperial J., Ugalde R. A., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Mol- mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae requiring high levels of molybdate for nitrogenase activity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1285–1287. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1285-1287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperial J., Ugalde R. A., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Role of the nifQ gene product in the incorporation of molybdenum into nitrogenase in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.187-194.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Maier R. J. Transcriptional regulation of hydrogenase synthesis by nickel in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18729–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Yu C., Maier R. J. Common cis-acting region responsible for transcriptional regulation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum hydrogenase by nickel, oxygen, and hydrogen. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):3993–3999. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.3993-3999.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Hancock R. E., Ingraham J. L. Properties of a Pseudomonas stutzeri outer membrane channel-forming protein (NosA) required for production of copper-containing N2O reductase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2096–2100. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2096-2100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):825–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.825-829.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Pihl T. D., Stults L., Sray W. Nickel accumulation and storage in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1905–1911. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1905-1911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merberg D., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum: analysis of mutants altered in regulation by carbon substrates and oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1236–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1236-1242.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Hausinger R. P. Sequence of the Klebsiella aerogenes urease genes and evidence for accessory proteins facilitating nickel incorporation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5837–5843. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5837-5843.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak P. D., Maier R. J. Identification of a Locus Upstream from the Hydrogenase Structural Genes That Is Involved in Hydrogenase Expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3051–3057. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3051-3057.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian M. R., Maier R. J. Hydrogen metabolism in Rhizobium: energetics, regulation, enzymology and genetics. Adv Microb Physiol. 1988;29:1–52. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brian M. R., Maier R. J. Isolation of a cytochrome aa(3) gene from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3219–3223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., Mallick S., Maier R. J. Nickel uptake in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1398-1402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Nickel is a component of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):153–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.153-158.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabillion R., Kaltwasser H. Energieabhängige 63Ni-Aufnahme bei Alcaligenes eutrophus Stamm H1 und H16. Arch Microbiol. 1977 May 13;113(1-2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00428595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolk C. P., Vonshak A., Kehoe P., Elhai J. Construction of shuttle vectors capable of conjugative transfer from Escherichia coli to nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Waugh R., Edmonds C. J., Holt S. E., Boxer D. H. Nickel deficiency gives rise to the defective hydrogenase phenotype of hydC and fnr mutants in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1709–1718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



