Abstract
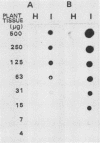
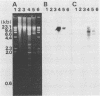
DNA was extracted from rice plants infected with mycoplasmalike organisms (MLOs) causing yellow dwarf disease. DNA of the causal agent was separated from the host DNA by repeated bisbenzimide-CsCl equilibrium density gradient centrifugations. MLO DNA cut by HindIII was ligated into plasmid Bluescript II and cloned in Escherichia coli NM522. The DNA inserts were labeled with peroxidase and employed as probes in hybridization. Southern analysis revealed that the insert in pRYD-12 consisted of one, presumably chromosomal, piece of MLO DNA, whereas the insert in pRYD-19, another recombinant plasmid, consisted of one, presumably extrachromosomal, piece of MLO DNA. Cloned DNA probes were successfully applied in dot blot hybridization for the detection of rice yellow dwarf disease MLOs in rice plants and in an insect vector, the green rice leafhopper (Nephotettix cincticeps).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyce T. M., Zwick M. E., Aquadro C. F. Mitochondrial DNA in the bark weevils: size, structure and heteroplasmy. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):825–836. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara H., Shikita M. Electroblotting of double-stranded DNA for hybridization experiments: DNA transfer is complete within 10 minutes after pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1990 Feb 1;184(2):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90670-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick B. C., Stenger D. C., Morris T. J., Purcell A. H. Cloning and Detection of DNA from a Nonculturable Plant Pathogenic Mycoplasma-like Organism. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4824.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuske C. R., Kirkpatrick B. C. Identification and characterization of plasmids from the western aster yellows mycoplasmalike organism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1628–1633. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1628-1633.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. M., Davis R. E., Dewitt N. D. Nonradioactive screening method for isolation of disease-specific probes to diagnose plant diseases caused by mycoplasmalike organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1471–1475. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1471-1475.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S., Warner B. D., Running J. A., Stempien M., Clyne J., Horn T. A comparison of non-radioisotopic hybridization assay methods using fluorescent, chemiluminescent and enzyme labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4937–4956. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]