Abstract
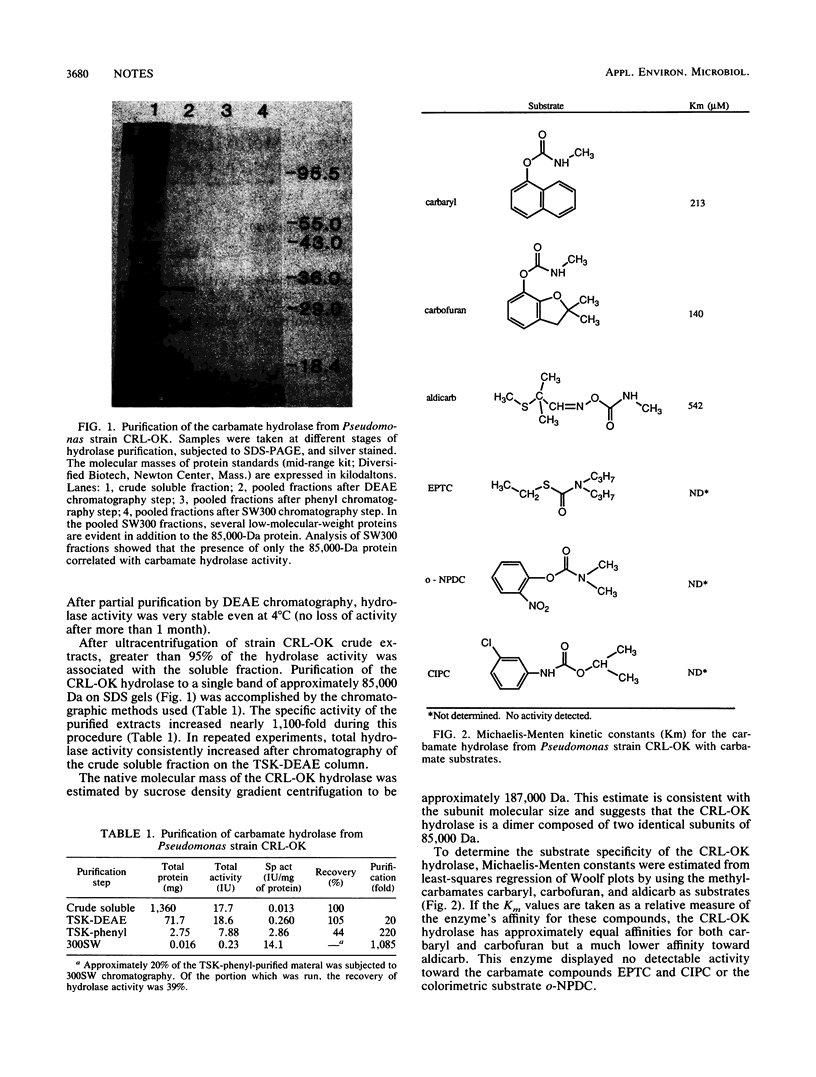
A unique cytosolic enzyme that hydrolyzes the carbamate linkage of the insecticide carbaryl (1-naphthyl N-methylcarbamate) was purified from extracts of Pseudomonas sp. strain CRL-OK. Substrates of the hydrolase include the N-methylcarbamate pesticides carbofuran and aldicarb but not the phenylcarbamate isopropyl m-chlorocarbanilate, the thiocarbamate S-ethyl N,N-dipropylthiocarbamate, or the dimethylcarbamate o-nitrophenyldimethylcarbamate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad N., Walgenbach D. D., Sutter G. R. Degradation rates of technical carbofuran and a granular formulation in four soils with known insecticide use history. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Nov;23(4-5):572–574. doi: 10.1007/BF01770005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapalamadugu S., Chaudhry G. R. Hydrolysis of carbaryl by a Pseudomonas sp. and construction of a microbial consortium that completely metabolizes carbaryl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):744–750. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.744-750.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Ali A. N. Bacterial metabolism of carbofuran. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1414-1419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsot A., Maddox J. V., Bruce W. Enhanced microbial degradation of carbofuran in soils with histories of Furadan use. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1981 Jun;26(6):781–788. doi: 10.1007/BF01622171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin M. J., Day M. J. The metabolism of carbaryl by three bacterial isolates, Pseudomonas spp. (NCIB 12042 & 12043) and Rhodococcus sp. (NCIB 12038) from garden soil. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;60(3):233–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb01078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulbry W. W., Karns J. S. Purification and characterization of three parathion hydrolases from gram-negative bacterial strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.289-293.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez L. D., Dorough H. W. Degradation of carbaryl by soil microorganisms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977;6(1):47–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02097748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam A. C., Behki R. M., Khan S. U. Isolation and characterization of an s-ethyl-N,N-dipropylthiocarbamate-degrading Arthrobacter strain and evidence for plasmid-associated s-ethyl-N,N-dipropylthiocarbamate degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1088-1093.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek P. H., Karns J. S. Cloning of a carbofuran hydrolase gene from Achromobacter sp. strain WM111 and its expression in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4038–4044. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4038-4044.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]