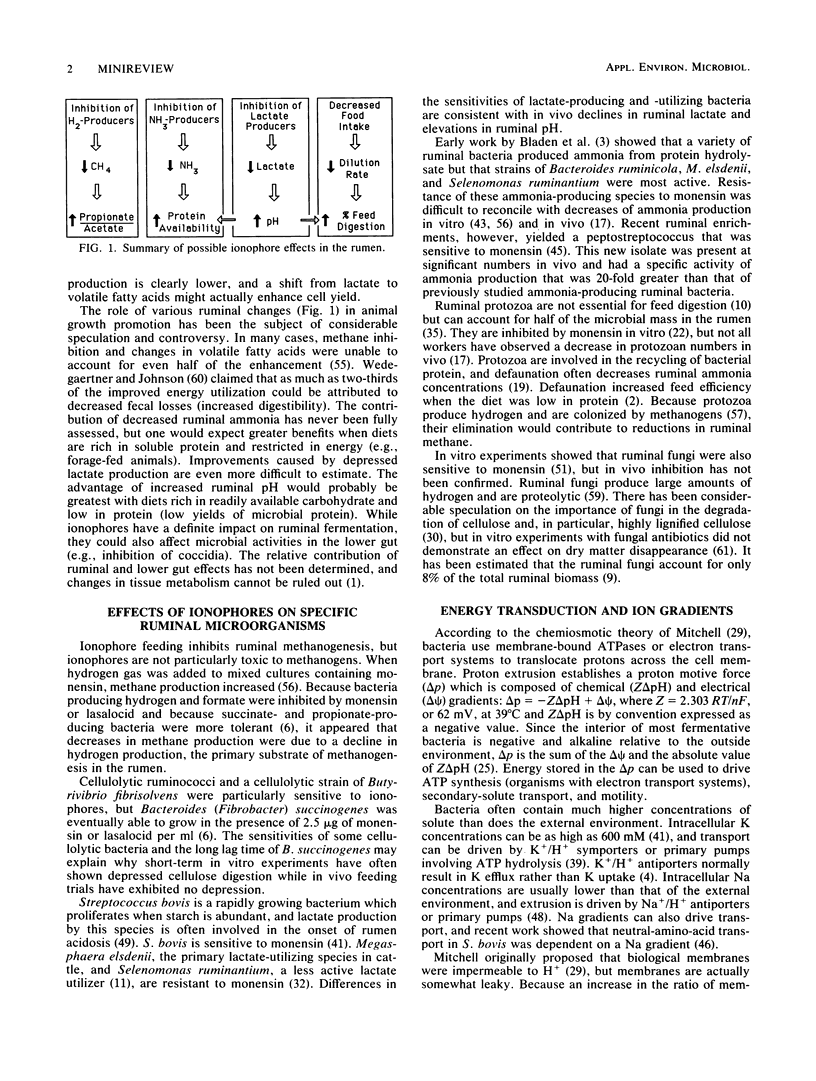
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergen W. G., Bates D. B. Ionophores: their effect on production efficiency and mode of action. J Anim Sci. 1984 Jun;58(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.2527/jas1984.5861465x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird S. H., Leng R. A. The effects of defaunation of the rumen on the growth of cattle on low-protein high-energy diets. Br J Nutr. 1978 Jul;40(1):163–167. doi: 10.1079/bjn19780108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Bryant M. P., Doetsch R. N. A Study of Bacterial Species from the Rumen Which Produce Ammonia from Protein Hydrolyzate. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.175-180.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Mitchell W. J., Hamilton W. A. Quantitative analysis of proton-linked transport systems. The lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):687–696. doi: 10.1042/bj1820687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Wolin M. J. Effect of monensin and lasalocid-sodium on the growth of methanogenic and rumen saccharolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Ultrastructure of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens: a gram-positive bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1506-1512.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Ball P. Transport of antibiotics into bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1982;23:183–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. S. Rumen ciliate protozoa. Adv Parasitol. 1980;18:121–173. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counotte G. H., Prins R. A., Janssen R. H., Debie M. J. Role of Megasphaera elsdenii in the Fermentation of dl-[2-C]lactate in the Rumen of Dairy Cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Oct;42(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.4.649-655.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crielaard W., Driessen A. J., Molenaar D., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Light-driven amino acid uptake in Streptococcus cremoris or Clostridium acetobutylicum membrane vesicles fused with liposomes containing bacterial reaction centers. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1820–1824. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1820-1824.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson K. A., Boling J. A. Effects of potassium ion concentrations on the antimicrobial activities of ionophores against ruminal anaerobes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2363–2367. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2363-2367.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson K. A., Boling J. A. Monensin-resistant bacteria in the rumens of calves on monensin-containing and unmedicated diets. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):160–164. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.160-164.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. M., Nagaraja T. G., Bartley E. E. Effects of lasalocid or monensin on lactate-producing or -using rumen bacteria. J Anim Sci. 1981 Feb;52(2):418–426. doi: 10.2527/jas1981.522418x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis S. M., Nagaraja T. G., Dayton A. D. Effect of lasalocid, monensin and thiopeptin on rumen protozoa. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Sep;41(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donius D. A., Simpson M. E., Marsh P. B. Effect of monensin fed with forage on digestion and the ruminal ecosystem of steers. J Anim Sci. 1976 Jan;42(1):229–234. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.421229x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eadie J. M., Gill J. C. The effect of the absence of rumen ciliate protozoa on growing lambs fed on a roughage-concentrate diet. Br J Nutr. 1971 Sep;26(2):155–167. doi: 10.1079/bjn19710022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Arents J. C., Scholte B. J., Westerhoff H. V. Bacteriorhodopsin in liposomes. II. Experimental evidence in support of a theoretical model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 11;547(3):561–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino T., Russell J. B. Relative contributions of ruminal bacteria and protozoa to the degradation of protein in vitro. J Anim Sci. 1987 Jan;64(1):261–270. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.641261x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino Y., Minakami S., Murakami H. The comparison of Golgi subfractions isolated from mitochondrial fraction with those from microsomal fraction. Exp Cell Res. 1981 May;133(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Russell J. B. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation of hexoses by ruminal bacteria: evidence for the phosphotransferase transport system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1348–1352. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1348-1352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja T. G., Avery T. B., Bartley E. E., Roof S. K., Dayton A. D. Effect of lasalocid, monensin or thiopeptin on lactic acidosis in cattle. J Anim Sci. 1982 Mar;54(3):649–658. doi: 10.2527/jas1982.543649x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja T. G., Taylor M. B. Susceptibility and resistance of ruminal bacteria to antimicrobial feed additives. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1620–1625. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1620-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold C. J., Wallace R. J., Watt N. D., Richardson A. J. Effect of the novel ionophore tetronasin (ICI 139603) on ruminal microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):544–547. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.544-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of solute transport in streptococci by external and internal pH values. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):498–508. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.498-508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Recent advances in bacterial ion transport. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:263–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsey T. S. Monensin in cattle: introduction. J Anim Sci. 1984 Jun;58(6):1461–1464. doi: 10.2527/jas1984.5861461x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. A proposed mechanism of monensin action in inhibiting ruminal bacterial growth: effects on ion flux and protonmotive force. J Anim Sci. 1987 May;64(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6451519x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J., Chen G. J. Enrichment and isolation of a ruminal bacterium with a very high specific activity of ammonia production. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.872-877.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Sodium-dependent transport of neutral amino acids by whole cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus bovis, a ruminal bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3531–3536. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3531-3536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J. Effects of additives on in vitro ruminal fermentation: a comparison of monensin and bacitracin, another gram-positive antibiotic. J Anim Sci. 1988 Feb;66(2):552–558. doi: 10.2527/jas1988.662552x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelling G. T. Monensin mode of action in the rumen. J Anim Sci. 1984 Jun;58(6):1518–1527. doi: 10.2527/jas1984.5861518x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slyter L. L. Influence of acidosis on rumen function. J Anim Sci. 1976 Oct;43(4):910–929. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.434910x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. S. Factors affecting the cellulolytic activity of rumen contents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):497–502. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.497-502.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. A theoretical study on the amount of ATP required for synthesis of microbial cell material. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(3):545–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02578899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. W. A continuous culture study of an ATPase-negative mutant of Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jun 20;113(3):185–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00492023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. H., Owens F. N. Monensin supplementation and in vivo methane production by steers. J Anim Sci. 1981 Mar;52(3):628–634. doi: 10.2527/jas1981.523628x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nevel C. J., Demeyer D. I. Effect of monensin on rumen metabolism in vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Sep;34(3):251–257. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.3.251-257.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Hoppe W. F., Stumm C. K. Association of methanogenic bacteria with rumen ciliates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.608-612.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN M. J., MANNING G. B., NELSON W. O. Ammonium salts as a sole source of nitrogen for the growth of Streptococcus bovis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):147–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.147-147.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Cheng K. J., Czerkawski J. W. Effect of monensin on fermentation characteristics of the artificial rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):672–674. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.672-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner T. C., Johnson D. E. Monensin effects on digestibility, methanogenesis and heat increment of a cracked corn-silage diet fed to steers. J Anim Sci. 1983 Jul;57(1):168–177. doi: 10.2527/jas1983.571168x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windham W. R., Akin D. E. Rumen fungi and forage fiber degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):473–476. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.473-476.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



