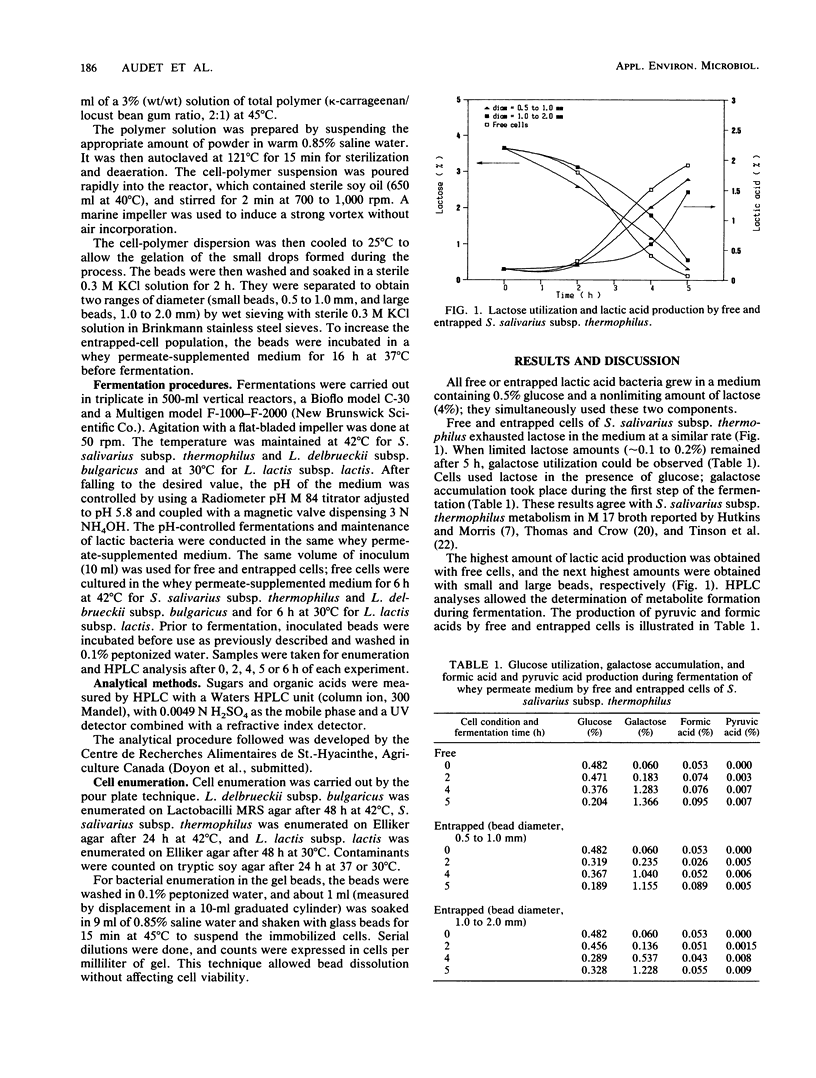
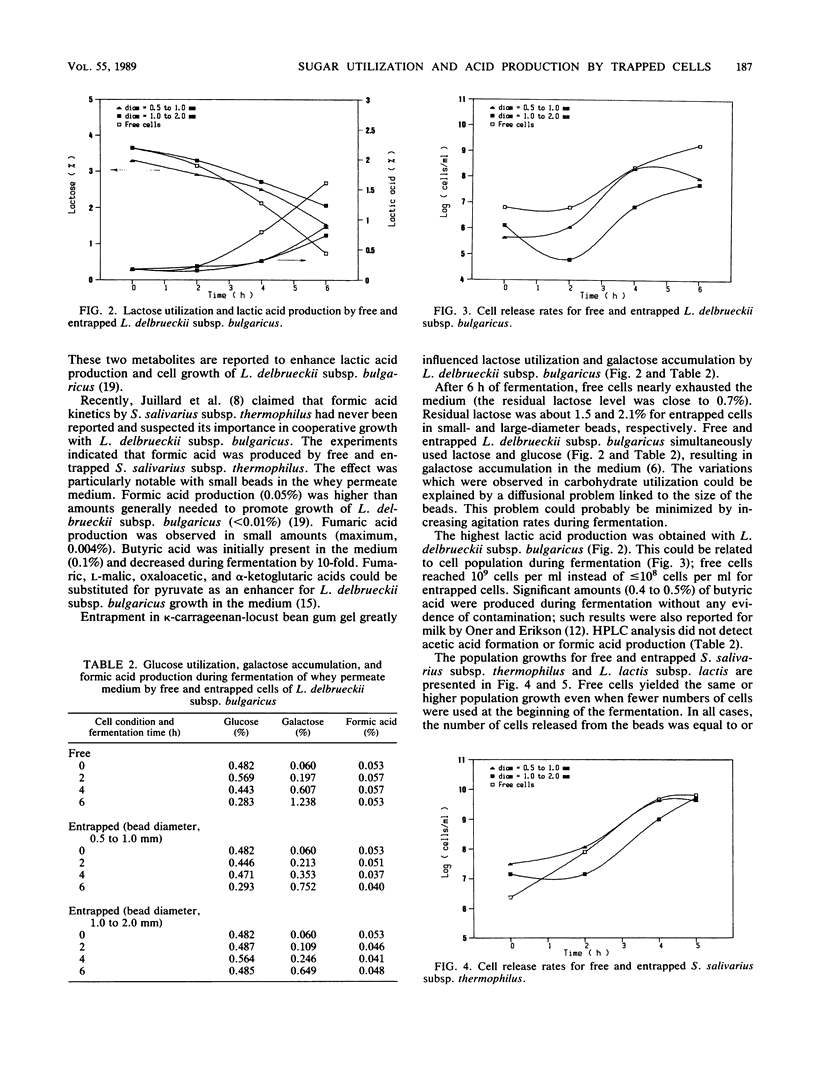
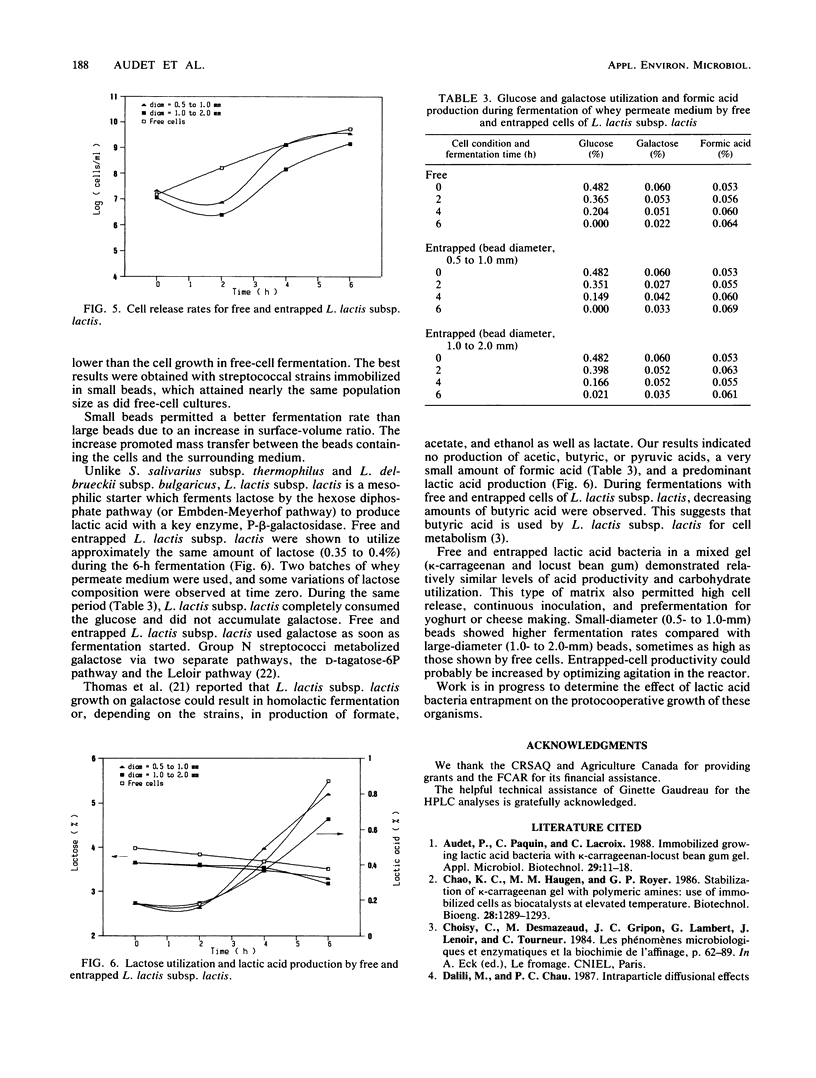
Abstract
Cells of Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis entrapped in k-carrageenan-locust bean gum gel performed similarly to free cells in the conversion of lactose to lactic acid. Bead diameter influenced the fermentation rate. Cells entrapped in smaller beads (0.5 to 1.0 mm) showed higher release rates, higher lactose, glucose, and formic acid utilization, higher galactose accumulation, and higher lactic acid production than did cells entrapped in larger beads (1.0 to 2.0 mm). Values for smaller beads were comparable with those for free cells. Immobilization affected the fermentation rate of lactic acid bacteria, especially Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Entrapped cells of L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus demonstrated a lower lactic acid production than did free cells in batch fermentation. The kinetics of the production of formic and pyruvic acids by L. lactis subsp. lactis and S. salivarius subsp. thermophilus are presented.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hickey M. W., Hillier A. J., Jago G. R. Transport and metabolism of lactose, glucose, and galactose in homofermentative lactobacilli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):825–831. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.825-831.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenson L. R., Klaenhammer T. R., Swaisgood H. E. Calcium alginate-immobilized cultures of lactic Streptococci are protected from bacteriophages. J Dairy Sci. 1987 Jun;70(6):1121–1127. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Turner K. W., Crow V. L. Galactose fermentation by Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris: pathways, products, and regulation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.672-682.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



