Abstract
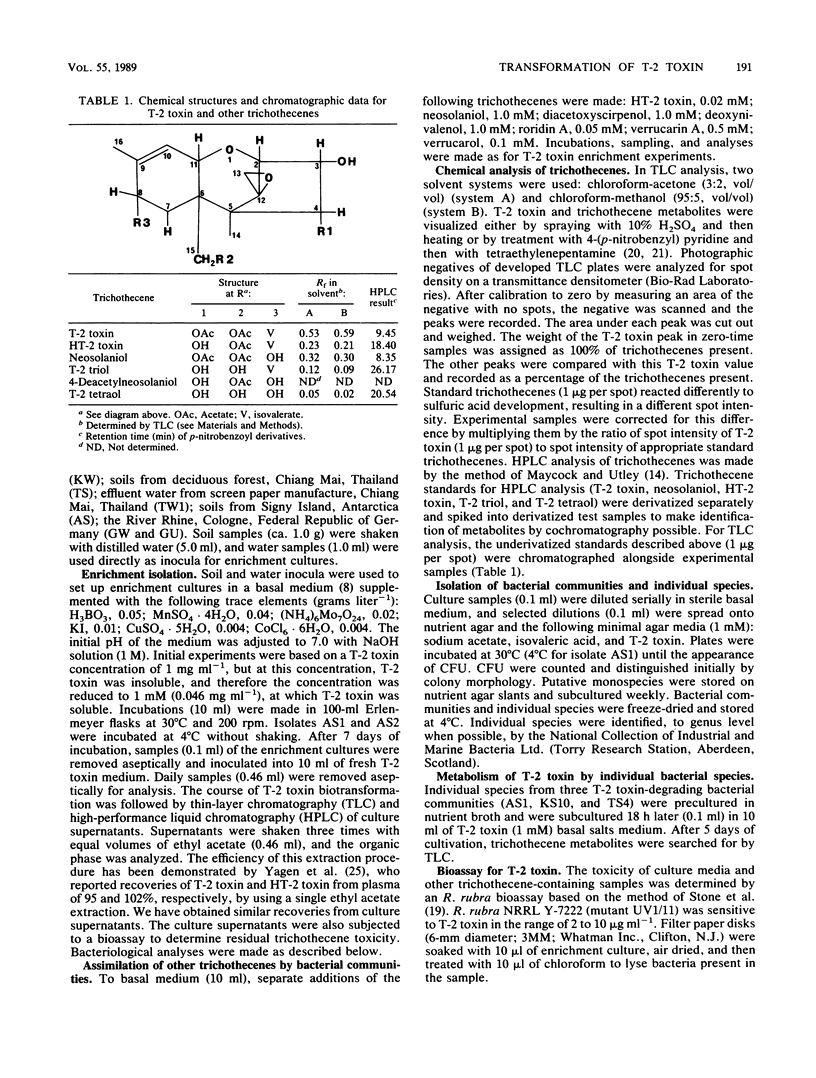
Bacterial communities isolated from 17 of 20 samples of soils and waters with widely diverse geographical origins utilized T-2 toxin as a sole source of carbon and energy for growth. These isolates readily detoxified T-2 toxin as assessed by a Rhodotorula rubra bioassay. The major degradation pathway of T-2 toxin in the majority of isolates involved side chain cleavage of acetyl moieties to produce HT-2 toxin and T-2 triol. A minor degradation pathway of T-2 toxin that involved conversion to neosolaniol and thence to 4-deacetyl neosolaniol was also detected. Some bacterial communities had the capacity to further degrade the T-2 triol or 4-deacetyl neosolaniol to T-2 tetraol. Two communities, TS4 and KS10, degraded the trichothecene nucleus within 24 to 48 h. These bacterial communities comprised 9 distinct species each. Community KS10 contained 3 primary transformers which were able to cleave acetate from T-2 toxin but which could not assimilate the side chain products, whereas community TS4 contained 3 primary transformers which were able to grow on the cleavage products, acetate and isovalerate. A third community, AS1, was much simpler in structure and contained only two bacterial species, one of which transformed T-2 toxin to T-2 triol in monoculture. In all cases, the complete communities were more active against T-2 toxin in terms of rates of degradation than any single bacterial component. Cometabolic interactions between species is suggested as a significant factor in T-2 toxin degradation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Claridge C. A., Schmitz H. Microbial and chemical transformations of some 12,13-epoxytrichothec-9,10-enes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):63–67. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.63-67.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. A., Kotsonis F. N. In vitro metabolism of T-2 toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):423–424. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.423-424.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. F., Mortimer P. H. The cytotoxicity of some transformation products of diacetoxyscirpenol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;18(6):1473–1478. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen H., Odden E., Lie O., Johnsen B. A., Fonnum F. Metabolism of T-2 toxin by rat liver carboxylesterase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 May 1;35(9):1469–1473. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling K. H., Pettersson H., Sandholm K., Olsen M. Metabolism of aflatoxin, ochratoxin, zearalenone, and three trichothecenes by intact rumen fluid, rumen protozoa, and rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1070–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1070-1073.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ito T., Ueno Y. Toxicological approaches to the metabolities of fusaria. XII. Fate and distribution of T-2 toxin in mice. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Oct;48(5):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maycock R., Utley D. Analysis of some trichothecene mycotoxins by liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1985 Nov 22;347(3):429–433. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)95518-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirocha C. J., Pathre S. V., Schauerhamer B., Christensen C. M. Natural occurrence of Fusarium toxins in feedstuff. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.553-556.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Ishii K., Ueno Y. Metabolism of trichothecene mycotoxins. I. Microsomal deacetylation of T-2 toxin in animal tissues. J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1591–1598. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly L. I., Hargreaves M. H. Two unusual budding bacteria isolated from a swimming pool. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;56(3):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takitani S., Asabe Y., Kato T., Suzuki M., Ueno Y. Spectrodensitometric determination of trichothecene mycotoxins with 4-(p-nitrobenzyl)pyridine on silica gel thin-layer chromatograms. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 21;172:335–342. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)90970-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Nakayama K., Ishii K., Tashiro F., Minoda Y., Omori T., Komagata K. Metabolism of T-2 toxin in Curtobacterium sp. strain 114-2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.120-127.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visconti A., Mirocha C. J. Identification of various T-2 toxin metabolites in chicken excreta and tissues. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1246–1250. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1246-1250.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake K., Mackie R. I., Dutton M. F. T-2 toxin metabolism by ruminal bacteria and its effect on their growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):587–592. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.587-592.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagen B., Bialer M., Sintov A. Gas chromatographic assay with pharmacokinetic applications for monitoring T-2 and HT-2 toxins in plasma. J Chromatogr. 1985 Sep 13;343(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Morooka N. Biological modification of trichothecene mycotoxins: acetylation and deacetylation of deoxynivalenols by Fusarium spp. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):54–58. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.54-58.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Onomoto C., Morooka N. Microbial acetyl conjugation of T-2 toxin and its derivatives. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):962–966. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.962-966.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Sakamoto T., Okamoto K. In vitro formation of 3'-hydroxy T-2 and 3'-hydroxy HT-2 toxins from T-2 toxin by liver homogenates from mice and monkeys. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):130–134. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.130-134.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Swanson S. P., Mirocha C. J. In vitro metabolism of T-2 toxin in rats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):901–906. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.901-906.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



