Abstract
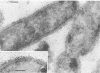
Xanthomonas maltophilia (later synonym of Pseudomonas maltophilia), an ubiquitous species, is known to show proteolytic and lipolytic activities. A cell-bound esterase which hydrolyzes beta-naphthyl acetate during growth has been extracted from a strain isolated from soil. Because of its strongly hydrophobic character, the enzyme could be efficiently solubilized only by Triton X-100. This nonionic detergent must be added in polyacrylamide gels to permit migration. Polyclonal rabbit antibodies raised against the Triton-soluble esterase complex were used to localize the enzyme at the ultrastructural level. Electron microscopy of cell sections of this organism and immunogold labeling demonstrated that the enzyme was located on the outer membrane. Such an envelope-bound esterase may produce assimilable substrates for X. maltophilia which can grow in various environments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boethling R. S. Purification and properties of a serine protease from Pseudomonas matophilia. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.933-941.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuil C., Kushner D. J. Lipase and esterase formation by psychrophilic and mesophilic Acinetobacter species. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):423–433. doi: 10.1139/m75-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debette J., Blondeau R. Caractérisation de bactéries telluriques assimilables à Pseudomonas maltophilia. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1123–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debette J., Blondeau R. Présence de Pseudomonas maltophilia dans la rhizosphère de quelques plantes cultivées. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):460–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debette J., Losfeld J., Blondeau R. Taxonomie numérique de bactéries telluriques non fermentantes à Gram-négatif. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Sep;21(9):1322–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P. Distinctive electrophoretic patterns of esterases from Klebsiella pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, Enterobacter aerogenes and E. gergoviae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):483–491. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Comparative esterase electrophoretic polymorphism of Escherichia coli isolates obtained from animal and human sources. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1843–1851. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Distinctive electrophoretic and isoelectric focusing patterns of esterases from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1471–1480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Brands R., Burke B., Louvard D., Warren G. Viral membrane proteins acquire galactose in trans Golgi cisternae during intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):781–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Klingler W. G., Ekel T. M., Montague P. M. Molecular weight estimation of Triton X-100 solubilized proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:113–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90512-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Lapage S. P., Easterling B. G. Distribution in clinical material and identification of Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):66–72. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouker G., Jaeger K. E. Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):211–213. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.211-213.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE S. H., MELNICK P. J., WEIMER H. E. A species comparison of serum proteins and enzymes by starch gel electrophoresis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:572–575. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. C., Fryer T. F., Reiter B. The production and characterization of lipases from a micrococcus and a pseudomonad. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Sep;48(3):401–418. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-3-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H., Bishop C. W., Blech J. E. Localization of proteolytic activity in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.574-583.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Nakaike S., Tamori Y., Nojima S. Detergent-resistant phospholipase A of Escherichia coli K-12. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):115–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Sjöberg L., Wadström T., Wretlind B. Characterization of three Aeromonas and nine pseudomonas species by extracellular enzymes and haemolysins. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(2):79–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02121748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M., Davis G. H. Enzymatic profile of Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):417–421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.417-421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa I., Shiga S., Kageyama M. An esterase on the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the hydrolysis of long chain acyl esters. J Biochem. 1979 Sep;86(3):643–656. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Munson R. Separation of the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M. Identification and localization of two membrane-bound esterases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.6-14.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Contribution of immunogold labelling to study of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Sep;4(9):270–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabtai Y., Gutnick D. L. Exocellular esterase and emulsan release from the cell surface of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1176–1181. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1176-1181.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
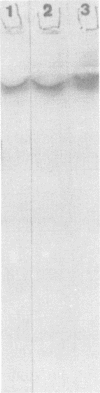
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Present state of immunocryoultramicrotomy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jan;31(1A):164–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIEL J. [Characterization of cholinesterase and other carboxylic esterases after electrophoresis and immunoelectrophoresis on agar. I. Application to the study of esterases of normal human serum]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Jul;101:104–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]