Abstract
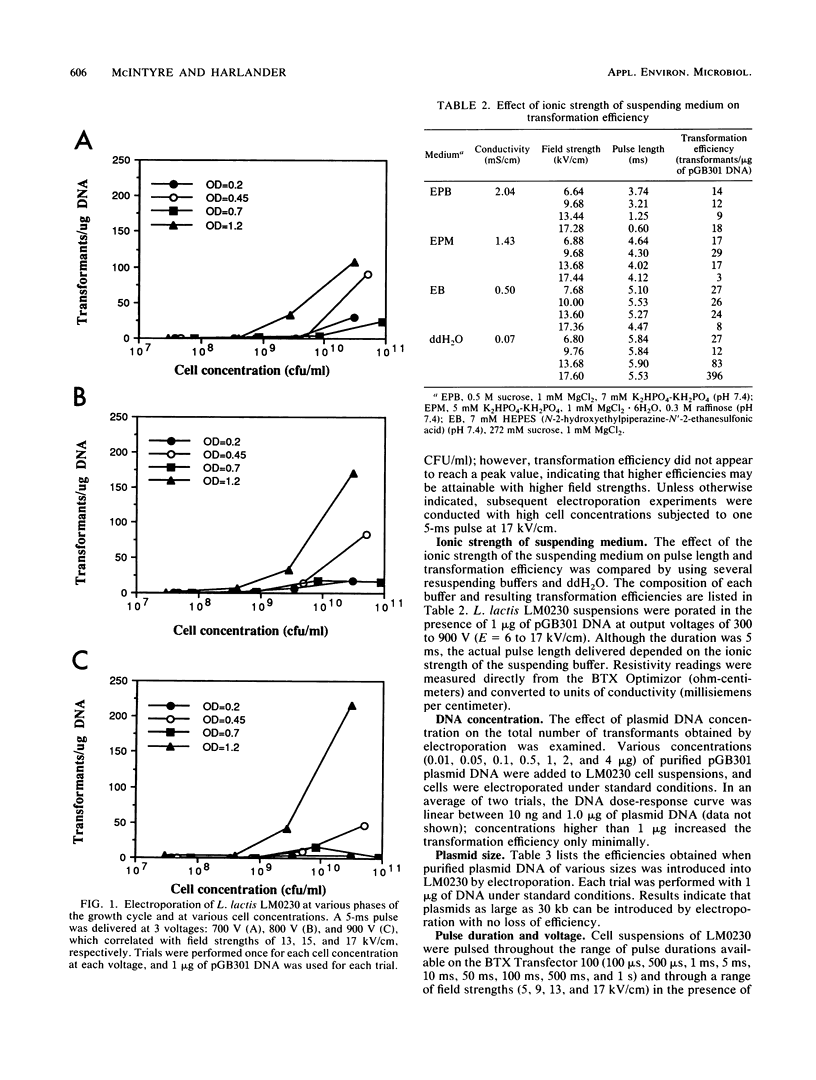
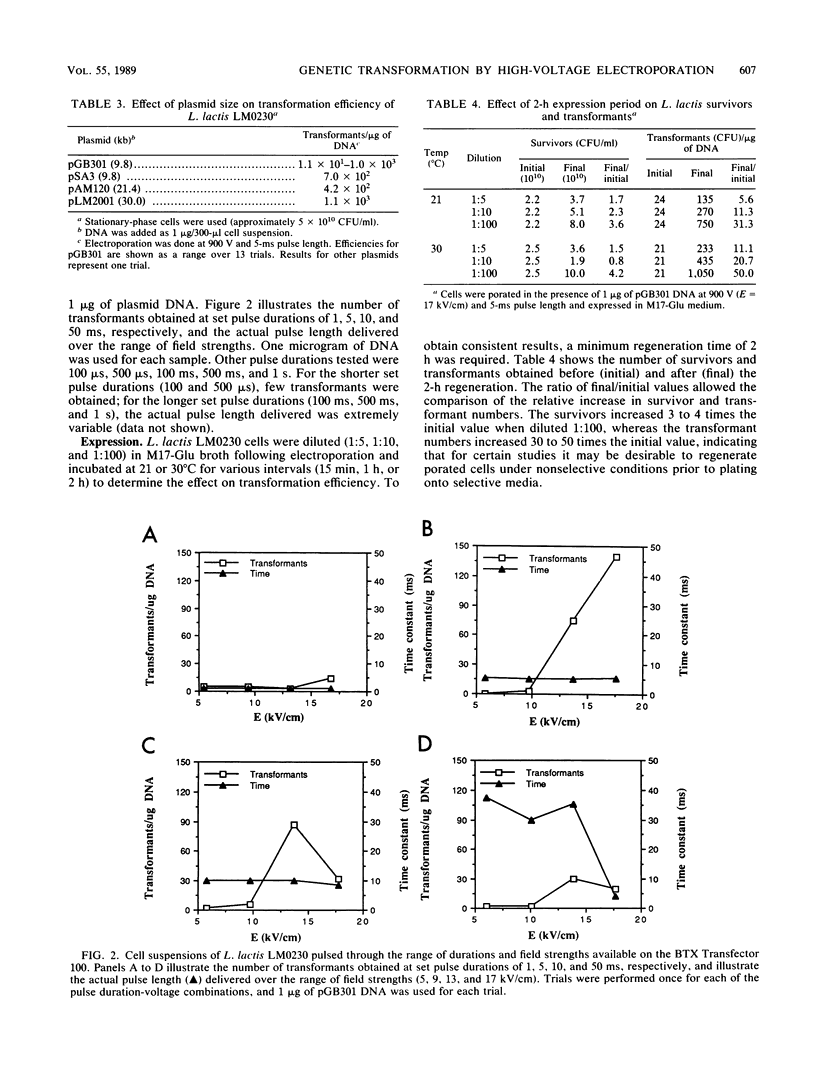
To apply recombinant DNA techniques for genetic manipulation of the industrially important lactococci, an efficient and reliable high-frequency transformation system must be available. High-voltage electric pulses have been demonstrated to enhance uptake of DNA into protoplasts and intact cells of numerous gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. The objective of this study was to develop a system for electroporating intact cells of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis LM0230 (previously designated Streptococcus lactis LM0230) with a commercially available electroporation unit (BTX Transfector 100; BTX, Inc., San Diego, Calif.). Parameters which influenced the efficiency of transformation included growth phase and final concentration of cells, ionic strength of the suspending medium, concentration of plasmid DNA, and the amplitude and duration of the pulse. Washed suspensions of intact cells suspended in deionized distilled water were subjected to one high-voltage electric pulse varying in voltage (300 to 900 V corresponding to field strengths of 5 to 17 kV/cm) and duration (100 microseconds to 1 s). Transformation efficiencies of 10(3) transformants per microgram of DNA were obtained when dense suspensions (final concentration, 5 x 10(10) CFU/ml) of stationary-phase cells were subjected to one pulse with a peak voltage of 900 V (field strength, 17 kV/cm) and a pulse duration of 5 ms in the presence of plasmid DNA. Dilution of porated cells in broth medium followed by an expression period of 2 h at 30 degrees C was beneficial in enhancing transformation efficiencies. Plasmids ranging in size from 9.8 to 30.0 kilobase pairs could be transformed by this procedure.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Gilmore M. S., Ferretti J. J. Plasmid pGB301, a new multiple resistance streptococcal cloning vehicle and its use in cloning of a gentamicin/kanamycin resistance determinant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):414–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00293929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin N. M., Hanawalt P. C. High-efficiency transformation of bacterial cells by electroporation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2796–2801. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2796-2801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao M. L., Ferretti J. J. Streptococcus-Escherichia coli shuttle vector pSA3 and its use in the cloning of streptococcal genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.115-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler S., Wirth R. Transformation of bacteria with plasmid DNA by electroporation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Apr;170(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5824–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Regeneration of insertionally inactivated streptococcal DNA fragments after excision of transposon Tn916 in Escherichia coli: strategy for targeting and cloning of genes from gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):214–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.214-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Transformation of Streptococcus lactis Protoplasts by Plasmid DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1213–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1213-1215.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercenier A., Chassy B. M. Strategies for the development of bacterial transformation systems. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Dower W. J., Tompkins L. S. High-voltage electroporation of bacteria: genetic transformation of Campylobacter jejuni with plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszkowski J., Shillito R. D., Saul M., Mandák V., Hohn T., Hohn B., Potrykus I. Direct gene transfer to plants. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2717–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell Ian B., Achen Marc G., Hillier Alan J., Davidson Barrie E. A Simple and Rapid Method for Genetic Transformation of Lactic Streptococci by Electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):655–660. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.655-660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Nicholson M. A. A method for genetic transformation of nonprotoplasted Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1730–1736. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1730-1736.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Zimmermann U. Giant human erythrocytes by electric-field-induced cell-to-cell fusion. Naturwissenschaften. 1981 Jan;68(1):45–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01047168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somkuti G. A., Steinberg D. H. Genetic transformation of Streptococcus thermophilus by electroporation. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopper H., Jones H., Zimmermann U. Large scale transfection of mouse L-cells by electropermeabilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. DNA transfection of Escherichia coli by electroporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 31;949(3):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbib D., Amalric F., Teissié J. Electric field mediated transformation: isolation and characterization of a TK+ subclone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91935-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




