Abstract
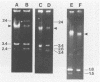
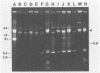
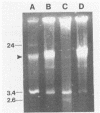
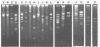
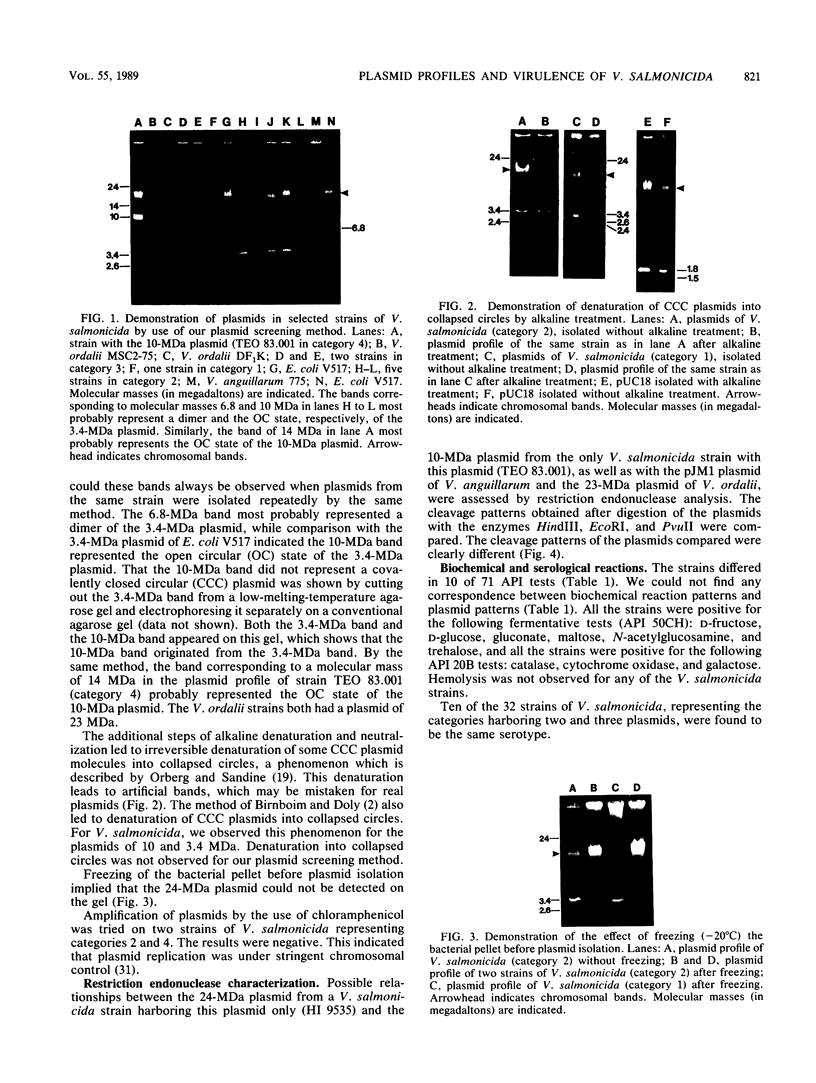
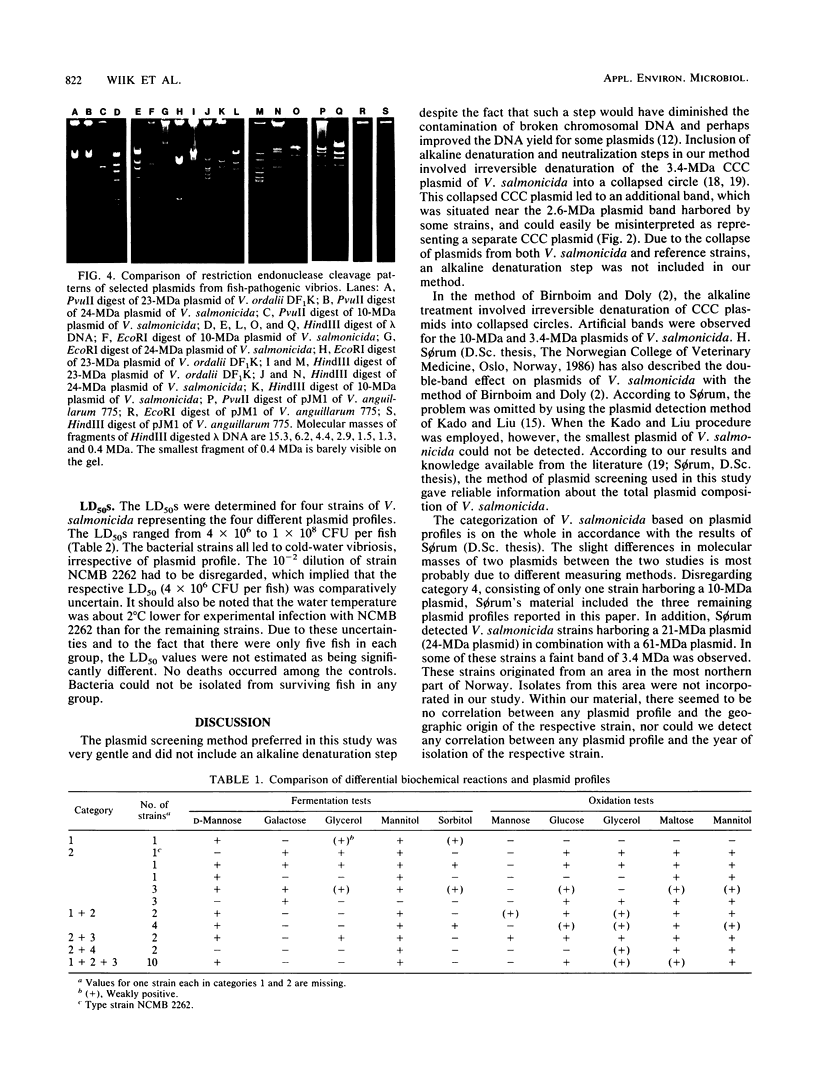
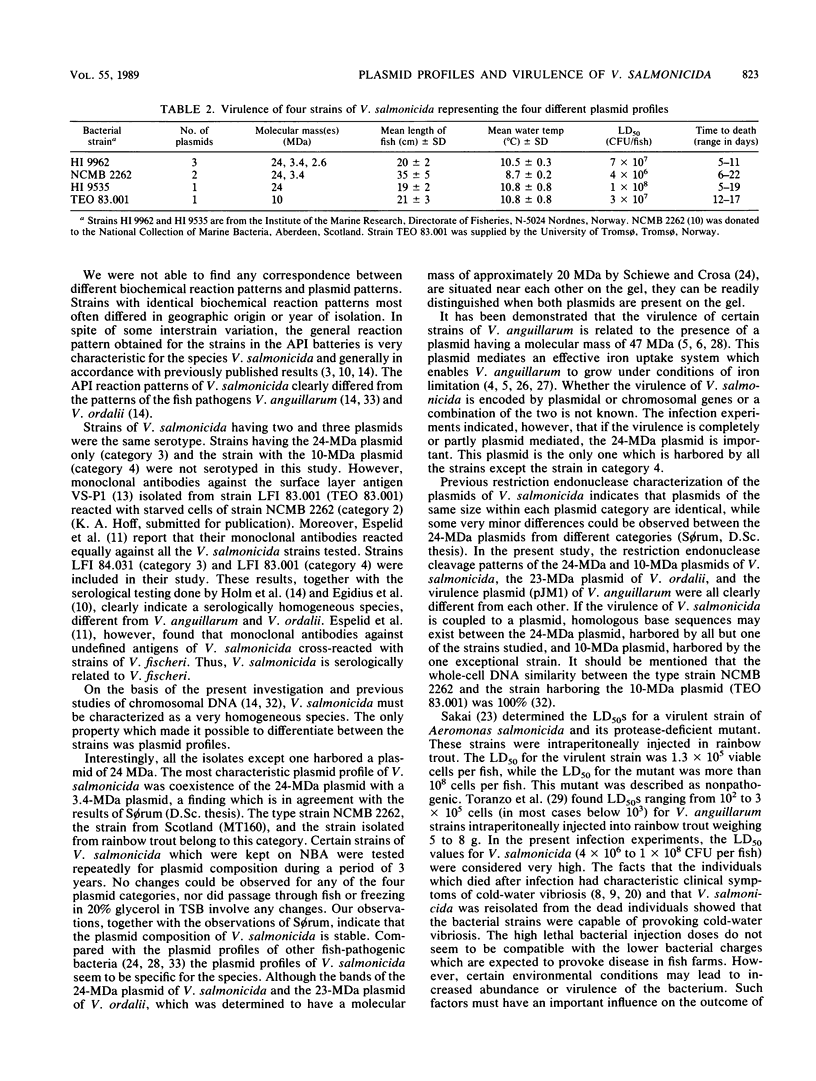
Strains of Vibrio salmonicida isolated from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) suffering from cold-water vibriosis could be divided on the basis of plasmid profiles into four different categories. Of 32 strains, 19% harbored three plasmids of 24, 3.4, and 26 megadaltons (MDa), 69% harbored the 24- and 3.4-MDa plasmids but not the 2.6-MDA plasmid, and 9% harbored only the 24-MDA plasmid. The fourth category, which consisted of only one strain, harbored a plasmid of 10 MDa. In spite of different plasmid patterns, the strains of V. salmonicida were very similar with respect to biochemical reactions. The one-third of the V. salmonicida strains which were serotyped were of the same type. The 50% lethal doses, which were determined by intraperitoneal injection, ranged from 4 x 106 to 1 x 108 CFU per fish.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Hodges L. L., Schiewe M. H. Curing of a plasmid is correlated with an attenuation of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.897-902.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Schiewe M. H., Falkow S. Evidence for plasmid contribution to the virulence of fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):509–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.509-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Möller A., Valle R. P., Nordheim A., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Antibody recognition of Z-DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):155–162. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Samulski R. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Rapid purification of covalently closed circular DNAs of bacterial plasmids and animal tumor viruses. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orberg P. K., Sandine W. E. Microscale method for rapid isolation of covalently closed circular plasmid DNA from group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.677-680.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1177/003591574203600109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Significance of Extracellular Protease for Growth of a Heterotrophic Bacterium, Aeromonas salmonicida. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1031–1037. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1031-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søorum H., Poppe T. T., Olsvik O. Plasmids in Vibrio salmonicida isolated from salmonids with hemorrhagic syndrome (Hitra disease). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1679–1683. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1679-1683.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Actis L. A., Crosa J. H. Genetic analysis of the iron uptake region of the Vibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1: molecular cloning of genetic determinants encoding a novel trans activator of siderophore biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1913–1919. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1913-1919.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Actis L. A., Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Crosa J. H. Plasmids mediating iron uptake in Vibrio anguillarum strains isolated from turbot in Spain. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1989–1997. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M. Characterization of plasmids in bacterial fish pathogen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.184-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik R., Hoff K. A., Andersen K., Daae F. L. Relationships between plasmids and phenotypes of presumptive strains of Vibrio anguillarum isolated from different fish species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):826–831. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.826-831.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]