Abstract
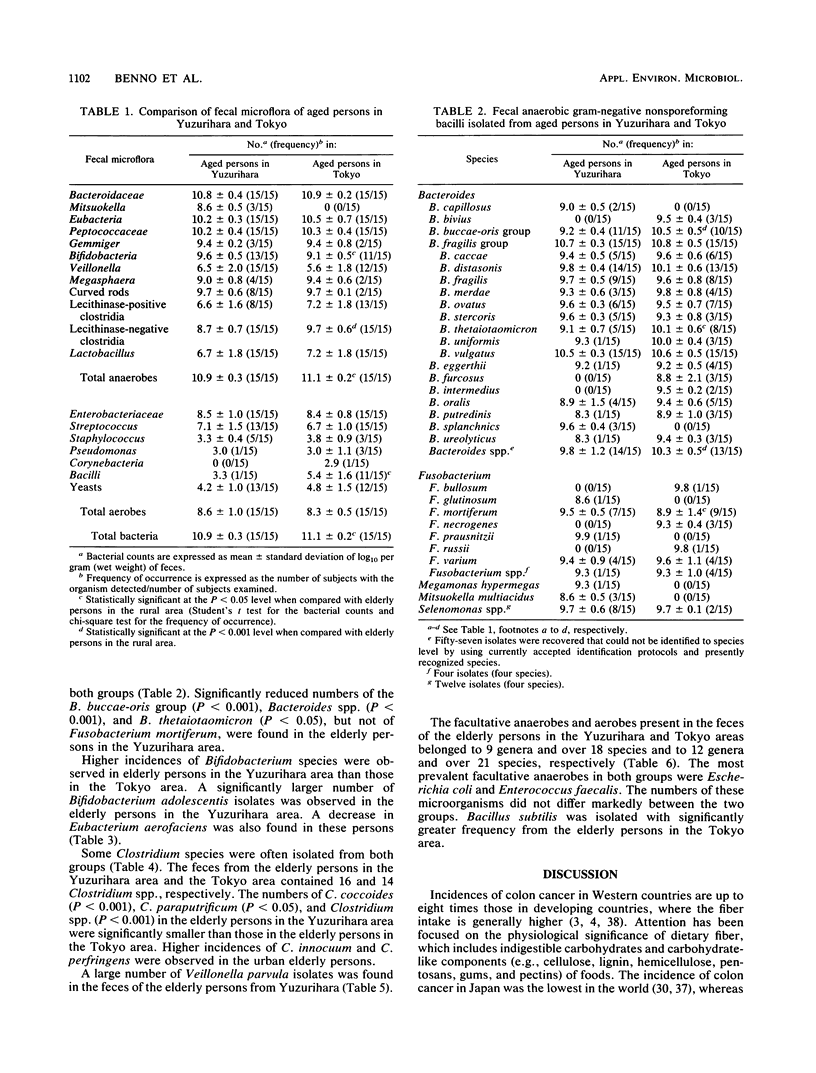
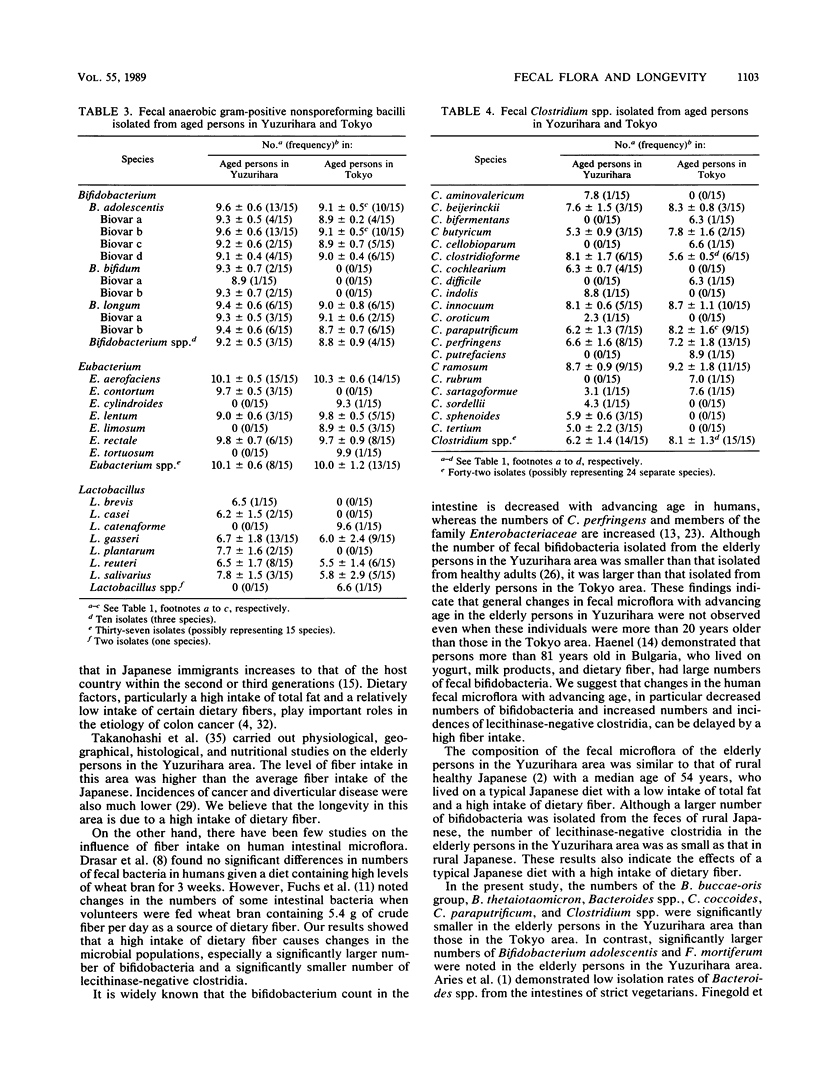
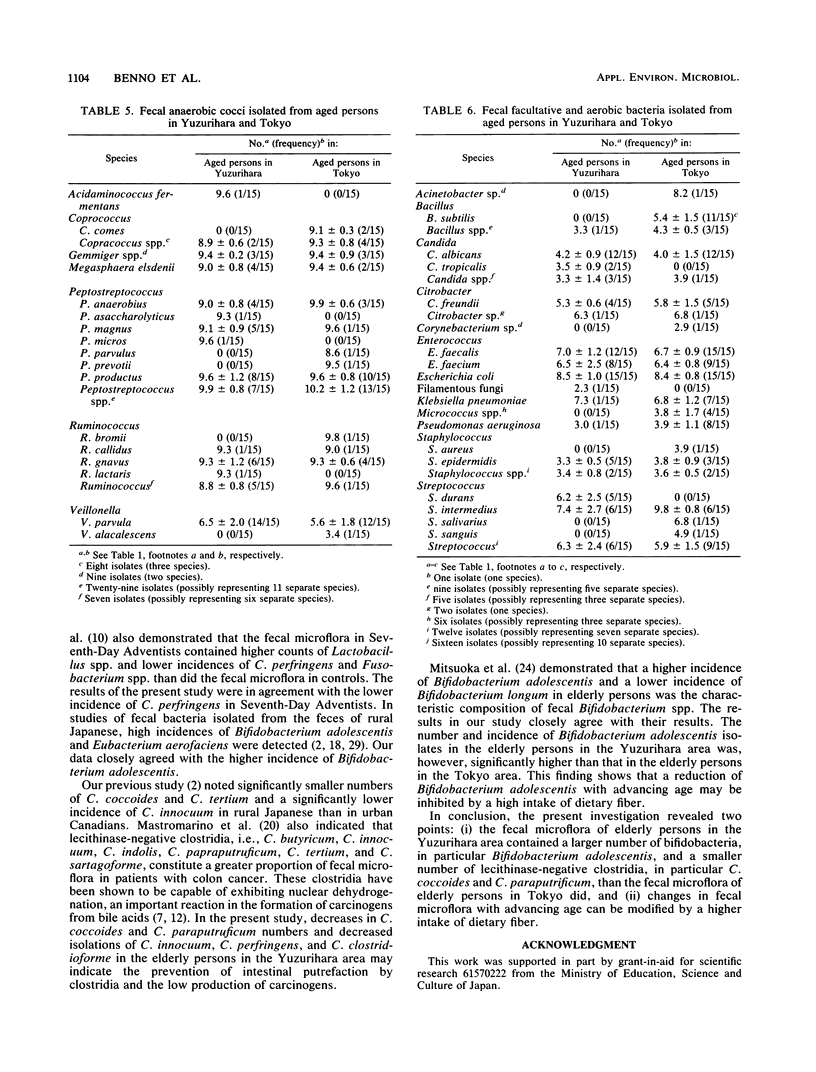
The Fecal microflora of 15 healthy elderly persons with a median age of 84 years in a rural area whose inhabitants tend to be long-lived (Yuzurihara-area, Uenohara, Yamanashi Prefecture) was compared with the microflora of individuals with a median age of 68 years in an urban area (Tokyo). The diet of the elderly persons in the Yuzurihara area is characterized by a high intake of dietary fiber. Total numbers of anaerobic bacteria were significantly smaller in the elderly persons in the Yuzurihara area than those in the Tokyo area. A significantly large number of bifidobacteria, but not of lecithinase-negative clostridia, was observed in the elderly persons in the Yuzurihara area. Large numbers and high incidences of bacilli and lecithinase-positive clostridia (mainly Clostridium perfringens) were found in the elderly persons in the Tokyo area. Twenty-five genera and over 81 species were isolated from the elderly persons in the Yuzurihara area, and 25 genera and over 92 species were isolated from the elderly persons in the Tokyo area. Furthermore, significantly larger numbers of Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Fusobacterium mortiferum strains were found in the Yuzurihara group, but significant reductions in the Bacteroides buccae-oris group, B. thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides spp., C. coccoides, C. paraputrificum, and Clostridium spp. were observed in the same group. A significantly higher isolation rate of Bacillus subtilis was observed in the elderly persons in the Tokyo area. The difference in the fecal microflora between elderly persons in Yuzurihara and those in the Tokyo area might be due to a difference in the intake of dietary fiber.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aries V. C., Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Ellis F. R. The effect of a strict vegetarian diet on the faecal flora and faecal steroid concentration. J Pathol. 1971 Jan;103(1):54–56. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benno Y., Suzuki K., Suzuki K., Narisawa K., Bruce W. R., Mitsuoka T. Comparison of the fecal microflora in rural Japanese and urban Canadians. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(6):521–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P. Epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1971 Jul;28(1):3–13. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197107)28:1<3::aid-cncr2820280104>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H. Microbial digestion of complex carbohydrates in man. Proc Nutr Soc. 1984 Jan;43(1):35–44. doi: 10.1079/pns19840025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Jenkins D. J., Cummings J. H. The influence of a diet rich in wheat fibre on the human faecal flora. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):423–431. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L., Sugihara P. T., Elder H. A., Lehmann S. M., Phillips R. L. Fecal microbial flora in Seventh Day Adventist populations and control subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Nov;30(11):1781–1792. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.11.1781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H-M, Dorfman S., Floch M. H. The effect of dietary fiber supplementation in man. II. Alteration in fecal physiology and bacterial flora. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Dec;29(12):1443–1447. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.12.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard P., Fernandez F., West B., Hill M. J., Barnes P. The nuclear dehydrogenation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):429–435. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenszel W., Berg J. W., Segi M., Kurihara M., Locke F. B. Large-bowel cancer in Hawaiian Japanese. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Dec;51(6):1765–1779. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.6.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornhof H. J., Richardson N. J., Wall D. M., Moore W. E. Fecal bacteria in South African rural blacks and other population groups. Isr J Med Sci. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino A. J., Reddy B. S., Wynder E. L. Fecal profiles of anaerobic microflora of large bowel cancer patients and patients with nonhereditary large bowel polyps. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4458–4462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Hayakawa K., Kimura N. Die Faekalflora bei Menschen. II. Die Zusammensetzung der Bifidobakterienflora der verschiedenen Altersgruppen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974 Jun;226(4):469–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Morishita Y., Terada A., Yamamoto S. A simple method ("plate-in-bottle method") for the cultivation of fastidious anaerobes. Jpn J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;13(4):383–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1969.tb00482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Ohno K., Benno Y., Suzuki K., Namba K. Die Faekalflora bei Menschen. IV. Mitteilung: Vergleich des neu entwickelten Verfahrens mit dem bisherigen üblichen Verfahren zur Darmfloraanalyse. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Mar;234(2):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Sega T., Yamamoto S. Eine verbesserte Methodik der qualitativen und quantitativen Analyse der Darmflora von Menschen und Tieren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Mar;195(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T. Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die Bifidobakterien aus dem Verdauungstakt von Menschen und Tieren (Zugleich die Beschreibung von B, thermophilum nov. spec. und B. pseudolongum nov. spec) Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969 May;210(1):52–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T. Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die Laktobazillen aus den Faeces von Menschen, Schweinen und Hühnern. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969 May;210(1):32–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Some current concepts in intestinal bacteriology. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Oct;31(10 Suppl):S33–S42. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.10.S33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasaka T., Watanabe H., Yamagata S., Munakata A., Tajima T. Statistical analysis of diverticulosis of the colon. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1975 Mar;115(3):271–275. doi: 10.1620/tjem.115.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. A. Anaerobiosis with iron wool. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Feb;33(1):33–37. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Cohen L. A., McCoy G. D., Hill P., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Nutrition and its relationship to cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1980;32:237–345. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., West S. E., Vercellotti J. R., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucins and plant polysaccharides by anaerobic bacteria from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):529–533. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.529-533.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedekind K. J., Mansfield H. R., Montgomery L. Enumeration and isolation of cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic bacteria from human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1530–1535. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1530-1535.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Kajitani T., Ishikawa S., Dodo H., Takano A. Environmental factors of cancer of the colon and rectum. II. Japanese epidemiological data. Cancer. 1969 May;23(5):1210–1220. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196905)23:5<1210::aid-cncr2820230530>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Reddy B. S. Dietary fat and fiber and colon cancer. Semin Oncol. 1983 Sep;10(3):264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


