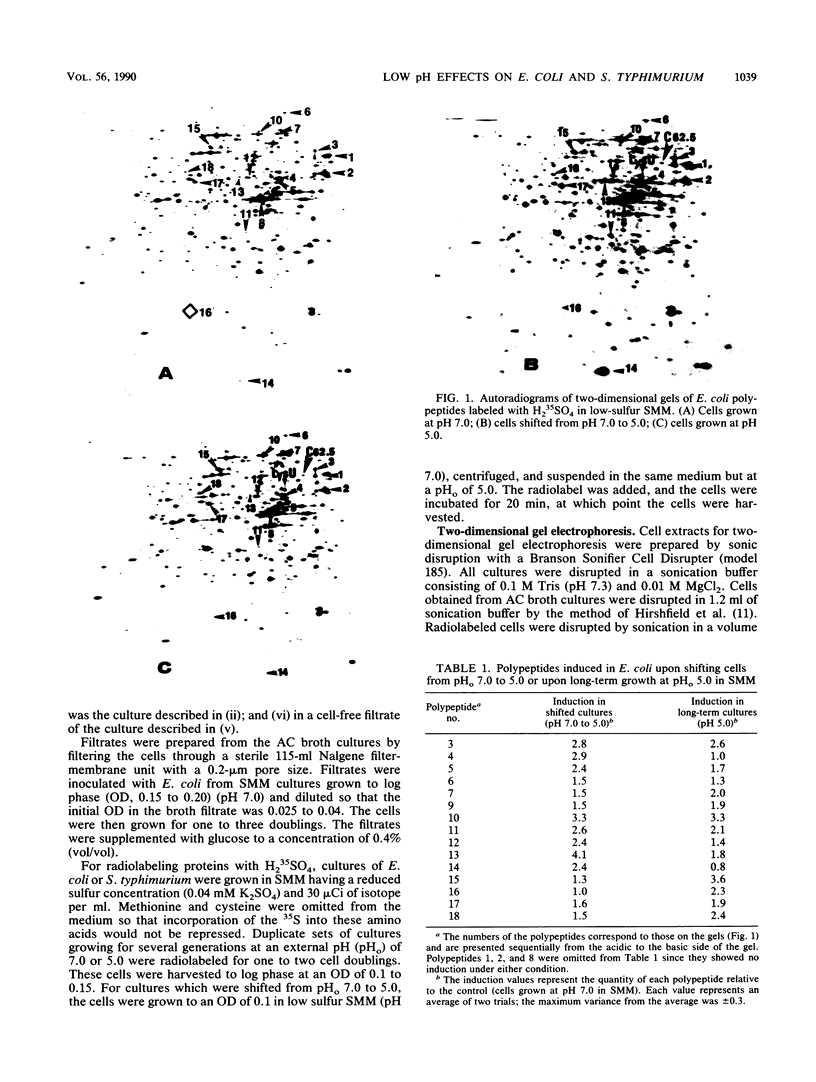
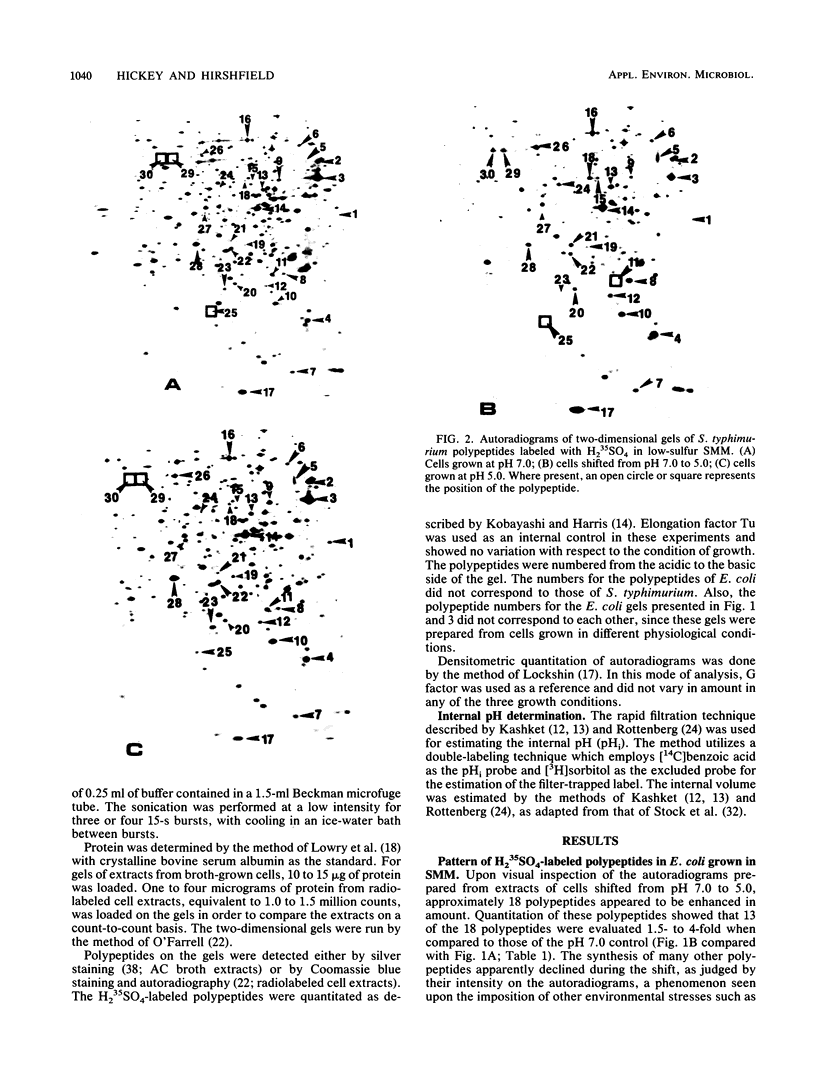
Abstract
Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium were grown in a supplemented minimal medium (SMM) at a pH of 7.0 or 5.0 or were shifted from pH 7.0 to 5.0. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of proteins labeled with H2(35)SO4 for 20 min during the shift showed that in E. coli, 13 polypeptides were elevated 1.5- to 4-fold, whereas in S. typhimurium, 19 polypeptides were increased 2- to 14-fold over the pH 7.0 control. Upon long-term growth at pH 5.0, almost double the number of polypeptides were elevated twofold or more in S. typhimurium compared with E. coli. In E. coli, there was no apparent induction of heat shock proteins upon growth at pH 5.0 in SMM. However, growth of E. coli in a complex broth to pH 5.0, or subsequent growth of fresh E. coli cells in the filtrate from this culture, showed that a subset of five polypeptides is uniquely induced by low pH. Two of these polypeptides, D60.5, the inducible lysyl-tRNA synthetase, and C62.5, are known heat shock proteins. Measurements of the internal pH (pHi) and growth rates of both organisms were made during growth in SMM at pH 7.0, pH 5.0, and upon the pH shift. The data show that the pHi of E. coli decreases more severely than that of S. typhimurium at an external pH of 5.0; the growth rate of E. coli is about one-half that of S. typhimurium at this pH, whereas the two organisms have the same growth rate at pH 7.0. The two-dimensional gel, growth, and pHi experiments collectively suggest that, at least in SMM, S. typhimurium is more adaptive to low-pH stress than is E. coli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. Quantitative measurements of the proton-motive force and its relation to steady state lactose accumulation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):573–581. doi: 10.1042/bj2000573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aliabadi Z., Park Y. K., Slonczewski J. L., Foster J. W. Novel regulatory loci controlling oxygen- and pH-regulated gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):842–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.842-851.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Clark M. A. Tetrathionate reduction and production of hydrogen sulfide from thiosulfate. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):192–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.192-205.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich R. V., Hirshfield I. N. Mapping of the constitutive lysyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5311–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5311-5313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F., Epps H. M. The effect of the pH of the medium during growth on the enzymic activities of bacteria (Escherichia coli and Micrococcus lysodeikticus) and the biological significance of the changes produced. Biochem J. 1942 Sep;36(7-9):600–618. doi: 10.1042/bj0360600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R. In situ bacterial metabolism and colon mutagens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:367–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshfield I. N., Tenreiro R., Vanbogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Escherichia coli K-12 lysyl-tRNA synthetase mutant with a novel reversion pattern. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):615–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.615-620.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Effects of aerobiosis and nitrogen source on the proton motive force in growing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):377–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.377-384.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The role of potassium transport in the generation of a pH gradient in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):691–698. doi: 10.1042/bj1980691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Vaughn V., Phillips T. A., Bloch P. L. Gene-protein index of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):231–284. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.231-284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond C. V., Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The effect of food preservatives on pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2845–2850. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Agmon V., Brandsma J., Cohen A., Friedman E., Padan E. Induction of SOS functions by alkaline intracellular pH in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):936–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.936-939.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J., Taylor B. L. Oxygen taxis and proton motive force in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10983–10988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Gonzalez T. N., Bartholomew F. M., Holt N. J. Mu d-directed lacZ fusions regulated by low pH in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3001–3006. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3001-3006.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Neidhardt F. C. Proteins induced by anaerobiosis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector M. P., Aliabadi Z., Gonzalez T., Foster J. W. Global control in Salmonella typhimurium: two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of starvation-, anaerobiosis-, and heat shock-inducible proteins. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):420–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.420-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglicht D., Padan E., Oppenheim A. B., Schuldiner S. An alkaline shift induces the heat shock response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):885–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.885-887.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Abston A. Accumulation and elimination of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium by hard clams in an in vitro system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):986–988. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.986-988.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Kelley P. M., Neidhardt F. C. Differential induction of heat shock, SOS, and oxidation stress regulons and accumulation of nucleotides in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.26-32.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]