Abstract
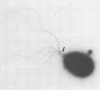
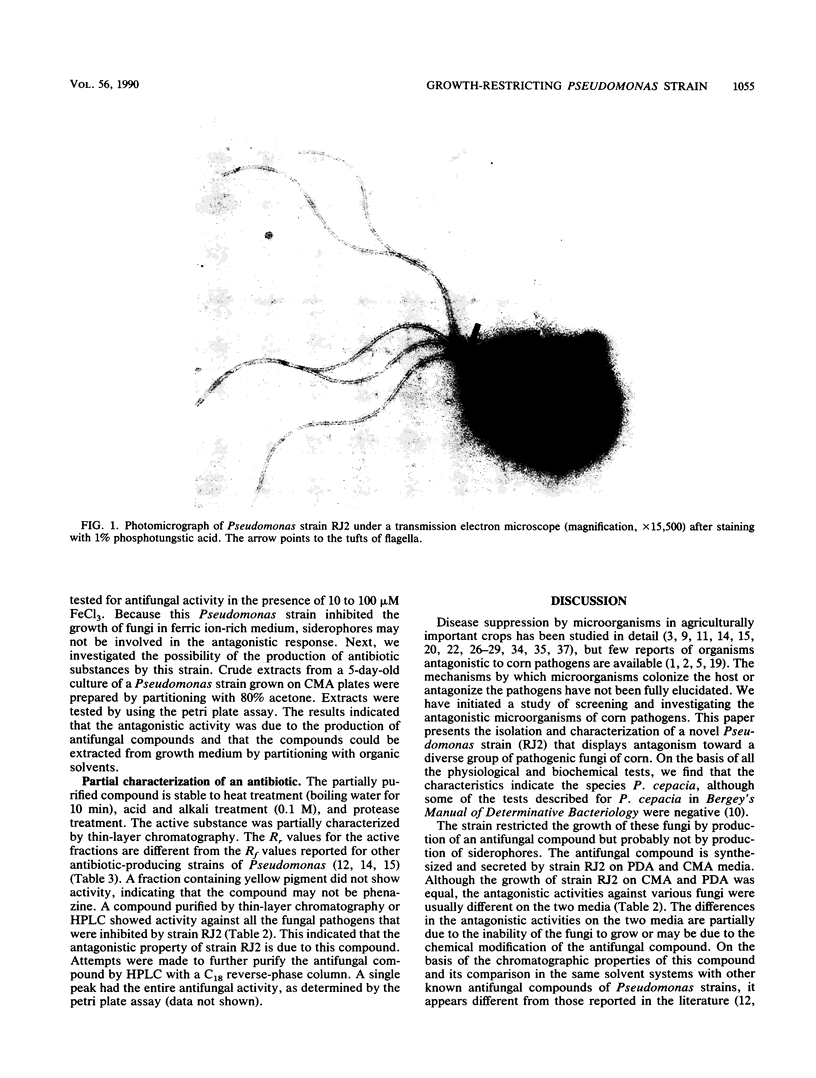
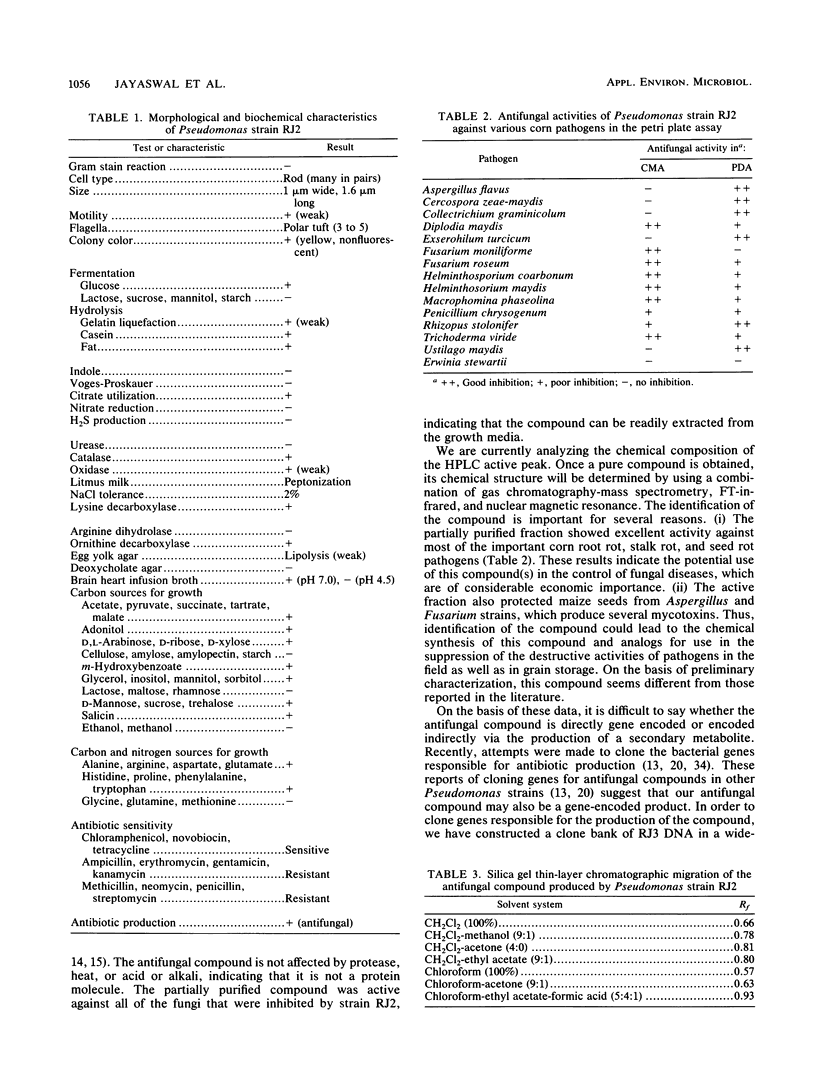
The characterization of a novel Pseudomonas strain exhibiting antagonism towards many important corn fungal pathogens is presented. This strain was isolated from the caryopses of the grass Tripsacum dactyloides and was identified as Pseudomonas cepacia. The antagonistic activity is due to the production of an antifungal compound. The chromatographic properties of this partially purified compound isolated from growth medium differ from those reported previously for other pseudomonads. The suppression of the growth of economically important phytopathogens by this strain and by the partially purified compound indicates a potential biocontrol agent.
Full text
PDF

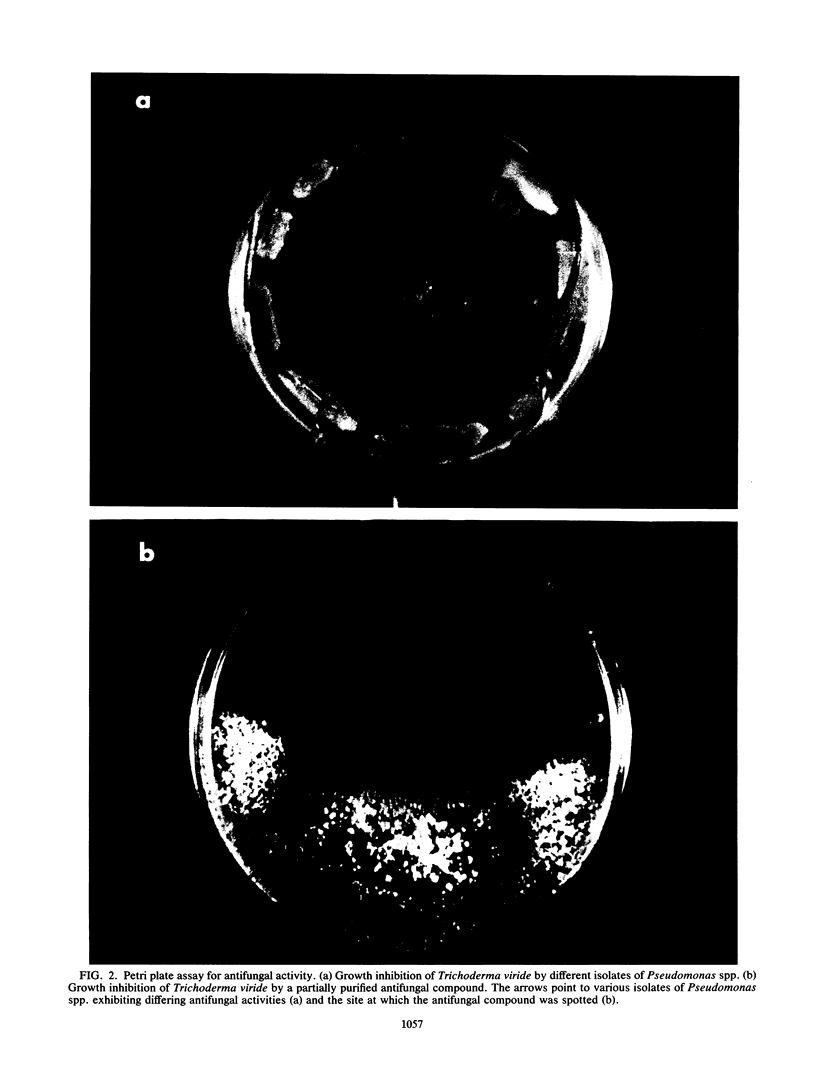

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurusiddaiah S., Weller D. M., Sarkar A., Cook R. J. Characterization of an antibiotic produced by a strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens inhibitory to Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici and Pythium spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):488–495. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterson N. I., Layton T. J., Ziegle J. S., Warren G. J. Molecular cloning of genetic determinants for inhibition of fungal growth by a fluorescent pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.696-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam B. S., Strobel G. A., Harrison L. A., Lam S. T. Transposon mutagenesis and tagging of fluorescent Pseudomonas: Antimycotic production is necessary for control of Dutch elm disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6447–6451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisinger T., Margraff R. Secondary metabolites of the fluorescent pseudomonads. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):422–442. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.422-442.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller P. C., Yokoyama M., Chang J. P. Ultracytochemical localization of glucose-6-phosphatase in Chang rat hepatoma in vivo and in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 May;58(5):1401–1405. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.5.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel N., Gnanamanickam S. S. Evaluation of Pseudomonas fluorescens for Suppression of Sheath Rot Disease and for Enhancement of Grain Yields in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2056–2059. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2056-2059.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth M. N., Hancock J. G. Disease-suppressive soil and root-colonizing bacteria. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1376–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.216.4553.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth M. N., Hancock J. G. Selected topics in biological control. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:453–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Suicide plasmid vehicles for insertion mutagenesis in Rhizobium meliloti and related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1292–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1292-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Weller D. M. Role of a phenazine antibiotic from Pseudomonas fluorescens in biological control of Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3499–3508. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3499-3508.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisard C., Keel C., Haas D., Dèfago G. Cyanide production by Pseudomonas fluorescens helps suppress black root rot of tobacco under gnotobiotic conditions. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):351–358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]