Abstract
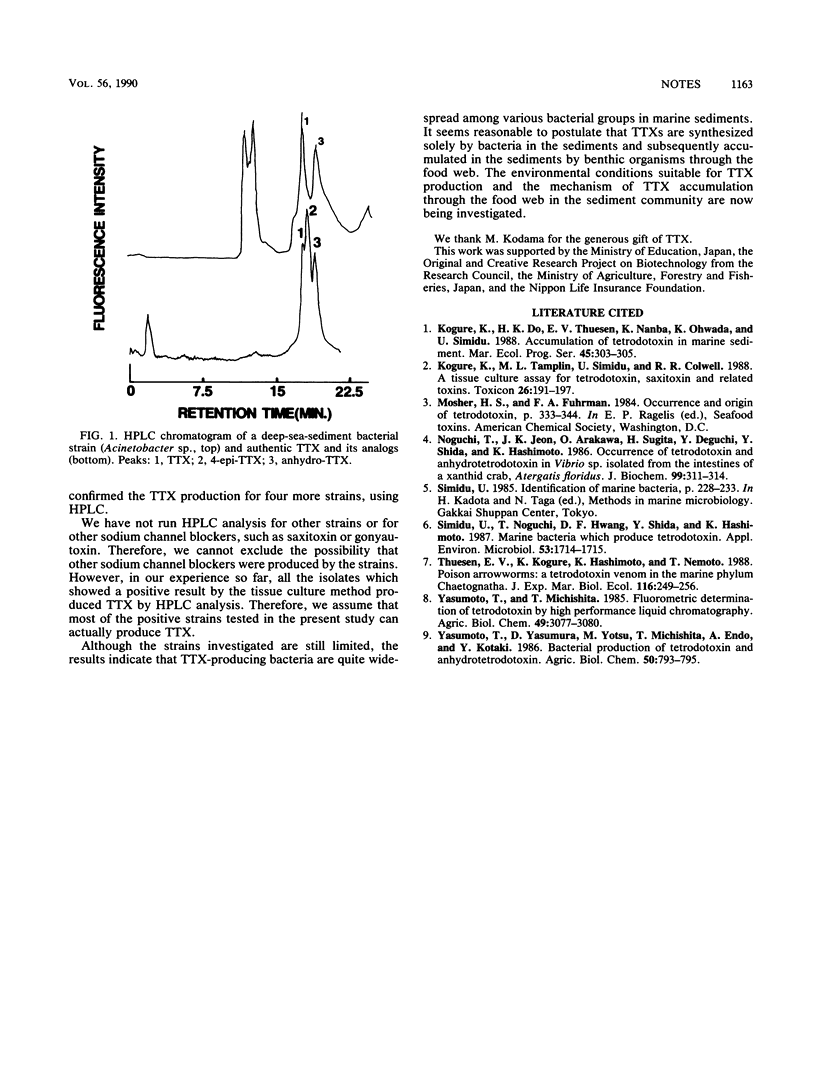
Forty-nine bacterial strains were isolated from deep-sea sediments. Among them, 22 strains were shown by the tissue culture assay method to produce sodium channel blockers. For some strains, high-performance liquid chromatography analysis confirmed that the blocker was tetrodotoxin. Tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria seem to be widespread in marine sediment.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kogure K., Tamplin M. L., Simidu U., Colwell R. R. A tissue culture assay for tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and related toxins. Toxicon. 1988;26(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Jeon J. K., Arakawa O., Sugita H., Deguchi Y., Shida Y., Hashimoto K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):311–314. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simidu U., Noguchi T., Hwang D. F., Shida Y., Hashimoto K. Marine bacteria which produce tetrodotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1714–1715. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1714-1715.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


