Abstract
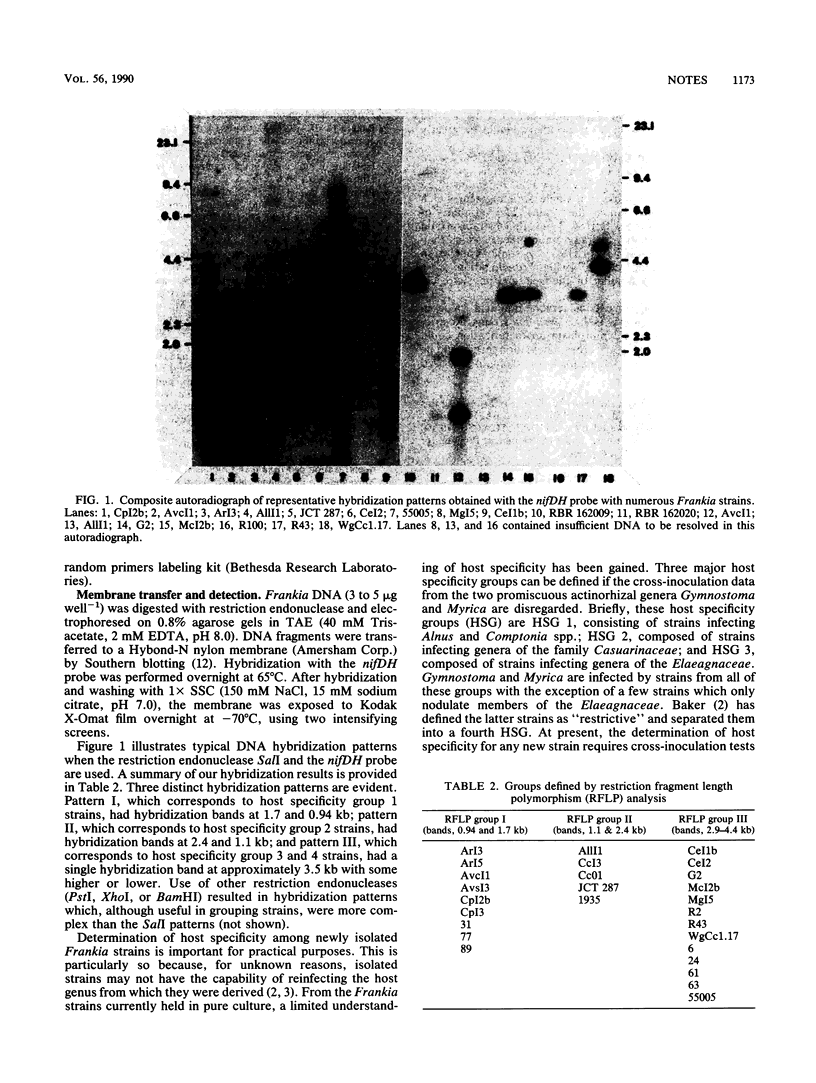
Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of numerous Frankia strains, using a nifDH probe, separated the strains into three distinct groups based on hybridization patterns. The groups identified in this study were well correlated with host specificity groups identified in earlier cross-inoculation studies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom R. A., Mullin B. C., Tate R. L., 3rd DNA restriction patterns and DNA-DNA solution hybridization studies of Frankia isolates from Myrica pennsylvanica (bayberry). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2155–2160. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2155-2160.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaham D., Deltredici P., Torrey J. G. Isolation and Cultivation in vitro of the Actinomycete Causing Root Nodulation in Comptonia. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):899–902. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4331.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand P., Simonet P., Bardin R. Conservation of nif sequences in Frankia. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):238–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00339587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]