Abstract
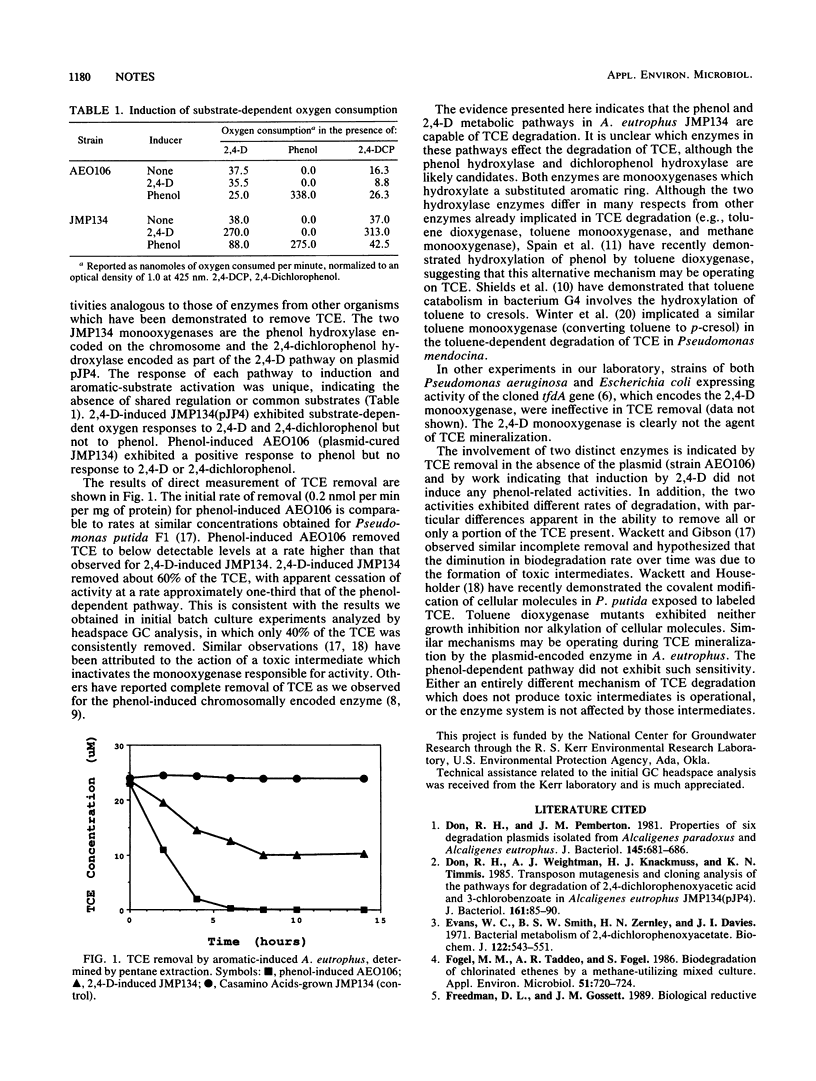
The bacterium Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4) degrades trichloroethylene (TCE) by a chromosomal phenol-dependent pathway and by the plasmid-encoded 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid pathway. The two pathways were independent and exhibited different rates of removal and capacities for quantity of TCE removed. The phenol-dependent pathway was more rapid (0.2 versus 0.06 nmol of TCE removed per min per mg of protein) and consumed all detectable TCE. The 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-dependent pathway removed 40 to 60% of detectable TCE.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Weightman A. J., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Transposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.85-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel M. M., Taddeo A. R., Fogel S. Biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes by a methane-utilizing mixed culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):720–724. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.720-724.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. L., Gossett J. M. Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2144–2151. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2144-2151.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Olsen R. H., Seidler R. J. Phenoxyacetic acid degradation by the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (TFD) pathway of plasmid pJP4: mapping and characterization of the TFD regulatory gene, tfdR. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):314–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.314-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Mahaffey W. R., Pritchard P. H. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene and involvement of an aromatic biodegradative pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):949–954. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.949-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Pritchard P. H. Trichloroethylene metabolism by microorganisms that degrade aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.604-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Zylstra G. J., Blake C. K., Gibson D. T. Monohydroxylation of phenol and 2,5-dichlorophenol by toluene dioxygenase in Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2648–2652. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2648-2652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S., Waclett L. P. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3155–3161. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3155-3161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T. M., McCarty P. L. Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinyl chloride, and carbon dioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1080-1083.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Householder S. R. Toxicity of Trichloroethylene to Pseudomonas putida F1 Is Mediated by Toluene Dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2723–2725. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2723-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson B. H. Biotransformation of trichloroethylene in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):242–243. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.242-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



