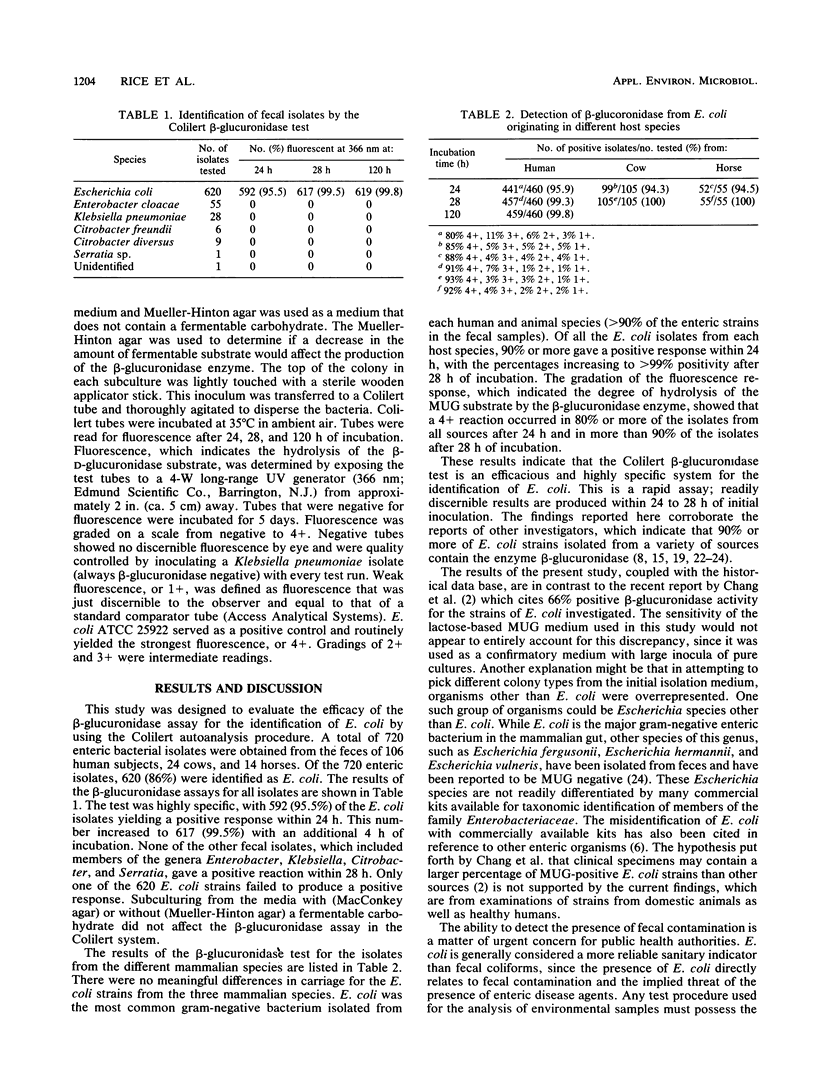
Abstract
In 1976, Kilian and Bulow described the association of beta-glucuronidase with the genus Escherichia (97% positive) and suggested that a beta-glucuronidase assay would be a useful identification test. Since that report, papers about the sensitivity and specificity of this enzyme for the identification of Escherichia coli from clinical sources, food, seawater, potable-water supplies, and various environmental sources have appeared. A study was undertaken to determine the efficacy and specificity of the defined-substrate technology beta-glucuronidase (Colilert) assay for the identification of this species from fecal samples. A total of 460 human, 105 cow, and 55 horse E. coli isolates were tested. Results showed 95.5% beta-glucuronidase-positive isolates in 24 h and 99.5% positive after 28 h of incubation. Only one E. coli isolate was negative. There were no significant differences in the percentage of beta-glucuronidase-positive isolates among the human or animal isolates. There were no non-E. coli isolates that were positive. All subjects carried beta-glucuronidase-positive E. coli.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD W. L., LICHSTEIN H. C. The effect of carbohydrates on the tryptophanase activity of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1955 May;69(5):584–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.5.584-589.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. W., Brill J., Lum R. Proportion of beta-D-glucuronidase-negative Escherichia coli in human fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):335–339. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.335-339.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour A. P., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter procedure for enumerating the component genera of the coliform group in seawater. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):826–833. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.826-833.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour A. P., Strickland E. R., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter method for enumerating Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1152-1158.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Allen M. J., Smith D. B. National field evaluation of a defined substrate method for the simultaneous enumeration of total coliforms and Escherichia coli from drinking water: comparison with the standard multiple tube fermentation method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1595–1601. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1595-1601.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Kontnick C. M. Comparison of beta-glucuronidase-based substrate systems for identification of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.368-371.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Piscitelli V., Cartter M. Phenotypic characteristics of coliform and noncoliform bacteria from a public water supply compared with regional and national clinical species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):474–478. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.474-478.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Trepeta R. W. Rapid and economical identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test methodology for urinary tract pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1287–1291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1287-1291.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng P. C., Hartman P. A. Fluorogenic assays for immediate confirmation of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1320–1329. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1320-1329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iritani B., Inzana T. J. Evaluation of a rapid tube assay for presumptive identification of Escherichia coli from veterinary specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):564–566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.564-566.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Bülow P. Rapid diagnosis of Enterobacteriaceae. I. Detection of bacterial glycosidases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Oct;84B(5):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Bülow P. Rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae. II. Use of a beta-glucuronidase detecting agar medium (PGUA agar) for the identification of E. coli in primary cultures of urine samples. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mara D. D. A single medium for the rapid detection of Escherichia coli at 44 degrees C. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):783–785. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates A., Schaffer M. Quantitative determination of Escherichia coli from faecal coliforms in seawater. Microbios. 1988;53(216-217):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moberg L. J., Wagner M. K., Kellen L. A. Fluorogenic assay for rapid detection of Escherichia coli in chilled and frozen foods: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):589–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison B. J. Evaluation of a fluorogenic assay for detection of Escherichia coli in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):285–288. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.285-288.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepeta R. W., Edberg S. C. Methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucuronide-based medium for rapid isolation and identification of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):172–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.172-174.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


