Abstract
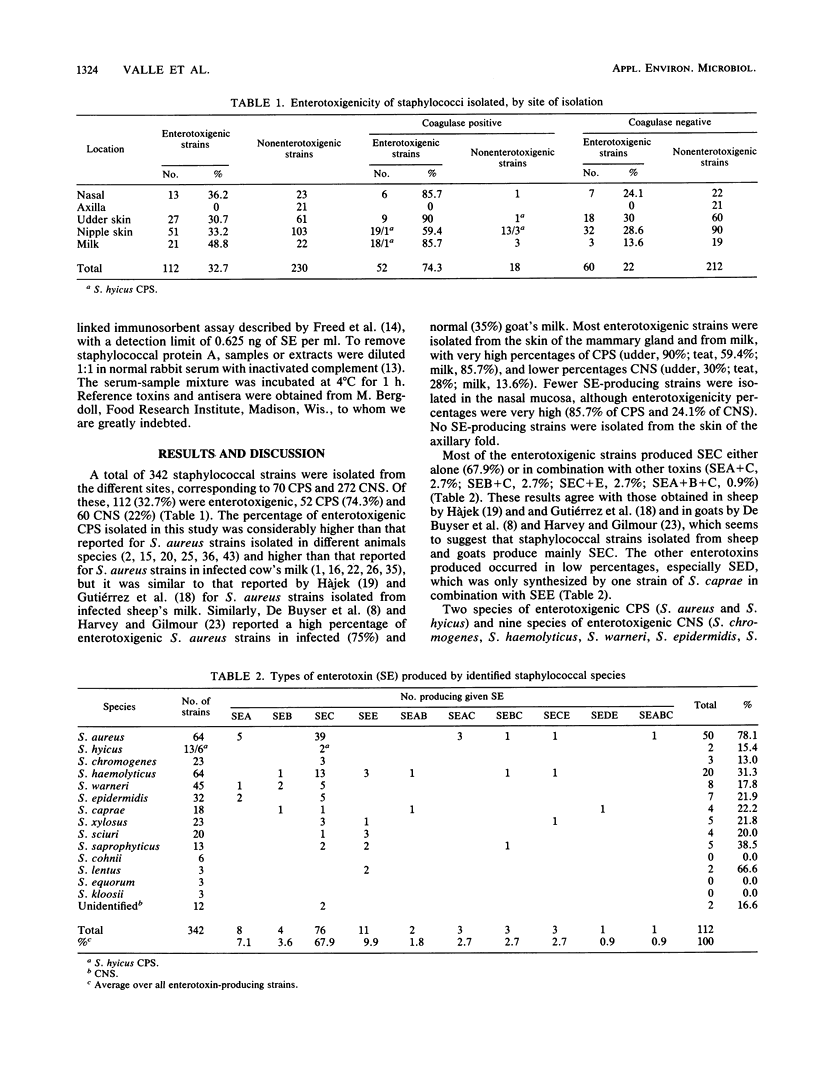
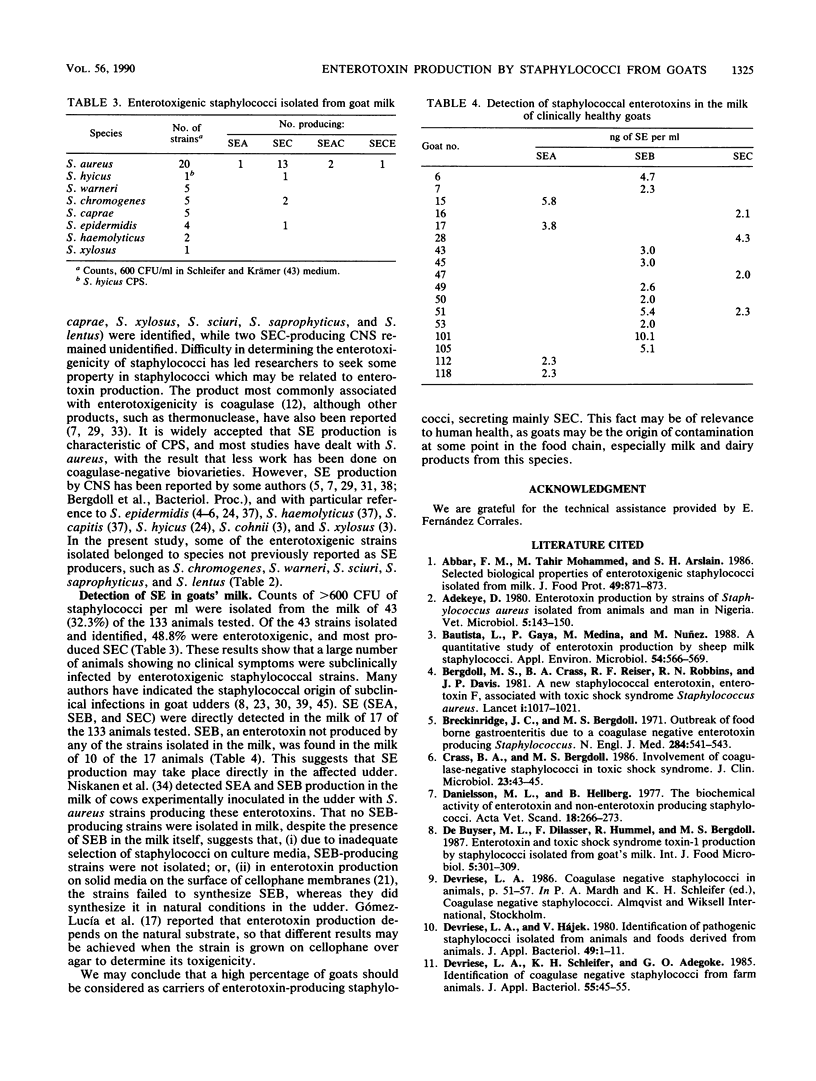
The ability of 342 staphylococcal isolates from different anatomical sites in healthy goats to produce staphylococcal enterotoxins (SE) was investigated. SE were produced by 74.3% of the 70 coagulase-positive strains and by 22% of the coagulase-negative strains studied. Most enterotoxigenic strains were isolated from the skin of udders and teats and from milk. SEC was the SE type most frequently produced, either alone (67.9%) or in combination with others. Five coagulase-negative species not previously reported as SE producers were identified (Staphylococcus chromogenes, S. warneri, S. sciuri, S. saprophyticus, and S. lentus). SEA, SEB, and SEC were detected in the milk of 17 of the 133 healthy goats studied. These results suggest that the goat is an important reservoir of enterotoxigenic staphylococci, most of which produce SEC.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautista L., Gaya P., Medina M., Nuñez M. A quantitative study of enterotoxin production by sheep milk staphylococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):566–569. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.566-569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckinridge J. C., Bergdoll M. S. Outbreak of food-borne gastroenteritis due to a coagulase-negative enterotoxin-producing staphylococcus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 11;284(10):541–543. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103112841010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Involvement of coagulase-negative staphylococci in toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):43–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.43-45.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson M. L., Hellberg B. The biochemical activity of enterotoxin and non-enterotoxin producing staphylococci. Acta Vet Scand. 1977;18(2):266–273. doi: 10.1186/BF03548455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Hájek V. Identification of pathogenic staphylococci isolated from animals and foods derived from animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;49(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A., Schleifer K. H., Adegoke G. O. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci from farm animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;58(1):45–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. B., BUETTNER L. G., NIVEN C. F., Jr Evaluation of the coagulase test in the study of staphylococci associated with food poisoning. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):481–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.481-484.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed R. C., Evenson M. L., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1349–1355. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1349-1355.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda S., Tokuno H., Ogawa H., Sasaki M., Kishimoto T., Kawano J., Shimizu A., Kimura S. Enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus intermedius strains isolated from dogs. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Dec;258(2-3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(84)80054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Moreno B., Bergdoll M. S. Characterization of staphylococci isolated from mastitic cows in Spain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.548-553.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lucía E., Goyache J., Orden J. A., Blanco J. L., Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria J. A., Domínguez L., Suárez G. Production of enterotoxin A by supposedly nonenterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1447–1451. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1447-1451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLANDER H. O. PRODUCTION OF LARGE QUANTITIES OF ENTEROTOXIN B AND OTHER STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS ON SOLID MEDIA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:299–305. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Gilmour A. Application of current methods for isolation and identification of staphylococci in raw bovine milk. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;59(3):207–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover D. G., Tatini S. R., Maltais J. B. Characterization of staphylococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):649–660. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.649-660.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hájek V. Identification of enterotoxigenic staphylococci from sheep and sheep cheese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):264–268. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.264-268.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hájek V., Marsálek E. The occurrence of enterotoxigenic staphylococcus aureus strains in hosts of different animal species. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Jan;223(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato E., Kaji Y., Kaneko K. Enterotoxigenic Staphylococci of canine origin. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Nov;39(11):1771–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato E., Kume T. Enterotoxigenicity of bovine staphylococci isolated from California mastitis test-positive milk in Japan. Jpn J Vet Res. 1980 Jul;28(3):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E. Natural populations of the genus Staphylococcus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:559–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Hoeprich P. D., Genigeorgis C. Nuclease production and lysostaphin susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and other catalase-positive cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):823–826. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.823-826.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerondelle C., Poutrel B. Characteristics of non-clinical mammary infections of goats. Ann Rech Vet. 1984;15(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotter L. P., Genigeorgis C. A. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition and biochemical properties of certain coagulase-negative enterotoxigenic cocci. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):152–158. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Hovelius B., Hovelius K., Nilsson P. O. Coagulase-negative, novobiocin-resistant staphylococci on the skin of animals and man, on meat and in milk. Acta Vet Scand. 1978;19(2):243–253. doi: 10.1186/BF03547629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niskanen A., Koranen L., Roine K. Staphylococcal enterotoxin and thermonuclease production during induced bovine mastitis and the clinical reaction of enterotoxin in udders. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):493–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.493-498.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. C., Jr, Casman E. P., Baer E. F., Stone J. E. Enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus cultures isolated from acute cases of bovine mastitis. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):605–607. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.605-607.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Berdal B. P., Fossum K., Omland T. Enterotoxin production by Staphylococcus aureus related to the origin of the strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Fossum K., Berdal B. P. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A, B, and C produced by coagulase-negative strains within the family Micrococcaceae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutrel B. Udder infection of goats by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Apr;9(2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kloos W. E. A simple test system for the separation of staphylococci from micrococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):337–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.337-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. C., Roguinsky M. Mastitis and other diseases of the goat's udder. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Dec 15;171(12):1241–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor R., Lachica F., Weiss K. F., Deibel R. H. Relationships among coagulase, enterotoxin, and heat-stable deoxyribonuclease production by Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.126-127.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Rheinbaben K. E., Hadlok R. M. Rapid distinction between micrococci and staphylococci with furazolidone agars. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981 Mar;47(1):41–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00399065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



