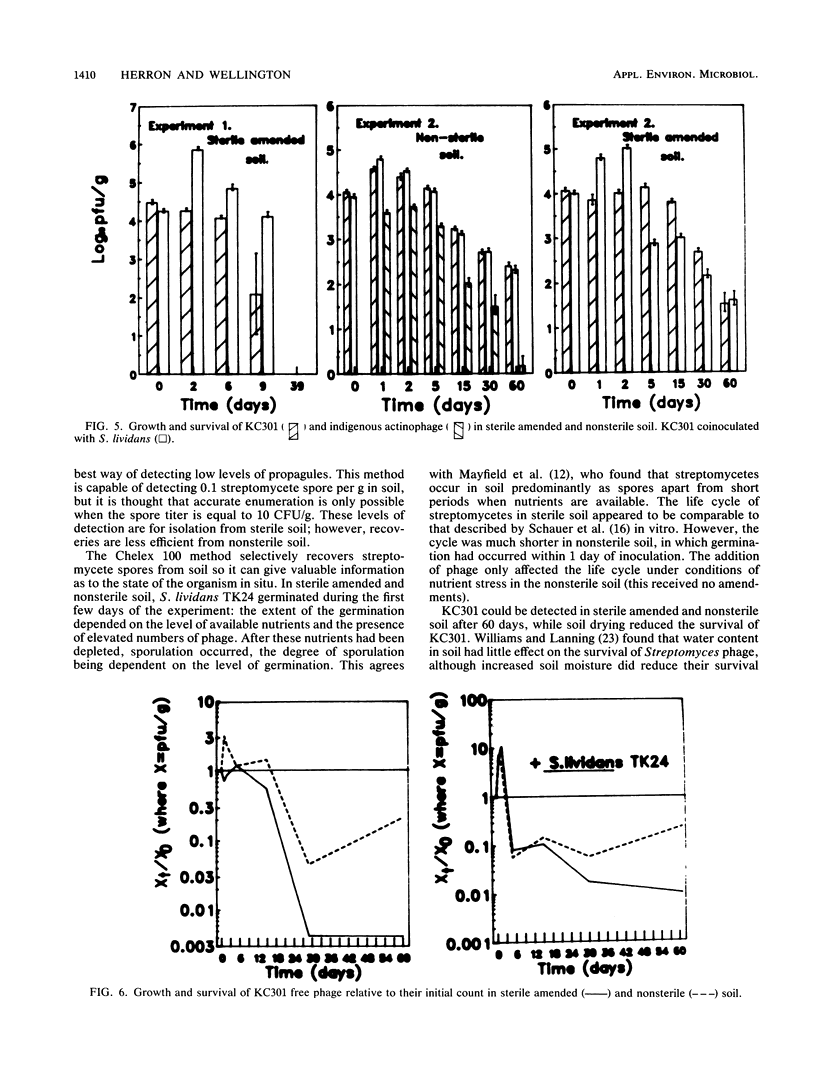
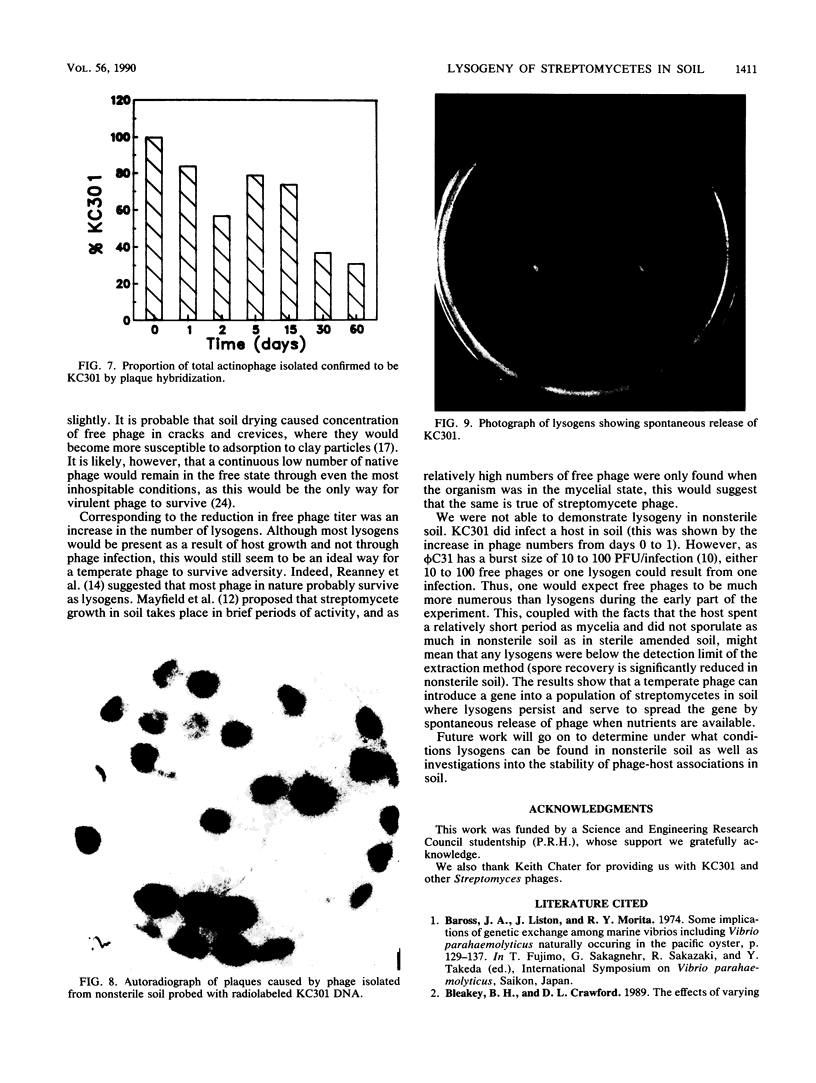
Abstract
A new method for the isolation and enumeration of streptomycete spores from soil was developed. This method makes use of a cation-exchange resin to disperse soil particles. It allowed the detection of 10 spores in 100 g of sterile soil, while ca. 103 could be accurately enumerated in 100 g. This method was applied to studying the fate of a marked actinophage in soil. In sterile amended and nonsterile soil, relatively high numbers of actinophages were only found during the first few days of the experiment when the host streptomycete was in the mycelial form. Later, after sporulation, lysogens could be detected in sterile amended soil and could still be found 60 days after inoculation. Although no lysogens were found in nonsterile soil, the introduced phage could still be detected in the free state after 60 days, albeit at a low titer.
Full text
PDF

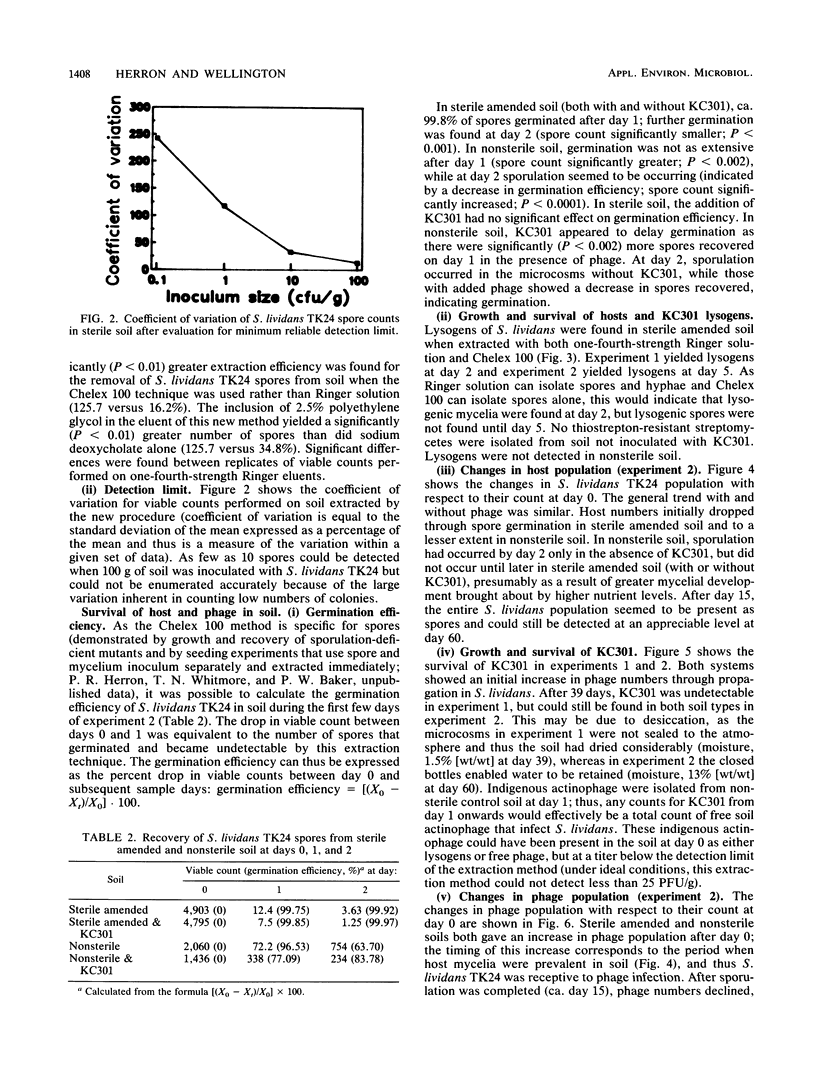
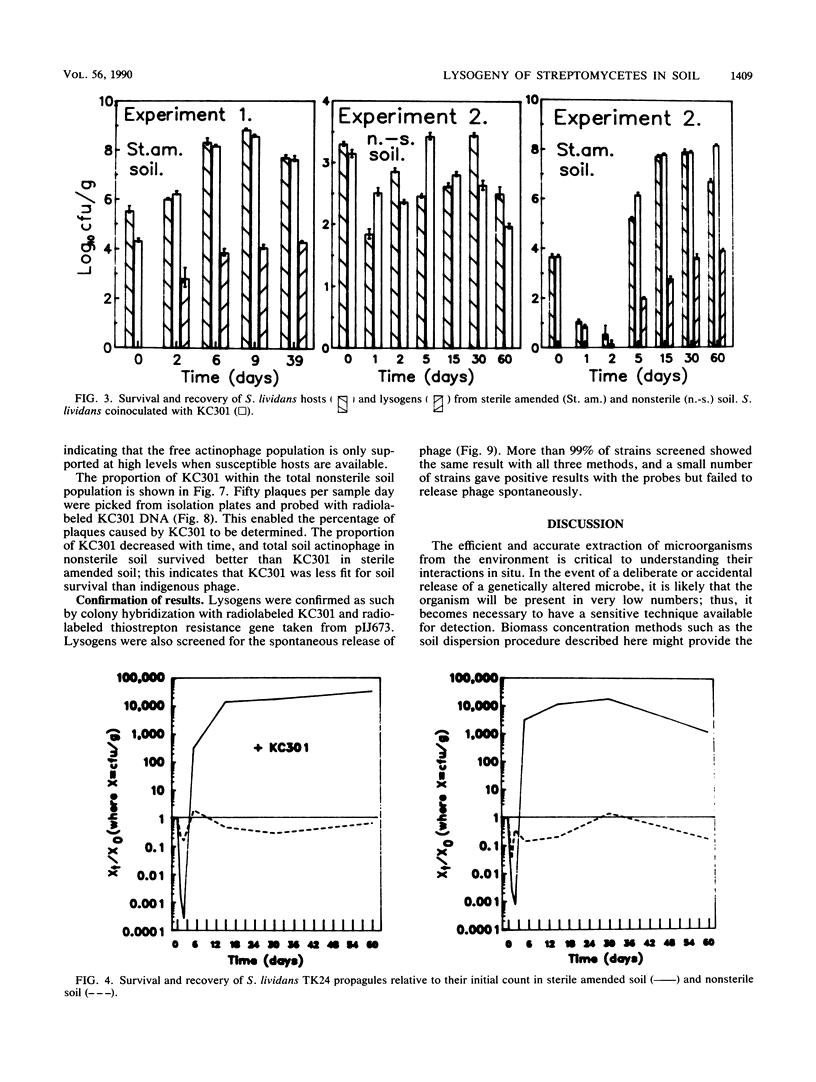

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Germida J. J., Khachatourians G. G. Transduction of Escherichia coli in soil. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):190–193. doi: 10.1139/m88-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser T., Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M., Thompson C. J. pIJ101, a multi-copy broad host-range Streptomyces plasmid: functional analysis and development of DNA cloning vectors. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00330791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya N. D., Chater K. F., Mkrtumian N. M. Genetics and molecular biology of Streptomyces bacteriophages. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):206–229. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.206-229.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya N. D., Mkrtumian N. M., Gostimskaya N. L., Danilenko V. N. Characterization of temperate actinophage phi C31 isolated from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):258–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.258-262.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. D., Miller R. V., Sayler G. S. Frequency of F116-mediated transduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):724–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.724-730.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye D. J., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Potential for transduction of plasmids in a natural freshwater environment: effect of plasmid donor concentration and a natural microbial community on transduction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.987-995.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer A., Ranes M., Santamaria R., Guijarro J., Lawlor E., Mendez C., Chater K., Losick R. Visualizing gene expression in time and space in the filamentous bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):768–772. doi: 10.1126/science.3363358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Survival of, and genetic transfer by, genetically engineered bacteria in natural environments. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1986;31:93–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuttard C. Transduction of auxotrophic markers in a chloramphenicol-producing strain of Streptomyces. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):479–482. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellington E. M., Cresswell N., Saunders V. A. Growth and survival of streptomycete inoculants and extent of plasmid transfer in sterile and nonsterile soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1413–1419. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1413-1419.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeph L. R., Onaga M. A., Stotzky G. Transduction of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage P1 in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1731–1737. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1731-1737.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeph L. R., Stotzky G. Use of a biotinylated DNA probe to detect bacteria transduced by bacteriophage P1 in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):661–665. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.661-665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]